【转自】http://download.oracle.com/docs/cd/B19306_01/server.102/b14200/statements_7004.htm#i2153503
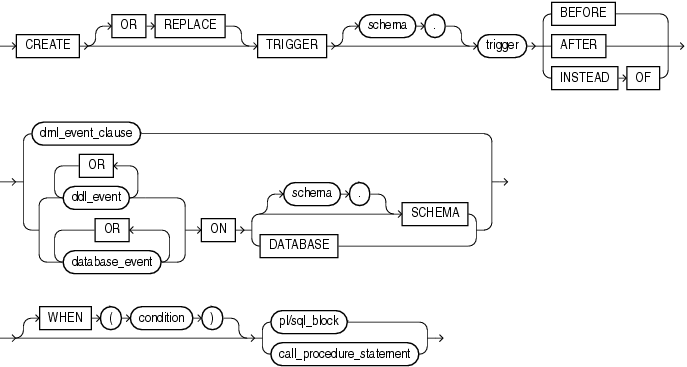
CREATE TRIGGER
Use the CREATE TRIGGER statement to create and enable a database trigger, which is:
-
A stored PL/SQL block associated with a table, a schema, or the database or
-
An anonymous PL/SQL block or a call to a procedure implemented in PL/SQL or Java
Oracle Database automatically executes a trigger when specified conditions occur.
When you create a trigger, the database enables it automatically. You can subsequently disable and enable a trigger with the DISABLE and ENABLE clause of the ALTER TRIGGER or ALTER TABLE statement.
See Also:
-
Oracle Database Concepts for a description of the various types of triggers and Oracle Database Application Developer's Guide - Fundamentals for more information on how to design triggers
-
ALTER TRIGGER and ALTER TABLE for information on enabling, disabling, and compiling triggers, and DROP TRIGGER for information on dropping a trigger
Before a trigger can be created, the user SYS must run a SQL script commonly called DBMSSTDX.SQL. The exact name and location of this script depend on your operating system.
-
To create a trigger in your own schema on a table in your own schema or on your own schema (
SCHEMA), you must have theCREATETRIGGERsystem privilege. -
To create a trigger in any schema on a table in any schema, or on another user's schema (
schema.SCHEMA), you must have theCREATEANYTRIGGERsystem privilege. -
In addition to the preceding privileges, to create a trigger on
DATABASE, you must have theADMINISTERDATABASETRIGGERsystem privilege.
If the trigger issues SQL statements or calls procedures or functions, then the owner of the trigger must have the privileges necessary to perform these operations. These privileges must be granted directly to the owner rather than acquired through roles.
DML_event_clause ::=
Specify OR REPLACE to re-create the trigger if it already exists. Use this clause to change the definition of an existing trigger without first dropping it.
Specify the schema to contain the trigger. If you omit schema, then Oracle Database creates the trigger in your own schema.
Specify the name of the trigger to be created.
If a trigger produces compilation errors, then it is still created, but it fails on execution. This means it effectively blocks all triggering DML statements until it is disabled, replaced by a version without compilation errors, or dropped. You can see the associated compiler error messages with the SQL*Plus command SHOW ERRORS.
Note:
If you create a trigger on a base table of a materialized view, then you must ensure that the trigger does not fire during a refresh of the materialized view. During refresh, theDBMS_MVIEW procedure
I_AM_A_REFRESH returns
TRUE.
Specify BEFORE to cause the database to fire the trigger before executing the triggering event. For row triggers, the trigger is fired before each affected row is changed.
Restrictions on BEFORE Triggers BEFORE triggers are subject to the following restrictions:
-
You cannot specify a
BEFOREtrigger on a view or an object view. -
You can write to the :
NEWvalue but not to the :OLDvalue.
Specify AFTER to cause the database to fire the trigger after executing the triggering event. For row triggers, the trigger is fired after each affected row is changed.
Restrictions on AFTER Triggers AFTER triggers are subject to the following restrictions:
-
You cannot specify an
AFTERtrigger on a view or an object view. -
You cannot write either the :
OLDor the :NEWvalue.
Note:
When you create a materialized view log for a table, Oracle Database implicitly creates anAFTER
ROW trigger on the table. This trigger inserts a row into the materialized view log whenever an
INSERT,
UPDATE, or
DELETE statement modifies data in the master table. You cannot control the order in which multiple row triggers fire. Therefore, you should not write triggers intended to affect the content of the materialized view.
See Also:
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW LOG for more information on materialized view logsSpecify INSTEAD OF to cause Oracle Database to fire the trigger instead of executing the triggering event. INSTEAD OF triggers are valid for DML events on views. They are not valid for DDL or database events.
If a view is inherently updatable and has INSTEAD OF triggers, then the triggers take preference. In other words, the database fires the triggers instead of performing DML on the view.
