Eat the Trees
Time Limit: 4000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 1012 Accepted Submission(s): 480
Problem Description
Most of us know that in the game called DotA(Defense of the Ancient), Pudge is a strong hero in the first period of the game. When the game goes to end however, Pudge is not a strong hero any more.
So Pudge’s teammates give him a new assignment—Eat the Trees!
The trees are in a rectangle N * M cells in size and each of the cells either has exactly one tree or has nothing at all. And what Pudge needs to do is to eat all trees that are in the cells.
There are several rules Pudge must follow:
I. Pudge must eat the trees by choosing a circuit and he then will eat all trees that are in the chosen circuit.
II. The cell that does not contain a tree is unreachable, e.g. each of the cells that is through the circuit which Pudge chooses must contain a tree and when the circuit is chosen, the trees which are in the cells on the circuit will disappear.
III. Pudge may choose one or more circuits to eat the trees.
Now Pudge has a question, how many ways are there to eat the trees?
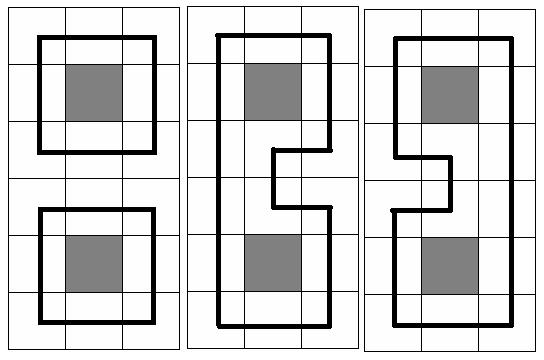
At the picture below three samples are given for N = 6 and M = 3(gray square means no trees in the cell, and the bold black line means the chosen circuit(s))
So Pudge’s teammates give him a new assignment—Eat the Trees!
The trees are in a rectangle N * M cells in size and each of the cells either has exactly one tree or has nothing at all. And what Pudge needs to do is to eat all trees that are in the cells.
There are several rules Pudge must follow:
I. Pudge must eat the trees by choosing a circuit and he then will eat all trees that are in the chosen circuit.
II. The cell that does not contain a tree is unreachable, e.g. each of the cells that is through the circuit which Pudge chooses must contain a tree and when the circuit is chosen, the trees which are in the cells on the circuit will disappear.
III. Pudge may choose one or more circuits to eat the trees.
Now Pudge has a question, how many ways are there to eat the trees?
At the picture below three samples are given for N = 6 and M = 3(gray square means no trees in the cell, and the bold black line means the chosen circuit(s))

Input
The input consists of several test cases. The first line of the input is the number of the cases. There are no more than 10 cases.
For each case, the first line contains the integer numbers N and M, 1<=N, M<=11. Each of the next N lines contains M numbers (either 0 or 1) separated by a space. Number 0 means a cell which has no trees and number 1 means a cell that has exactly one tree.
For each case, the first line contains the integer numbers N and M, 1<=N, M<=11. Each of the next N lines contains M numbers (either 0 or 1) separated by a space. Number 0 means a cell which has no trees and number 1 means a cell that has exactly one tree.
Output
For each case, you should print the desired number of ways in one line. It is guaranteed, that it does not exceed 2
63 – 1. Use the format in the sample.
Sample Input
2 6 3 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 2 4 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Sample Output
Case 1: There are 3 ways to eat the trees. Case 2: There are 2 ways to eat the trees.
Source
Recommend
wangye
分析:插头DP中最简单的题目了。。。尽管看了题解,一次性敲对的说,却因为“There"打成"there",改了一晚上,我承认我好挫,没啥好说的,等搞完这个专题再做一个专门的总结吧,先不解释了。。。比赛临近了,这种失误。。。
插头DP简单题,多条回路
代码:
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
int i,j,k,m,n,p,q,ok,c=0,t;
__int64 f[2][1<<12];//表示该状态下的最值
bool x,y,g,h;//g,h为滚动指标x,y为存在标记
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
scanf("%d%d",&m,&n);
memset(f,0,sizeof(f));//这个你懂的
f[0][0]=g=1;//这个你懂的
for(h=i=0; i<m; ++i)//枚举行
{
for(j=1;g=!g,h=!h,j<=n; ++j)//枚举列
for(scanf("%d",&ok),k=0; k<1<<n<<1; ++k)//枚举状态k
{
p=1<<j,q=p>>1,x=k&p,y=k&q;//记录第j-1,j位是否为1
if(ok)//该位置可放
{
f[h][k]=f[g][k^p^q];//所有情况
if(x^y)f[h][k]+=f[g][k];//j-1,j只有一个1的情况
}
else f[h][k]=x|y?0:f[g][k];//该位置不可放
}
memset(f[h],0,sizeof(f[h]));//这个你懂的
for(j=0;j<1<<n; ++j)f[h][j<<1]=f[g][j];//换到下一行转移,最右边的右插头移到下一行的最左边
}
printf("Case %d: There are %I64d ways to eat the trees.\n",++c,f[h][0]);
}
return 0;
}







 本文介绍了一个基于插头动态规划(DP)算法解决的游戏问题——在DotA游戏中如何有效率地让英雄Pudge吃掉地图上的树木。文章通过具体示例详细解释了问题的背景、输入输出格式,并提供了一份简洁的C++实现代码。
本文介绍了一个基于插头动态规划(DP)算法解决的游戏问题——在DotA游戏中如何有效率地让英雄Pudge吃掉地图上的树木。文章通过具体示例详细解释了问题的背景、输入输出格式,并提供了一份简洁的C++实现代码。
















 2761
2761

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








