上一篇:Python OpenCV Image Processing-图像处理
1. 傅里叶变换 Fourier Transform (cv2.dft)
# DFT in numpy
img = cv2.imread('1.jpg', 0)
f = np.fft.fft2(img)
fshift = np.fft.fftshift(f)
magnitude_spectrum = 20*np.log(np.abs(fshift))
imshow('magnitude_spectrum',magnitude_spectrum)
# DFT in opencv
dft = cv2.dft(np.float32(img), flags=cv2.DFT_COMPLEX_OUTPUT)
dft_shift = np.fft.fftshift(dft)
magnitude_spectrum = 20*np.log(cv2.magnitude(dft_shift[:,:,0], dft_shift[:,:,1]))
# 图像来自OpenCV官方文档
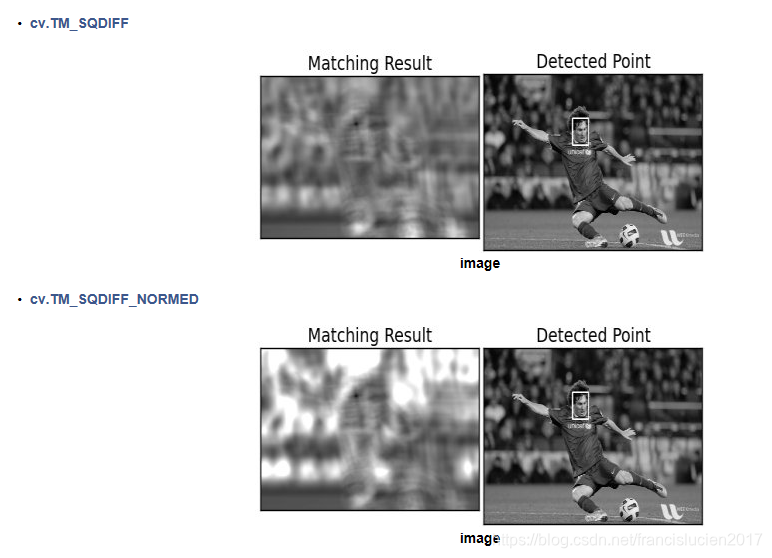
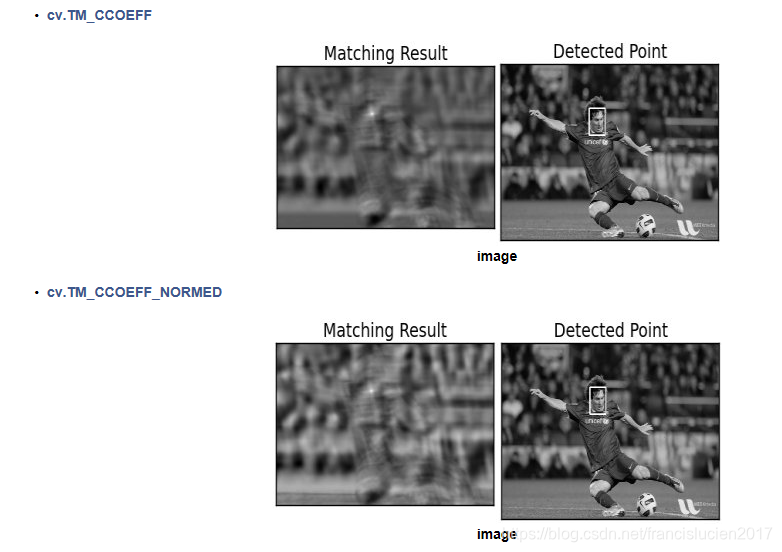
2. 模板匹配 (cv2.matchTemplate)
img = cv2.imread('1.jpg', 0)
img2 = img.copy()
template = cv2.imread('2.jpg', 0)
w, h = template.shape[::-1]
methods = ['cv2.TM_CCOEFF', 'cv2.TM_CCOEFF_NORMED', 'cv2.TM_CCORR',
'cv2.TM_CCORR_NORMED', 'cv2.TM_SQDIFF', 'cv2.TM_SQDIFF_NORMED']
for meth in method:
img = img2.copy()
method = eval(meth)
res = cv2.matchTemplate(img, template, method)
min_val, max_val, min_loc, max_loc = cv2.minMaxLoc(res)
# If the method is TM_SQDIFF or TM_SQDIFF_NORMED, take minimum
if method in [cv.TM_SQDIFF, cv.TM_SQDIFF_NORMED]:
top_left = min_loc
else:
top_left = max_loc
bottom_right = (top_left[0] + w, top_left[1] + h)
# 图像来自OpenCV官方文档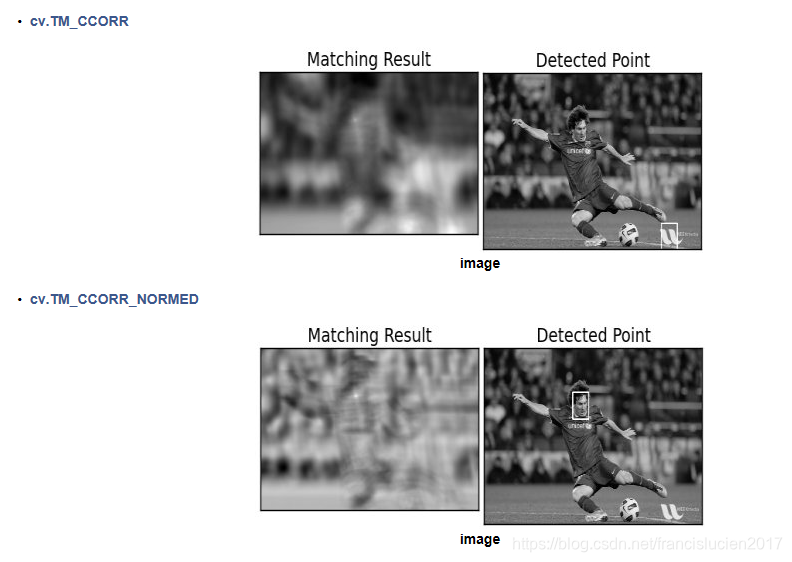


3. 多物体匹配 (cv2.matchTemplate)
img_rgb = cv2.imread('1.jpg')
img_gray = cv2.cvtColor(img_rgb, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
template = cv2.imread('2.jpg', 0)
w,h = template.shape[::-1]
res = cv2.matchTemplate(img_gray, template, cv2.TM_CCOEFF_NORMED)
threshold = 0.8
loc = np.where(res >= threshold)
for pt in zip(*loc[::-1]):
cv2.rectangle(img_rgb, pt, (pt[0]+w, pt[1]+h), (0,0,255), 2)
cv2.imwrite('3.jpg', img_rgb)
# 图像来自OpenCV官方文档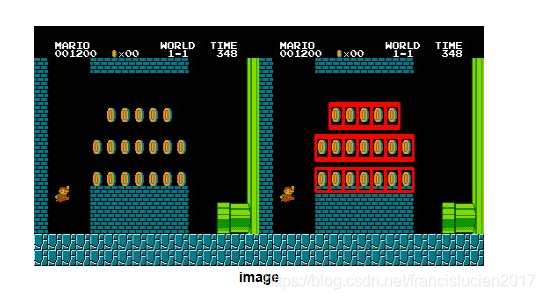
4. 霍夫直线检测(cv2.HoughLines; cv2.HoughLinesP)
