implementation 'com.google.code.gson:gson:2.8.4'
Gson基础使用案例一
Gson gson = new Gson();
//输出"1",单个字符也可以序列化
System.out.println(gson.toJson("1"));
//输出 "fw123"
System.out.println(gson.toJson("fw123"));
//打印结果:[1,2,3] ---这种形式是数组吗?
int[] value = {1,2,3};
System.out.println(gson.toJson(value));
//上面的序列化结果都是转化成字符串类型的
// 下面是反序列化的过程
//这是一个泛型入参的函数,打印的结果: i 的值为: 1
int i = gson.fromJson("1",int.class);
System.out.println("i 的值为: " + i);
//打印出来的值为: gsonBean的值为: {"mInt":1,"mStr":"22"}--- 这个是序列化格式
String gsonBean = gson.toJson(new GsonBean(1,"22"));
System.out.println("gsonBean的值为: " + gsonBean);
SerializedName注解的使用:
public class JsonAdepterTest {
static class SerializedNameTestClass {
@SerializedName("name") //给a设置Key值为:name
String a;
@SerializedName(value = "name1", alternate = {"name2", "name3"})
String b;
String c;
public SerializedNameTestClass(String a, String b, String c) {
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
this.c = c;
}
public static void test() {
SerializedNameTestClass target =
new SerializedNameTestClass("v1", "v2", "v3");
Gson gson = new Gson();
String json = gson.toJson(target);
System.out.println(json);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SerializedNameTestClass.test();
}
}
执行结果为:{"name":"v1","name1":"v2","c":"v3"}
JsonAdapter注解的使用:
@JsonAdapter(UserJsonAdapter.class)
static
class User {
public final String firstName, lastName;
public User(String firstName, String lastName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"firstName='" + firstName + '\'' +
", lastName='" + lastName + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
class UserJsonAdapter extends TypeAdapter<User> {
@Override
public void write(JsonWriter out, User user) throws IOException {
out.beginObject();
out.name("firstKey:");
out.value(user.firstName);
out.endObject();
out.beginObject();
out.name("secondKey");
out.value(user.lastName);
out.endObject();
}
@Override
public User read(JsonReader in) throws IOException {
in.beginObject();
in.nextName();
String nameParts1 = in.nextString();
in.endObject();
in.beginObject();
in.nextName();
String nameParts2 = in.nextString();
in.endObject();
return new User(nameParts1, nameParts2);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
User user = new User("gg","Zero");
Gson gson = new GsonBuilder()
.setVersion(1.2).create();
String gsonStr = gson.toJson(user);
System.out.println("gsonStr=" + gsonStr);
user = gson.fromJson(gsonStr,User.class);
System.out.println("user: " + user);
}
输出结果:
gsonStr={"firstKey:":"gg"}{"secondKey":"Zero"}
user: User{firstName='gg', lastName='Zero'}
public class GsonError1 {
private String name;
private List<AuthorsBean> authors;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "GsonError1{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", authors=" + authors +
'}';
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public List<AuthorsBean> getAuthors() {
return authors;
}
public void setAuthors(List<AuthorsBean> authors) {
this.authors = authors;
}
public static class AuthorsBean {
private String id;
private String name;
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "AuthorsBean{" +
"id='" + id + '\'' +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
public static void test1() {
//TODO:
String json = "{\n" +
" \"name\": \"java\",\n" +
" \"authors\": [\n" +
" {\n" +
" \"id\": \"1'\",\n" +
" \"name\": \"Joshua Bloch'\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" {\n" +
" \"id\": \"2'\",\n" +
" \"name\": \"Tom\"\n" +
" }\n" +
" ]\n" +
"}";
Gson gson = new Gson();
GsonError1 gsonError1 = gson.fromJson(json, GsonError1.class);
System.out.println(gsonError1);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
test1();
}
输出结果:
GsonError1{name='java', authors=[AuthorsBean{id='1'', name='Joshua Bloch''}, AuthorsBean{id='2'', name='Tom'}]}
