题目描述
请你为 最不经常使用(LFU)缓存算法设计并实现数据结构。它应该支持以下操作:get 和 put。
// 在此问题中,当存在平局(即两个或更多个键具有相同使用频率)时,应该去除 最近 最少使用的键。
LFUCache cache = new LFUCache( 2 /* capacity (缓存容量) */ );
cache.put(1, 1);
cache.put(2, 2);
cache.get(1); // 返回 1
cache.put(3, 3); // 去除 key 2
cache.get(2); // 返回 -1 (未找到key 2)
cache.get(3); // 返回 3
cache.put(4, 4); // 去除 key 1
cache.get(1); // 返回 -1 (未找到 key 1)
cache.get(3); // 返回 3
cache.get(4); // 返回 4
**进阶:**你是否可以在 O(1) 时间复杂度内执行两项操作?
解题思路
本题其实就是在第146题:LRU缓存机制(先做!)的基础上,在删除策略里多考虑了一个维度(「访问次数」)的信息(LRU就是喜新厌旧,淘汰在缓存里呆的时间最久的元素。在删除元素的时候,只看「时间」这一个维度)。本题的核心思想:先考虑访问次数,在访问次数相同的情况下,再考虑缓存的时间。
-
哈希表 + 双向链表(推荐简要阅读):
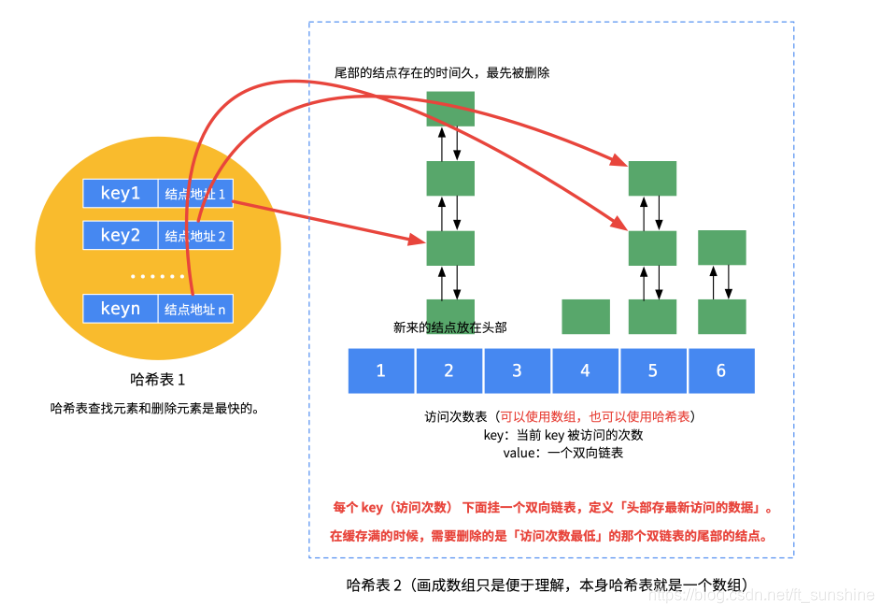
- 由于题目的时间复杂度要求 O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1),空间肯定不能省,存取数据时间性能最好的就是哈希表,因此底层的数据结构一定是一个哈希表;
- 又由于缓存大小有限制,删除策略是**「先看访问频次,再看访问时间」**,所以需要记录每个数据已经访问的频次。
- 「删除某个数据」得 O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1),访问某个数据,时间优先级得提前(提前到当前频次的时间优先级最高处),这样的数据结构符合在头尾访问数据最快,并且删除其中一个结点也得是 O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1),这种数据结构是「双向链表」;
- 「链表」结点得记录:1、
key(在哈希表里删除的时候用得上),2、value,3、访问次数信息freq,以便知道下一个访问次数是多少; - 哈希表存储的
key就是题目的key,方便快速查询和删除,value是自定义Node的“迭代器”,方便对结点进行操作。 - 每次访问一个已经存在的元素的时候:应该先把结点类从当前所属的访问次数双链表里删除,然后再添加到它「下一个访问次数」的双向链表的头部。(双链表的头部看做当前频次链表中时间优先级最高的地方)
内存结构示意图如下:
参考代码
// 缓存的节点信息
struct Node {
int key, val, freq;
Node(int _key, int _val, int _freq): key(_key), val(_val), freq(_freq){}
};
class LFUCache {
private:
int minfreq; // 当前所有Node的最小使用频率(重要!)
int capacity;
unordered_map<int, list<Node>::iterator> umap;
unordered_map<int, list<Node> > freq_list;
public:
LFUCache(int _capacity) {
minfreq = 0;
capacity = _capacity;
umap.clear();
freq_list.clear();
}
int get(int key) {
if (capacity == 0)
return -1;
auto iter = umap.find(key);
if (iter == umap.end())
return -1;
list<Node>::iterator node = iter->second;
int val = node->val;
int freq = node->freq;
freq_list[freq].erase(node);
// 如果当前链表为空,我们需要在哈希表中删除,且更新minFreq
if (freq_list[freq].size() == 0) {
freq_list.erase(freq);
if (minfreq == freq)
minfreq += 1;
}
// 插入到 freq + 1 中
freq_list[freq + 1].push_front(Node(key, val, freq + 1));
umap[key] = freq_list[freq + 1].begin();
return val;
}
void put(int key, int value) {
if (capacity == 0)
return;
auto iter = umap.find(key);
if (iter == umap.end()) {
// 缓存已满,需要进行删除操作
if (umap.size() == capacity) {
// 通过 minFreq 拿到 freq_list[minFreq] 链表的末尾节点
Node iter2 = freq_list[minfreq].back();
freq_list[minfreq].pop_back();
umap.erase(iter2.key);
if (freq_list[minfreq].size() == 0) {
freq_list.erase(minfreq);
// if (minfreq == freq) // 这里加这个if其实没用,因为这种情况下minfreq最后都要被置为 1
// minfreq += 1;
}
}
freq_list[1].push_front(Node(key, value, 1));
umap[key] = freq_list[1].begin();
minfreq = 1; // 当前所有Node的最小使用频率为 1
} else {
// 与 get 操作基本一致,除了需要更新缓存的值
list<Node>::iterator node = iter->second;
int freq = node->freq;
freq_list[freq].erase(node);
if (freq_list[freq].size() == 0) {
freq_list.erase(freq);
if (minfreq == freq)
minfreq += 1;
}
freq_list[freq + 1].push_front(Node(key, value, freq + 1));
umap[key] = freq_list[freq + 1].begin();
}
}
};





 本文详细介绍了一种改进型缓存算法——最不经常使用(LFU)算法的设计与实现,该算法在考虑缓存时间的同时,引入了访问频率作为删除策略的一个维度,通过哈希表与双向链表的结合,实现了O(1)时间复杂度内的get和put操作。
本文详细介绍了一种改进型缓存算法——最不经常使用(LFU)算法的设计与实现,该算法在考虑缓存时间的同时,引入了访问频率作为删除策略的一个维度,通过哈希表与双向链表的结合,实现了O(1)时间复杂度内的get和put操作。
















 2603
2603

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