If the view belongs to a hierarchy, then the trigger is not inherited by subviews.
Note:
Oracle Database fine-grained access control lets you define row-level security policies on views. These policies enforce specified rules in response to DML operations. If anINSTEAD
OF trigger is also defined on the view, then the database will not enforce the row-level security policies, because the database fires the
INSTEAD
OF trigger instead of executing the DML on the view.
-
INSTEADOFtriggers are valid only for views. You cannot specify anINSTEADOFtrigger on a table. -
You can read both the :
OLDand the :NEWvalue, but you cannot write either the :OLDor the :NEWvalue.
BEFORE,
AFTER, or
INSTEAD
OF) that fire for the same statement on the same table. The order in which Oracle Database fires these triggers is indeterminate. If your application requires that one trigger be fired before another of the same type for the same statement, then combine these triggers into a single trigger whose trigger action performs the trigger actions of the original triggers in the appropriate order.
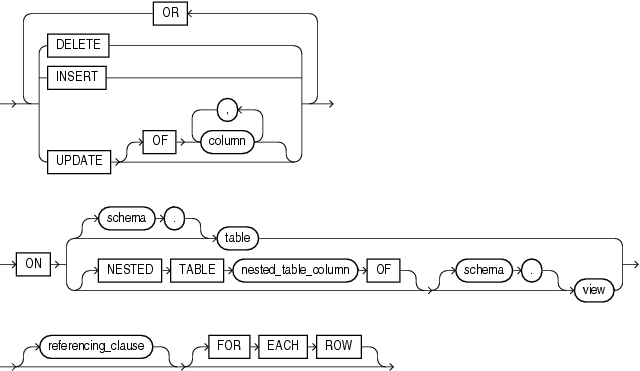
The DML_event_clause lets you specify one of three DML statements that can cause the trigger to fire. Oracle Database fires the trigger in the existing user transaction.
You cannot specify the MERGE keyword in the DML_event_clause. If you want a trigger to fire in relation to a MERGE operation, you must create triggers on the INSERT and UPDATE operations to which the MERGE operation decomposes.
See Also:
"Creating a DML Trigger: Examples"Specify DELETE if you want the database to fire the trigger whenever a DELETE statement removes a row from the table or removes an element from a nested table.
Specify INSERT if you want the database to fire the trigger whenever an INSERT statement adds a row to a table or adds an element to a nested table.
Specify UPDATE if you want the database to fire the trigger whenever an UPDATE statement changes a value in one of the columns specified after OF. If you omit OF, then the database fires the trigger whenever an UPDATEstatement changes a value in any column of the table or nested table.
For an UPDATE trigger, you can specify object type, varray, and REF columns after OF to indicate that the trigger should be fired whenever an UPDATE statement changes a value in one of the columns. However, you cannot change the values of these columns in the body of the trigger itself.
Note:
Using OCI functions or theDBMS_LOB package to update LOB values or LOB attributes of object columns does not cause Oracle Database to fire triggers defined on the table containing the columns or the attributes.
Restrictions on Triggers on UPDATE Operations The UPDATE clause is subject to the following restrictions:
-
You cannot specify
UPDATEOFfor anINSTEADOFtrigger. Oracle Database firesINSTEADOFtriggers whenever anUPDATEchanges a value in any column of the view. -
You cannot specify a nested table or LOB column in the
UPDATEOFclause.
See Also:
AS
subquery clause of
CREATE VIEW for a list of constructs that prevent inserts, updates, or deletes on a view
Performing DML operations directly on nested table columns does not cause Oracle Database to fire triggers defined on the table containing the nested table column.
Specify one or more types of DDL statements that can cause the trigger to fire. You can create triggers for these events on DATABASE or SCHEMA unless otherwise noted. You can create BEFORE and AFTER triggers for these events. Oracle Database fires the trigger in the existing user transaction.
Restriction on Triggers on DDL Events You cannot specify as a triggering event any DDL operation performed through a PL/SQL procedure.
See Also:
"Creating a DDL Trigger: Example"The following ddl_event values are valid:
ALTER Specify ALTER to fire the trigger whenever an ALTER statement modifies a database object in the data dictionary.
Restriction on Triggers on ALTER Operations The trigger will not be fired by an ALTER DATABASE statement.
ANALYZE Specify ANALYZE to fire the trigger whenever the database collects or deletes statistics or validates the structure of a database object.
See Also:
ANALYZE for information on various ways of collecting statisticsASSOCIATE STATISTICS Specify ASSOCIATE STATISTICS to fire the trigger whenever the database associates a statistics type with a database object.
AUDIT Specify AUDIT to fire the trigger whenever the database tracks the occurrence of a SQL statement or tracks operations on a schema object.
COMMENT Specify COMMENT to fire the trigger whenever a comment on a database object is added to the data dictionary.