String json = "{\n" +
" \"name\": \"java\",\n" +
" \"authors\": \"\"\n" +
"}";
Gson gson = new Gson();
GsonError1 gsonError1 = gson.fromJson(json, GsonError1.class);
System.out.println(gsonError1);
如果上面的Json序列化形式不对,
就会上报错误:
Caused by: java.lang.IllegalStateException: Expected BEGIN_ARRAY but was STRING at line 3 column 17 path $.authors
为了解决由于Json中某些字段缺省的情况,方案一:
package com.android.serializable;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import com.google.gson.GsonBuilder;
import com.google.gson.JsonDeserializationContext;
import com.google.gson.JsonDeserializer;
import com.google.gson.JsonElement;
import com.google.gson.JsonObject;
import com.google.gson.JsonParseException;
import java.lang.reflect.Type;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
public class GsonError1 {
private String name;
private List<AuthorsBean> authors;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "GsonError1{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", authors=" + authors +
'}';
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public List<AuthorsBean> getAuthors() {
return authors;
}
public void setAuthors(List<AuthorsBean> authors) {
this.authors = authors;
}
public static class AuthorsBean {
private String id;
private String name;
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "AuthorsBean{" +
"id='" + id + '\'' +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
static class GsonError1Deserializer implements JsonDeserializer<GsonError1> {
@Override
public GsonError1 deserialize(JsonElement json, Type typeOfT, JsonDeserializationContext context) throws JsonParseException {
final JsonObject jsonObject = json.getAsJsonObject();
final JsonElement jsonTitle = jsonObject.get("name");
final String name = jsonTitle.getAsString();
JsonElement jsonAuthors = jsonObject.get("authors");
GsonError1 gsonError1 = new GsonError1();
if (jsonAuthors.isJsonArray()) {//如果数组类型,此种情况是我们需要的
//关于context在文章最后有简单说明
GsonError1.AuthorsBean[] authors = context.deserialize(jsonAuthors, GsonError1.AuthorsBean[].class);
gsonError1.setAuthors(Arrays.asList(authors));
} else {//此种情况为无效情况
gsonError1.setAuthors(null);
}
gsonError1.setName(name);
return gsonError1;
}
}
static class AuthorDeserializer implements JsonDeserializer {
@Override
public Object deserialize(JsonElement json, Type typeOfT, JsonDeserializationContext context) throws JsonParseException {
final JsonObject jsonObject = json.getAsJsonObject();
final GsonError1.AuthorsBean author = new GsonError1.AuthorsBean();
author.setId(jsonObject.get("id").getAsString());
author.setName(jsonObject.get("name").getAsString());
return author;
}
}
public static void test3() {
//TODO:
String json = "{\n" +
" \"name\": \"java\",\n" +
" \"authors\": \"\"\n" +
"}";
GsonBuilder gsonBuilder = new GsonBuilder();
//注册TypeAdapter
gsonBuilder.registerTypeAdapter(GsonError1.class, new GsonError1Deserializer());
gsonBuilder.registerTypeAdapter(GsonError1.AuthorsBean.class, new AuthorDeserializer());
Gson gson = gsonBuilder.create();
GsonError1 gsonError1 = gson.fromJson(json, GsonError1.class);
System.out.println(gsonError1);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
test3();
}
}
解决方法二: 参照上面自定义TypeAdapter
Gson的源码解析
JsonToken是枚举类型.---定义Json数据的类型
/**
* A structure, name or value type in a JSON-encoded string.
*/
public enum JsonToken {
/**
* The opening of a JSON array. Written using {@link JsonWriter#beginObject}
* and read using {@link JsonReader#beginObject}.
*/
BEGIN_ARRAY,
/**
* The closing of a JSON array. Written using {@link JsonWriter#endArray}
* and read using {@link JsonReader#endArray}.
*/
END_ARRAY,
/**
* The opening of a JSON object. Written using {@link JsonWriter#beginObject}
* and read using {@link JsonReader#beginObject}.
