今天,我将带来数据结构中的线性表之顺序表。
目录
线性表
线性表(linear list)是n个具有相同特征的数据元素的有限序列。线性表是一种在实际中广泛利用的数据结构,常见的线性表:顺序表、链表、栈、队列、字符串…
线性表在逻辑上是线性结构,也就是说是连续的一条直线。但是在物理结构上并不一定是连续的,线性表在物理上存储时,通常以数组和链式结构的形式存储。
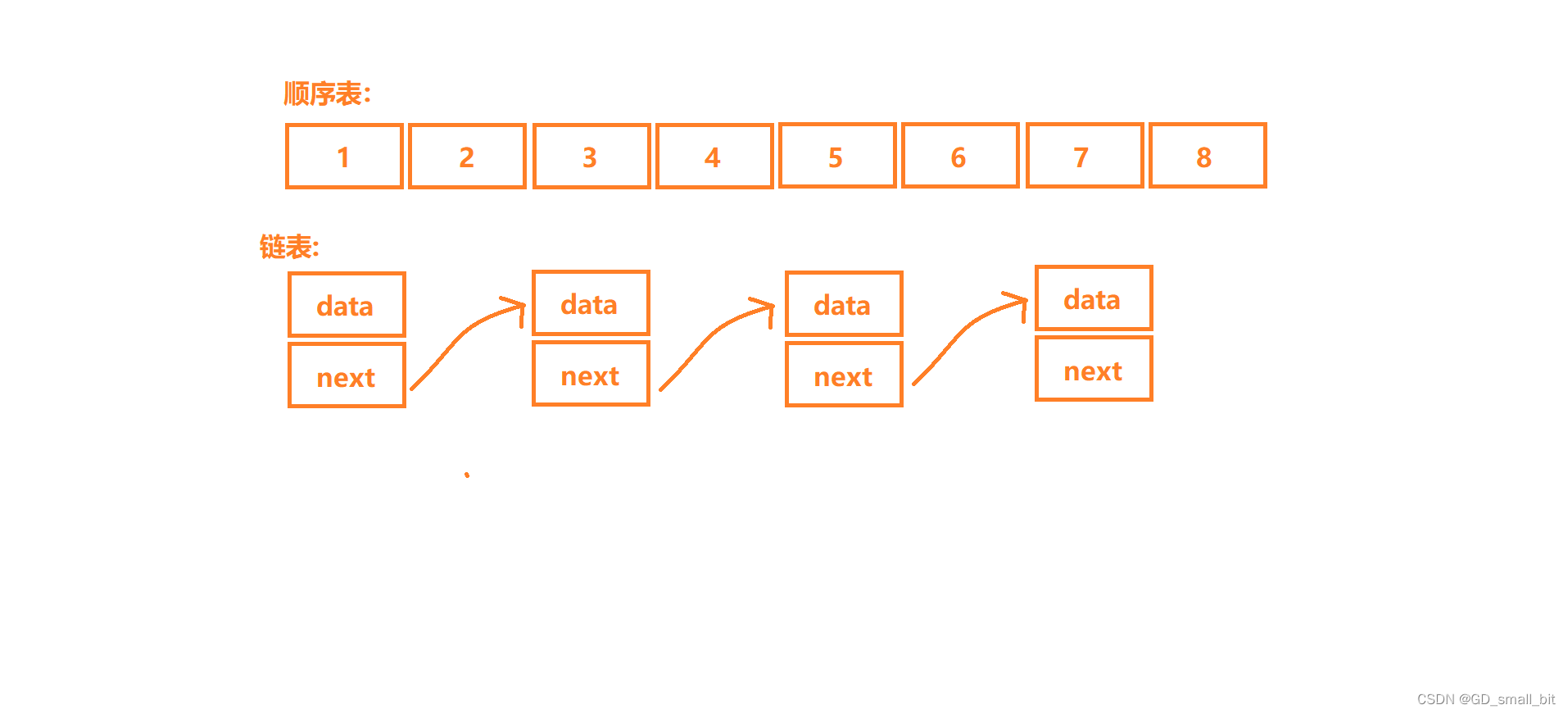
顺序表
顺序表是用一段物理地址连续的存储单元依次存储数据元素的线性结构,一般情况下采用数组存储。在数组上完成数据的增删查改。
顺序表一般分为:
1.静态顺序表:使用定长数组存储元素
2.动态顺序表:使用动态开辟的数组存储
动态顺序表的数据是要按顺序存储的,不跟以前文章中开辟的数组一样,可以在任意位置存储数据。如:一个有10个字节空间的普通的char类型数组,可以在0下标和9下标进行存储,而动态顺序表中的数组不行。
接下来,我来写一下动态顺序表。至于静态顺序表,无非就是在动态顺序表的基础上,将动态开辟的代码进行修改,我就不再进行讲解。
注意我在顺序表的实现代码中,加入了大量的assert防止越界,如:中间插入函数和中间删除函数,我就对pos位置使用assert进行检查,防止pos为负数或者过大导致的越界访问。
如果pos位置为负数或者大过了现在已经有的数据元素个数,那么assert直接拦停程序和报错,因为这些都会导致越界访问,也就是说在后续使用该顺序表时,如果选择一个功能,程序直接停下来,那么就要观察一下是否是中间删除时,输入的pos位置为负数,或者大于元素个数,还是在没有元素的情况下,还要进行尾删和头删。
动态顺序表的三个文档
SeqList.h --------- 头文件的引用和函数的声明
SeqList.c --------- 函数的定义
test.c --------- 顺序表的检验
初始化函数
void InitSeqList(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps != NULL);
ps->data = NULL;
ps->size = 0;
ps->capacity = 0;
}
检查空间是否满的函数
void CheckSeqList(SL* ps)
{
SeqListType* tmp = NULL;
int newcapacity = 0;
assert(ps != NULL);
if(ps->size == ps->capacity)
{
newcapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
tmp = (SeqListType*)realloc(ps->data,newcapacity * sizeof(SeqListType));
if(tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
ps->data = tmp;
ps->capacity = newcapacity;
}
}
打印函数
void PrintSeqList(SL* ps)
{
int i = 0;
for(i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
printf("%d ",ps->data[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
销毁顺序表的函数
void DestroySeqList(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps != NULL);
if(ps->data != NULL)
{
free(ps->data);
ps->data = NULL;
ps->size = 0;
ps->capacity = 0;
}
}
尾插和尾删函数
void SLPushBack(SL* ps,SeqListType x)
{
SLInsert(ps,ps->size,x);
}
void SLPopBack(SL* ps)
{
SLErase(ps,ps->size - 1);
}
头插和头删函数
void SLPushFront(SL* ps,SeqListType x)
{
SLInsert(ps,0,x);
}
void SLPopFront(SL* ps)
{
SLErase(ps,0);
}
中间插入数据和中间删除数据的函数
void SLInsert(SL* ps,int pos,SeqListType x)
{
int end = ps->size - 1;
assert(ps != NULL);
assert(ps >= 0);
assert(pos <= ps->size);
CheckSeqList(ps);
while(pos <= end)
