1、简介
JDBC: Java DataBase Connectivity 可以为多种关系型数据库DBMS 提供统一的访问方式,用java操作数据库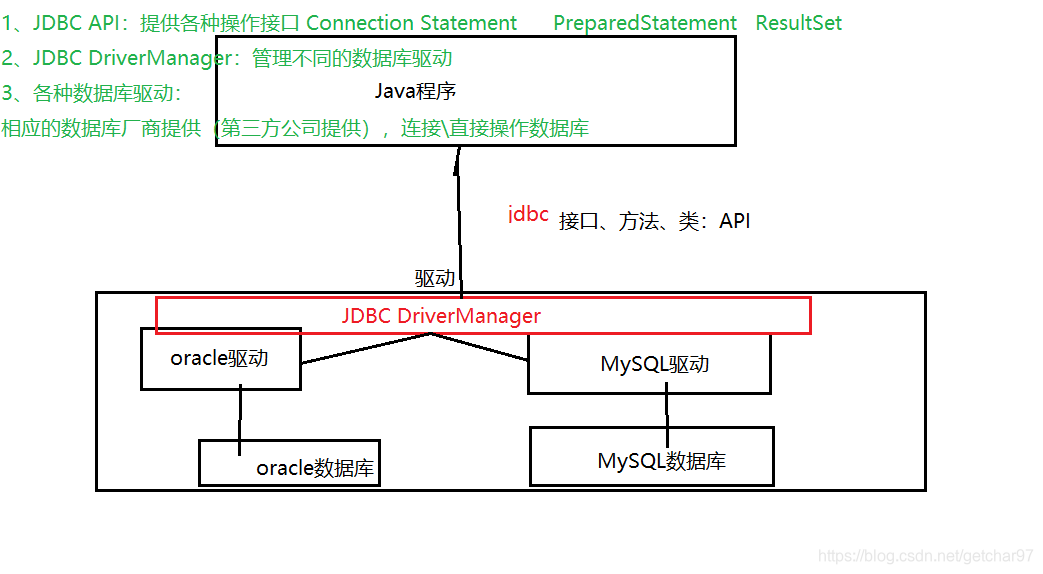
API主要功能
具体是通过一下类/接口实现:
DriverManager : 管理JDBC驱动
Connection : 连接(通过DriverManager产生)
Statement(子类PreparedStatement):增删改查(通过Statement产生)
CallableStatement : 调用数据库中的存储过程和函数(通过Statement产生)
Result : 返回的结果集(通过Statement产生)
Connection产生操作数据库的对象
Connection产生Statement对象:createStatement()
Connection产生PreparedStatement对象:createStatement()
Connection产生CallableStatement对象:prepareCall()
Statement操作数据库:
增删改:executeUpdate()
查:executeQuery()
PreparedStatement数据库操作
public interface PreparedStatement extends Statement
增删改:executeUpdate()
查:executeQuery()
操作: setXXX();
Statement 与PreparedStatement 区别:
1、 Statement
sql
executeUpdate(sql);
需要对sql进行拼接
2、PreparedStatement
sql(可能存在站位符?)
在创建PreparedStatement 对象时 将sql预编译 PreparedStatement(sql)
setXxx()替换站位
executeUpdate()
推荐用PreparedStatement:原因
1、编码更简洁
2、 提高性能
都执行100条数据:
statement:
String sql = “”
executeUpdate(sql)
编译执行100次;
PreparedStatement:
编译1次
执行100次;
3、 安全(可以有效防止sql注入)
statement: 存在被sql注入风险
输入:用户名:任意值’or 1=1—
密码: 任意值
select count(*) from login where uname=‘任意值’ or 1=1—and upwd=’任意值’
- 表示注释,后面为true
PreparedStatement:有效防止
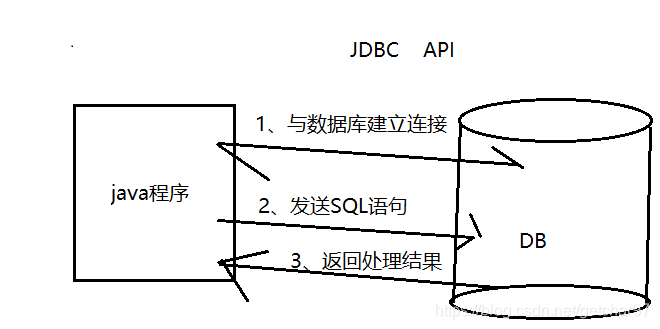
3、JDBC访问步骤
a、导入驱动,加载具体的驱动类
b、也数据库建立连接
c、发送sql,执行
d、处理结果集(查询)
4、数据库驱动
| 驱动 | 具体驱动类 | 连接字符串 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oracle | ojdbc-x.jar | oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver | JDBC:oracle:thin@localhost:1524:ORCL |
| MySQL | musql-connector-java-x.jar | com.mysql.jdbc.Driver | jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/数据库实例名 |
| SqlServer | sqljdbc-x.jar | com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerDriver | jdbc:microsoft:sqlserver:localhost:1433;databasename=数据库实例名 |
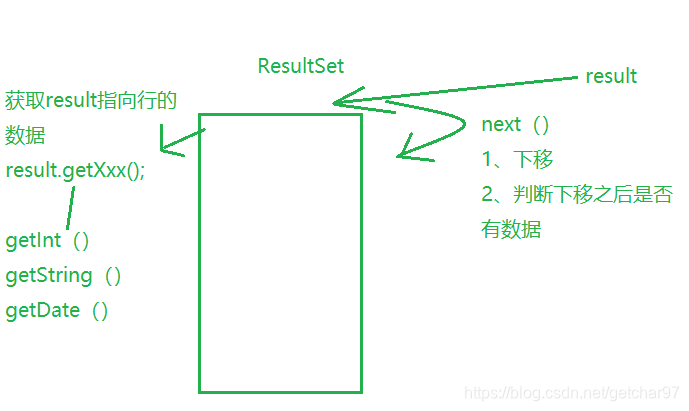
结果集:ResultSet :
while(rs.next()) { //l类似于集合中的迭代器
count = rs.getXxx(xxx) ; //获取字段(与数据库中字段对应)
}
异常 :处理Class.fofName()抛出ClassNotFoundException其余全是SQLException
案例:
private static final String URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test";
private static final String USERNAME = "root";
private static final String PWD = "root";
public static void update() {// 增删改
Connection connection = null;
Statement stmt = null;
try {
// a.导入驱动,加载具体的驱动类
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");// 加载具体的驱动类
// b.与数据库建立连接
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(URL, USERNAME, PWD);
// c.发送sql,执行(增删改、查)
stmt = connection.createStatement();
String sql = "update student set STUNAME='ls' where stuno=1";
// 执行SQL
int count = stmt.executeUpdate(sql); // 返回值表示 增删改 几条数据
// d.处理结果
if (count > 0) {
System.out.println("操作成功!");
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
try {
if(stmt!=null) stmt.close();// 对象.方法
if(connection!=null)connection.close();
}catch(SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