*/
BEGIN_OBJECT,
/**
* The closing of a JSON object. Written using {@link JsonWriter#endObject}
* and read using {@link JsonReader#endObject}.
*/
END_OBJECT,
/**
* A JSON property name. Within objects, tokens alternate between names and
* their values. Written using {@link JsonWriter#name} and read using {@link
* JsonReader#nextName}
*/
NAME,
/**
* A JSON string.
*/
STRING,
/**
* A JSON number represented in this API by a Java {@code double}, {@code
* long}, or {@code int}.
*/
NUMBER,
/**
* A JSON {@code true} or {@code false}.
*/
BOOLEAN,
/**
* A JSON {@code null}.
*/
NULL,
/**
* The end of the JSON stream. This sentinel value is returned by {@link
* JsonReader#peek()} to signal that the JSON-encoded value has no more
* tokens.
*/
END_DOCUMENT
}
JsonElement
Json 解析全靠TypeAdapter, 将Json文件 转换到bean使用的是TypeAdapter中的read,反过来用的是write 方法。
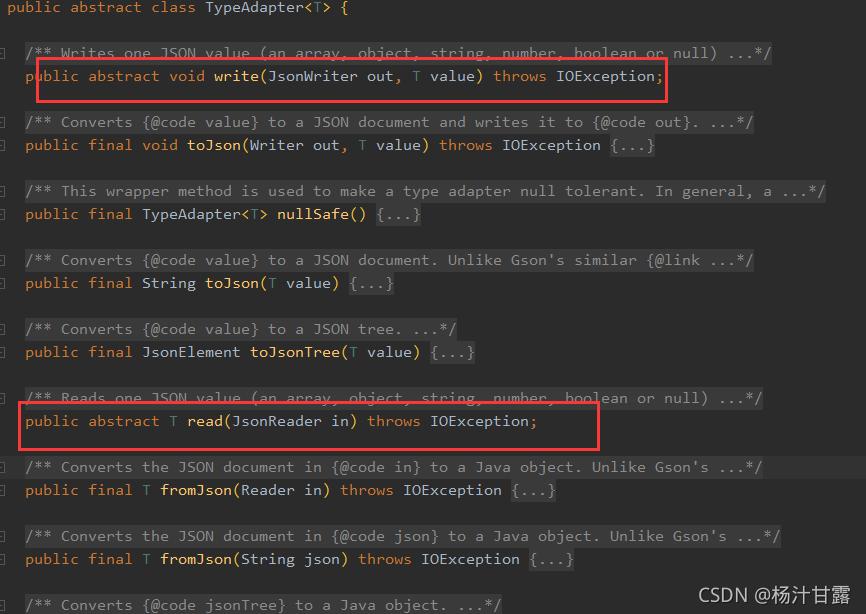 任意的一种类型都对应一个TypeAdapter 基本数据类型
任意的一种类型都对应一个TypeAdapter 基本数据类型
其他的要么是自定义,要么是使用ReflectiveTypeAdapterFactory类中的Adapter进行解析:
下面就是使用ReflectiveTypeAdapterFactory中的TypeAdapter来进行读写的
public static final class Adapter<T> extends TypeAdapter<T> {
@Override public T read(JsonReader in) throws IOException {
T instance = constructor.construct();
in.beginObject();
while (in.hasNext()) {
String name = in.nextName();
BoundField field = boundFields.get(name);
if (field == null || !field.deserialized) {
in.skipValue();
} else {
field.read(in, instance);
}
}
in.endObject();
return instance;
}
@Override public void write(JsonWriter out, T value) throws IOException {
out.beginObject();
for (BoundField boundField : boundFields.values()) {
if (boundField.writeField(value)) {
out.name(boundField.name);
boundField.write(out, value);
}
}
out.endObject();
}
}
public interface TypeAdapterFactory {
/**
* Returns a type adapter for {@code type}, or null if this factory doesn't
* support {@code type}.