{
ps->data[end + 1] = ps->data[end];
end--;
}
ps->data[pos] = x;
ps->size++;
}
void SLErase(SL* ps,int pos)
{
int begin = pos + 1;
assert(ps != NULL);
assert(pos >= 0);
assert(pos < ps->size);
while(begin < ps->size)
{
ps->data[begin - 1] = ps->data[begin];
begin++;
}
ps->size--;
}
查找函数
int Find(SL* ps,int TargetNumber,int begin)
{
int i = begin;
assert(ps != NULL);
while(i < ps->size)
{
if(ps->data[i] == TargetNumber)
{
return i;
}
i++;
}
return -1;
}
菜单和主函数
void menu()
{
printf("***************************************************\n");
printf("**** 1.尾插 2.尾删 ****\n");
printf("**** 3.头插 4.头删 ****\n");
printf("**** 5.中间插入数据 6.中间删除数据 ****\n");
printf("**** 7.查找数据 8.打印数据 ****\n");
printf("**** 0.退出 ****\n");
printf("***************************************************\n");
}
int main()
{
int input = 0;
int number = 0;
int address = 0;
int location = 0;
SL SeqList;
InitSeqList(&SeqList);
do
{
menu();
printf("请选择:>");
scanf("%d",&input);
switch(input)
{
case 1:
printf("请输入你要尾插的数据:>");
scanf("%d",&number);
SLPushBack(&SeqList,number);
break;
case 2:
SLPopBack(&SeqList);
printf("尾删成功\n");
break;
case 3:
printf("请输入你要头插的数据:>");
scanf("%d",&number);
SLPushFront(&SeqList,number);
break;
case 4:
SLPopFront(&SeqList);
break;
case 5:
printf("请输入你要在中间插入的数据:>");
scanf("%d",&number);
printf("请输入你要插入的位置:>");
scanf("%d",&address);
SLInsert(&SeqList,address-1,number);
break;
case 6:
printf("请输入你要删除的的数据的位置:>");
scanf("%d",&address);
SLErase(&SeqList,address-1);
break;
case 7:
printf("请输入你要查找的数据:>");
scanf("%d",&number);
printf("请输入你要从哪个位置开始查找:>");
scanf("%d",&address);
location = Find(&SeqList,number,address);
if(location == -1)
{
printf("找不到\n");
}
else
{
printf("该数字的位置是%d\n",location+1);
}
break;
case 8:
PrintSeqList(&SeqList);
break;
case 0:
DestroySeqList(&SeqList);
break;
default:
printf("选择错误,请重新选择\n");
break;
}
}while(input);
}
函数的声明和结构体的定义
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef int SeqListType;
typedef struct SeqList
{
SeqListType* data;
int size;
int capacity;
}SL;
//初始化函数
void InitSeqList(SL* ps);
//检查空间是否满的函数
void CheckSeqList(SL* ps);
//打印函数
void PrintSeqList(SL* ps);
//销毁函数