存储过程 与 存储函数
CallableStatement:调用存储过程 、存储函数
connection.prepareCall(参数:存储过程 或 存储函数名)
格式:
过程(无返回值,用out代替):{call 存储过程名(参数列表)}
函数(有返回值):{?call 存储函数名(参数列表)}
存储过程过程:
1、 调用存储对象(CallableStatement):cstmt = connection.prepareCall("{call 存储过程名(?,?,?)} ");
2、 通过cstmt.setXxx()设置输入参数
3、设置输出参数类型:cstmt.registerOutParameter(3, Types.INTEGER);
4、执行:cstmt.execute();
5、获取结果 int count = cstmt.getInt(3);
// c.发送sql,执行(增删改、查) num1+num2 ->num3
cstmt = connection.prepareCall( "{ call addTwoNum(?,?,?) }" ) ;
cstmt.setInt(1, 30);
cstmt.setInt(2, 40);
//设置输出参数的类型
cstmt.registerOutParameter(3, Types.INTEGER);
cstmt.execute() ;//num1+num2 ,execute()之前处理 输入参数以及输出参数类型,之后接受输出参数值
int result = cstmt.getInt(3) ;//获取计算结果
存储函数:
1、 调用存储对象(CallableStatement):cstmt = connection.prepareCall("{?=call 存储函数名(?,?)}");
2、 通过cstmt.setXxx()设置输入参数
3、设置输出参数类型:cstmt.registerOutParameter(3, Types.INTEGER);
4、执行:cstmt.execute();
5、获取结果 int count = cstmt.getInt(1);
// c.发送sql,执行(增删改、查) num1+num2 ->num3
cstmt = connection.prepareCall( "{? = call addTwoNumfunction (?,?) }" ) ;
cstmt.setInt(2, 30);
cstmt.setInt(3,40);
//设置输出参数的类型
cstmt.registerOutParameter(1, Types.INTEGER);
cstmt.execute() ;//num1+num2 ,execute()之前处理 输入参数以及输出参数类型,之后接受输出参数值
int result = cstmt.getInt(1) ;//获取计算结果
提醒:注意两者参数位置;
处理text /BLOB类型;(填写对应参数)
处理稍大的文件方法:
a、存储路径: —> 取路径 -–>根据IO操作处理
b、
TEXT:大文本数据
数据表为 :id 与文字
增:
String sql = "insert into testText values(?,?)";
// c.发送sql,执行(增删改、查)
pstmt = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setInt(1, 1);
File file = new File("E:\\test.txt");
InputStream in = new FileInputStream( file) ;
Reader reader = new InputStreamReader( in ,"UTF-8") ;//转换流 可以设置编码
pstmt.setCharacterStream(2, reader, (int)file.length());
int count =pstmt.executeUpdate() ;
// d.处理结果
if (count > 0) {
System.out.println("操作成功!");
}
查:
String sql = "select novel from testText where id = ? ";
// c.发送sql,执行(查)
pstmt = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setInt(1, 1);
rs = pstmt.executeQuery() ;
//setXxxx getXxxx setInt getInt
if(rs.next())
{
Reader reader = rs.getCharacterStream("novel ") ;
Writer writer = new FileWriter("src/test.txt");
//通过流进行读取
char[] chs = new char[100] ;
int len = -1;
while( (len = reader.read(chs)) !=-1 ) {
writer.write( chs,0,len );
}
writer.close();
reader.close();
}
BLOB:二进制
增:
File file = new File("d:\\test.mp3");
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(file );
pstmt.setBinaryStream(2,in ,(int)file.length() );
int count =pstmt.executeUpdate() ;
查:
if(rs.next())
{
InputStream in = rs.getBinaryStream("music") ;
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("src/music.mp3") ;
byte[] chs = new byte[100] ;
int len = -1;
while( (len = in.read(chs)) !=-1 ) {
out.write( chs,0,len );
}
out.close();
in.close();
}




















 171
171

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