*/
<T> TypeAdapter<T> create(Gson gson, TypeToken<T> type);
}
自定义的TypeAdapter实现Gson的原理:
public static void main(String[] args) {
User user = new User("gg","Zero");
GsonBuilder gsonBuilder = new GsonBuilder();
gsonBuilder.registerTypeAdapter(User.class, new UserJsonAdapter()); //1
Gson gson = gsonBuilder.create(); // 2
String gsonStr = gson.toJson(user); //
System.out.println("gsonStr=" + gsonStr);
user = gson.fromJson(gsonStr,User.class);
System.out.println("user: " + user);
}
//上面1处就是将自定义的TypeAdapter添加到
//private final List<TypeAdapterFactory> factories = new ArrayList<TypeAdapterFactory>();
// 这个集合里面。
public GsonBuilder registerTypeAdapter(Type type, Object typeAdapter) {
$Gson$Preconditions.checkArgument(typeAdapter instanceof JsonSerializer<?>
|| typeAdapter instanceof JsonDeserializer<?>
|| typeAdapter instanceof InstanceCreator<?>
|| typeAdapter instanceof TypeAdapter<?>);
if (typeAdapter instanceof InstanceCreator<?>) {
instanceCreators.put(type, (InstanceCreator) typeAdapter);
}
//这是自定义JsonSerializer类型的序列化
//这是自定义过程的反序列化JsonDeserializer
if (typeAdapter instanceof JsonSerializer<?> || typeAdapter instanceof JsonDeserializer<?>) {
TypeToken<?> typeToken = TypeToken.get(type);
factories.add(TreeTypeAdapter.newFactoryWithMatchRawType(typeToken, typeAdapter));
}
//如果是自定义TypeAdapter类型将走这里
if (typeAdapter instanceof TypeAdapter<?>) {
factories.add(TypeAdapters.newFactory(TypeToken.get(type), (TypeAdapter)typeAdapter));
}
return this;
}
//上面2处的
Gson gson = gsonBuilder.create();
将上面创建的TypeAdapterFactory添加到Gson类的成员变量final List<TypeAdapterFactory> factories;当中
代码:
factories.addAll(this.factories);
// users' type adapters
factories.addAll(factoriesToBeAdded);//使用自定义的factory
//上面3处:
public String toJson(Object src) {
if (src == null) {
return toJson(JsonNull.INSTANCE);
}
return toJson(src, src.getClass());// 这里
}
public String toJson(Object src, Type typeOfSrc) {
StringWriter writer = new StringWriter();
toJson(src, typeOfSrc, writer); // 这里
return writer.toString();
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void toJson(Object src, Type typeOfSrc, JsonWriter writer) throws JsonIOException {
// 最重要的是这里
TypeAdapter<?> adapter = getAdapter(TypeToken.get(typeOfSrc));
boolean oldLenient = writer.isLenient();
boolean oldHtmlSafe = writer.isHtmlSafe();
writer.setHtmlSafe(htmlSafe);
boolean oldSerializeNulls = writer.getSerializeNulls();
writer.setSerializeNulls(serializeNulls);
try {
// 从getAdapter获取TypeAdapter就需要执行自定义的write方法。
((TypeAdapter<Object>) adapter).write(writer, src);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new JsonIOException(e);
} finally {
writer.setLenient(oldLenient);
writer.setHtmlSafe(oldHtmlSafe);
writer.setSerializeNulls(oldSerializeNulls);
}
}
public <T> TypeAdapter<T> getAdapter(TypeToken<T> type) {
//看factories为new ArrayList<TypeAdapterFactory>();动态数组类型,
//他是按照添加元素的顺序先后来查找的
for (TypeAdapterFactory factory : factories) {
TypeAdapter<T> candidate = factory.create(this, type);//1
if (candidate != null) {
。。。。
return candidate;
}
}
}
//上面的1处就是要找到上面的factory,调用里面的create方法,获得自定义的TypeAdapter。