void DestroySeqList(SL* ps);
//尾插函数
void SLPushBack(SL* ps,SeqListType x);
//尾删函数
void SLPopBack(SL* ps);
//头插函数
void SLPushFront(SL* ps,SeqListType x);
//头删函数
void SLPopFront(SL* ps);
//在pos位置插入
void SLInsert(SL* ps,int pos,SeqListType x);
//删除pos位置的函数
void SLErase(SL* ps,int pos);
//查找元素
int Find(SL* ps,int TargetNumber ,int begin);
SeqList.c文档的全部代码
#include"SeqList.h"
void InitSeqList(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps != NULL);
ps->data = NULL;
ps->size = 0;
ps->capacity = 0;
}
void CheckSeqList(SL* ps)
{
SeqListType* tmp = NULL;
int newcapacity = 0;
assert(ps != NULL);
if(ps->size == ps->capacity)
{
newcapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
tmp = (SeqListType*)realloc(ps->data,newcapacity * sizeof(SeqListType));
if(tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
ps->data = tmp;
ps->capacity = newcapacity;
}
}
void DestroySeqList(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps != NULL);
if(ps->data != NULL)
{
free(ps->data);
ps->data = NULL;
ps->size = 0;
ps->capacity = 0;
}
}
void SLPushBack(SL* ps,SeqListType x)
{
SLInsert(ps,ps->size,x);
}
void SLPopBack(SL* ps)
{
SLErase(ps,ps->size - 1);
}
void SLPushFront(SL* ps,SeqListType x)
{
SLInsert(ps,0,x);
}
void SLPopFront(SL* ps)
{
SLErase(ps,0);
}
void SLInsert(SL* ps,int pos,SeqListType x)
{
int end = ps->size - 1;
assert(ps != NULL);
assert(ps >= 0);
assert(pos <= ps->size);
CheckSeqList(ps);
while(pos <= end)
{
ps->data[end + 1] = ps->data[end];
end--;
}
ps->data[pos] = x;
ps->size++;
}
void SLErase(SL* ps,int pos)
{
int begin = pos + 1;
assert(ps != NULL);
assert(pos >= 0);
assert(pos < ps->size);
while(begin < ps->size)
{
ps->data[begin - 1] = ps->data[begin];
begin++;
}
ps->size--;
}
int Find(SL* ps,int TargetNumber,int begin)
{
int i = begin;
assert(ps != NULL);
while(i < ps->size)
{
if(ps->data[i] == TargetNumber)
{
return i;
}
i++;
}
return -1;
}
void PrintSeqList(SL* ps)
{
int i = 0;
for(i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
printf("%d ",ps->data[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
SeqList.h文档的全部代码
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef int SeqListType;