# 霍夫直线检测 params: img, rho, theta, threshold
lines = cv2.HoughLines(edges, 1, np.pi/180, 200)
for line in lines:
rho, theta = line[0]
a = np.cos(theta)
b = np.sin(theta)
x0 = a*rho
y0 = b*rho
x1 = int(x0 + 1000*(-b))
y1 = int(y0 + 1000*(a))
x2 = int(x0 - 1000*(-b))
y2 = int(y0 - 1000*(a))
cv2.line(img, (x1,y1), (x2,y2), (0,0,255), 2)
# 霍夫概率直线检测(速度快,绘制方便)
lines = cv2.HoughLinesP(edges, 1, np.pi/180, 100, minLineLength=100, maxLineGap=10)
for line in lines:
x1,y1,x2,y2 = line[0]
cv2.line(img, (x1,y1), (x2,y2), (0,0,255), 2)
5. 霍夫圆检测 (cv2.HoughCircles)
circles = cv2.HoughCircles(img, cv2.HOUGH_GRADIENT, 1, 20, param1=50, param2=30, minRadius=0, maxRadius=0)
circles = np.uint16(np.around(circles))
for i in circle[0, :]:
cv2.circle(img, (i[0], i[1]), i[2], (0,255,0),2) # 圆
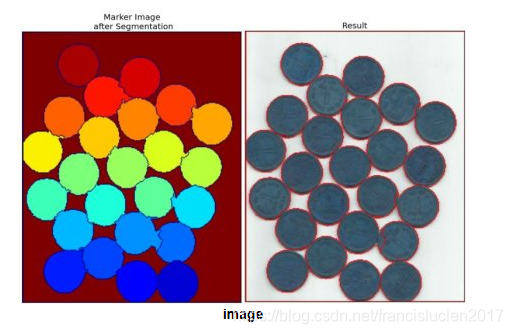
cv2.circle(img, (i[0],i[1]),2,(0,0,255),3) # 圆心6.分水岭算法(图像分割;cv2.watershed)
img = cv2.imread('1.jpg')
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
ret, thresh = cv2.threshold(gray, 0, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY + cv2.THRESH_OTST)
kernel = np.ones((3,3), np.uint8)
opening = cv2.morphologyEx(thresh, cv2.MORPH_OPEN, kernel, iterations=2)
bg = cv2.dilate(opening, kernel, iterations=3)
dist = cv2.distanceTransform(opening, cv2.DIST_L2, 5) # 计算距离0像素最近的距离
ret, fg = cv2.threshold(dist, 0.7*dist.max(), 255, 0)
fg = np.uint8(fg)
unknown = cv2.subtract(bg, fg)
ret, marker = cv2.connectedComponets(fg)
marker = marker + 1
marker[unknown==255] = 0
marker = cv2.watershed(img, marker)
img[marker==-1] = [255,0,0]
# 原图和效果图如下(图片来自OpenCV官方文档)







 本文深入探讨了OpenCV库中的关键图像处理技术,包括傅里叶变换、模板匹配、霍夫直线与圆检测、分水岭算法等,通过实例展示了如何使用这些技术进行图像分析与处理。
本文深入探讨了OpenCV库中的关键图像处理技术,包括傅里叶变换、模板匹配、霍夫直线与圆检测、分水岭算法等,通过实例展示了如何使用这些技术进行图像分析与处理。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