总结: 就要通过实现TypeAdapterFactory 接口的工厂的Create方法来创建TypeAdapter,再调用里面的writer 和read方法。
在流程中关键点是创建Gson构造函数的时候。
Gson(final Excluder excluder, final FieldNamingStrategy fieldNamingStrategy,
final Map<Type, InstanceCreator<?>> instanceCreators, boolean serializeNulls,
boolean complexMapKeySerialization, boolean generateNonExecutableGson, boolean htmlSafe,
boolean prettyPrinting, boolean lenient, boolean serializeSpecialFloatingPointValues,
LongSerializationPolicy longSerializationPolicy, String datePattern, int dateStyle,
int timeStyle, List<TypeAdapterFactory> builderFactories,
List<TypeAdapterFactory> builderHierarchyFactories,
List<TypeAdapterFactory> factoriesToBeAdded) {
this.excluder = excluder; // 使用@Expose标注的就拒绝序列化或者反序列化
this.fieldNamingStrategy = fieldNamingStrategy;
this.instanceCreators = instanceCreators;
this.constructorConstructor = new ConstructorConstructor(instanceCreators);
this.serializeNulls = serializeNulls;
this.complexMapKeySerialization = complexMapKeySerialization;
this.generateNonExecutableJson = generateNonExecutableGson;
this.htmlSafe = htmlSafe;
this.prettyPrinting = prettyPrinting;
this.lenient = lenient;
this.serializeSpecialFloatingPointValues = serializeSpecialFloatingPointValues;
this.longSerializationPolicy = longSerializationPolicy;
this.datePattern = datePattern;
this.dateStyle = dateStyle;
this.timeStyle = timeStyle;
this.builderFactories = builderFactories;
this.builderHierarchyFactories = builderHierarchyFactories;
List<TypeAdapterFactory> factories = new ArrayList<TypeAdapterFactory>();
// built-in type adapters that cannot be overridden
factories.add(TypeAdapters.JSON_ELEMENT_FACTORY);
factories.add(ObjectTypeAdapter.FACTORY);
// the excluder must precede all adapters that handle user-defined types
factories.add(excluder);
// users' type adapters
factories.addAll(factoriesToBeAdded);//添加自定义的factory
// type adapters for basic platform types
factories.add(TypeAdapters.STRING_FACTORY);
factories.add(TypeAdapters.INTEGER_FACTORY);
factories.add(TypeAdapters.BOOLEAN_FACTORY);
factories.add(TypeAdapters.BYTE_FACTORY);
factories.add(TypeAdapters.SHORT_FACTORY);
TypeAdapter<Number> longAdapter = longAdapter(longSerializationPolicy);
factories.add(TypeAdapters.newFactory(long.class, Long.class, longAdapter));
factories.add(TypeAdapters.newFactory(double.class, Double.class,
doubleAdapter(serializeSpecialFloatingPointValues)));
factories.add(TypeAdapters.newFactory(float.class, Float.class,
floatAdapter(serializeSpecialFloatingPointValues)));
factories.add(TypeAdapters.NUMBER_FACTORY);
factories.add(TypeAdapters.ATOMIC_INTEGER_FACTORY);
factories.add(TypeAdapters.ATOMIC_BOOLEAN_FACTORY);
factories.add(TypeAdapters.newFactory(AtomicLong.class, atomicLongAdapter(longAdapter)));
factories.add(TypeAdapters.newFactory(AtomicLongArray.class, atomicLongArrayAdapter(longAdapter)));
factories.add(TypeAdapters.ATOMIC_INTEGER_ARRAY_FACTORY);
factories.add(TypeAdapters.CHARACTER_FACTORY);
factories.add(TypeAdapters.STRING_BUILDER_FACTORY);
factories.add(TypeAdapters.STRING_BUFFER_FACTORY);
factories.add(TypeAdapters.newFactory(BigDecimal.class, TypeAdapters.BIG_DECIMAL));