typedef struct SeqList
{
SeqListType* data;
int size;
int capacity;
}SL;
//初始化函数
void InitSeqList(SL* ps);
//检查空间是否满的函数
void CheckSeqList(SL* ps);
//打印函数
void PrintSeqList(SL* ps);
//销毁函数
void DestroySeqList(SL* ps);
//尾插函数
void SLPushBack(SL* ps,SeqListType x);
//尾删函数
void SLPopBack(SL* ps);
//头插函数
void SLPushFront(SL* ps,SeqListType x);
//头删函数
void SLPopFront(SL* ps);
//在pos位置插入
void SLInsert(SL* ps,int pos,SeqListType x);
//删除pos位置的函数
void SLErase(SL* ps,int pos);
//查找元素
int Find(SL* ps,int TargetNumber ,int begin);
test.c文档的全部代码
#include "SeqList.h"
void menu()
{
printf("***************************************************\n");
printf("**** 1.尾插 2.尾删 ****\n");
printf("**** 3.头插 4.头删 ****\n");
printf("**** 5.中间插入数据 6.中间删除数据 ****\n");
printf("**** 7.查找数据 8.打印数据 ****\n");
printf("**** 0.退出 ****\n");
printf("***************************************************\n");
}
int main()
{
int input = 0;
int number = 0;
int address = 0;
int location = 0;
SL SeqList;
InitSeqList(&SeqList);
do
{
menu();
printf("请选择:>");
scanf("%d",&input);
switch(input)
{
case 1:
printf("请输入你要尾插的数据:>");
scanf("%d",&number);
SLPushBack(&SeqList,number);
break;
case 2:
SLPopBack(&SeqList);
printf("尾删成功\n");
break;
case 3:
printf("请输入你要头插的数据:>");
scanf("%d",&number);
SLPushFront(&SeqList,number);
break;
case 4:
SLPopFront(&SeqList);
break;
case 5:
printf("请输入你要在中间插入的数据:>");
scanf("%d",&number);
printf("请输入你要插入的位置:>");
scanf("%d",&address);
SLInsert(&SeqList,address-1,number);
break;
case 6:
printf("请输入你要删除的的数据的位置:>");
scanf("%d",&address);
SLErase(&SeqList,address-1);
break;
case 7:
printf("请输入你要查找的数据:>");
scanf("%d",&number);
printf("请输入你要从哪个位置开始查找:>");
scanf("%d",&address);
location = Find(&SeqList,number,address);
if(location == -1)
{
printf("找不到\n");
}
else
{
printf("该数字的位置是%d\n",location+1);
}
break;
case 8:
PrintSeqList(&SeqList);
break;
case 0:
DestroySeqList(&SeqList);
break;
default:
printf("选择错误,请重新选择\n");
break;
}
}while(input);
}
今天的讲解就到这里了,关注点一点,下期更精彩。





 本文详细介绍了顺序表的基本概念和操作实现,包括初始化、增删改查等核心功能,并提供了完整的代码示例。
本文详细介绍了顺序表的基本概念和操作实现,包括初始化、增删改查等核心功能,并提供了完整的代码示例。



