factories.add(TypeAdapters.newFactory(BigInteger.class, TypeAdapters.BIG_INTEGER));
factories.add(TypeAdapters.URL_FACTORY);
factories.add(TypeAdapters.URI_FACTORY);
factories.add(TypeAdapters.UUID_FACTORY);
factories.add(TypeAdapters.CURRENCY_FACTORY);
factories.add(TypeAdapters.LOCALE_FACTORY);
factories.add(TypeAdapters.INET_ADDRESS_FACTORY);
factories.add(TypeAdapters.BIT_SET_FACTORY);
factories.add(DateTypeAdapter.FACTORY);
factories.add(TypeAdapters.CALENDAR_FACTORY);
factories.add(TimeTypeAdapter.FACTORY);
factories.add(SqlDateTypeAdapter.FACTORY);
factories.add(TypeAdapters.TIMESTAMP_FACTORY);
factories.add(ArrayTypeAdapter.FACTORY);
factories.add(TypeAdapters.CLASS_FACTORY);
// type adapters for composite and user-defined types
factories.add(new CollectionTypeAdapterFactory(constructorConstructor));
factories.add(new MapTypeAdapterFactory(constructorConstructor, complexMapKeySerialization));
this.jsonAdapterFactory = new JsonAdapterAnnotationTypeAdapterFactory(constructorConstructor);//使用注解添加factory
factories.add(jsonAdapterFactory);
factories.add(TypeAdapters.ENUM_FACTORY);
//最后使用反射来兜底的创建工厂
factories.add(new ReflectiveTypeAdapterFactory(
constructorConstructor, fieldNamingStrategy, excluder, jsonAdapterFactory));
this.factories = Collections.unmodifiableList(factories);
}
来看看注解的实现:
this.jsonAdapterFactory = new JsonAdapterAnnotationTypeAdapterFactory(constructorConstructor);//使用注解添加factory
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.FIELD})
public @interface JsonAdapter {
/** Either a {@link TypeAdapter} or {@link TypeAdapterFactory}, or one or both of {@link JsonDeserializer} or {@link JsonSerializer}. */
Class<?> value();
/** false, to be able to handle {@code null} values within the adapter, default value is true. */
boolean nullSafe() default true;
}
@Override
public <T> TypeAdapter<T> create(Gson gson, TypeToken<T> targetType) {
Class<? super T> rawType = targetType.getRawType();
JsonAdapter annotation = rawType.getAnnotation(JsonAdapter.class);
if (annotation == null) {
return null;
}
return (TypeAdapter<T>) getTypeAdapter(constructorConstructor, gson, targetType, annotation);
}
@SuppressWarnings({ "unchecked", "rawtypes" }) // Casts guarded by conditionals.
TypeAdapter<?> getTypeAdapter(ConstructorConstructor constructorConstructor, Gson gson,
TypeToken<?> type, JsonAdapter annotation) {
Object instance = constructorConstructor.get(TypeToken.get(annotation.value())).construct();
TypeAdapter<?> typeAdapter;
if (instance instanceof TypeAdapter) {
typeAdapter = (TypeAdapter<?>) instance;
}
return typeAdapter;
}





 这篇博客主要介绍了Gson库在处理Json时的基础使用,包括应对Json字段缺失的解决方案,以及如何自定义TypeAdapter进行详细解析。通过分析JsonToken枚举类型和JsonElement,揭示了Gson将Json转换为Java对象的机制。同时,讨论了反射类型的Adapter以及注解在Gson中的应用,强调了TypeAdapterFactory在Gson构造过程中的关键作用。
这篇博客主要介绍了Gson库在处理Json时的基础使用,包括应对Json字段缺失的解决方案,以及如何自定义TypeAdapter进行详细解析。通过分析JsonToken枚举类型和JsonElement,揭示了Gson将Json转换为Java对象的机制。同时,讨论了反射类型的Adapter以及注解在Gson中的应用,强调了TypeAdapterFactory在Gson构造过程中的关键作用。
















 3416
3416

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