CREATE Specify CREATE to fire the trigger whenever a CREATE statement adds a new database object to the data dictionary.
Restriction on Triggers on CREATE Operations The trigger will not be fired by a CREATE DATABASE or CREATE CONTROLFILE statement.
DISASSOCIATE STATISTICS Specify DISASSOCIATE STATISTICS to fire the trigger whenever the database disassociates a statistics type from a database object.
DROP Specify DROP to fire the trigger whenever a DROP statement removes a database object from the data dictionary.
GRANT Specify GRANT to fire the trigger whenever a user grants system privileges or roles or object privileges to another user or to a role.
NOAUDIT Specify NOAUDIT to fire the trigger whenever a NOAUDIT statement instructs the database to stop tracking a SQL statement or operations on a schema object.
RENAME Specify RENAME to fire the trigger whenever a RENAME statement changes the name of a database object.
REVOKE Specify REVOKE to fire the trigger whenever a REVOKE statement removes system privileges or roles or object privileges from a user or role.
TRUNCATE Specify TRUNCATE to fire the trigger whenever a TRUNCATE statement removes the rows from a table or cluster and resets its storage characteristics.
DDL Specify DDL to fire the trigger whenever any of the preceding DDL statements is issued.
Specify one or more particular states of the database that can cause the trigger to fire. You can create triggers for these events on DATABASE or SCHEMA unless otherwise noted. For each of these triggering events, Oracle Database opens an autonomous transaction scope, fires the trigger, and commits any separate transaction (regardless of any existing user transaction).
SERVERERROR Specify SERVERERROR to fire the trigger whenever a server error message is logged.
The following errors do not cause a SERVERERROR trigger to fire:
-
ORA-01403: no data found -
ORA-01422: exact fetch returns more than requested number of rows -
ORA-01423: error encountered while checking for extra rows in exact fetch -
ORA-01034: ORACLE not available -
ORA-04030: out of process memory when trying to allocatestringbytes (string,string)
LOGON Specify LOGON to fire the trigger whenever a client application logs onto the database.
LOGOFF Specify LOGOFF to fire the trigger whenever a client application logs off the database.
STARTUP Specify STARTUP to fire the trigger whenever the database is opened.
SHUTDOWN Specify SHUTDOWN to fire the trigger whenever an instance of the database is shut down.
SUSPEND Specify SUSPEND to fire the trigger whenever a server error causes a transaction to be suspended.
DB_ROLE_CHANGE In a Data Guard configuration, specify DB_ROLE_CHANGE to fire the trigger whenever a role change occurs from standby to primary or from primary to standby.
Notes:
-
Only
AFTERtriggers are relevant forLOGON,STARTUP,SERVERERROR,SUSPEND, andDB_ROLE_CHANGE. -
Only
BEFOREtriggers are relevant forLOGOFFandSHUTDOWN. -
AFTERSTARTUPandBEFORESHUTDOWNtriggers apply only toDATABASE.
See Also:
PL/SQL User's Guide and Reference for more information on autonomous transaction scopeThe ON clause lets you determine the database object on which the trigger is to be created. Specify the schema and table or view name of one of the following on which the trigger is to be created:
-
Table or view
-
Object table or object view
-
A column of nested-table type
If you omit schema, then Oracle Database assumes the table is in your own schema. You can create triggers on index-organized tables.
Restriction on Schema You cannot create a trigger on a table in the schema SYS.
Specify the nested_table_column of a view upon which the trigger is being defined. Such a trigger will fire only if the DML operates on the elements of the nested table.
Restriction on Triggers on Nested Tables You can specify NESTED TABLE only for INSTEAD OF triggers.
Specify DATABASE to define the trigger on the entire database. The trigger fires whenever any database user initiates the triggering event.
Specify SCHEMA to define the trigger on the current schema. The trigger fires whenever any user connected as schema initiates the triggering event.
See Also:
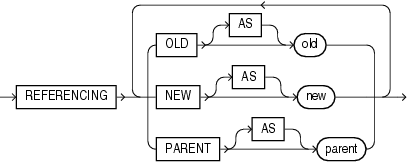
"Creating a SCHEMA Trigger: Example"The referencing_clause lets you specify correlation names. You can use correlation names in the PL/SQL block and WHEN condition of a row trigger to refer specifically to old and new values of the current row. The default correlation names are OLD and NEW. If your row trigger is associated with a table named OLD or NEW, use this clause to specify different correlation names to avoid confusion between the table name and the correlation name.
-
If the trigger is defined on a nested table, then
OLDandNEWrefer to the row of the nested table, andPARENTrefers to the current row of the parent table. -
If the trigger is defined on an object table or view, then
OLDandNEWrefer to object instances.
Restriction on the referencing_clause The referencing_clause is not valid with INSTEAD OF triggers on CREATE DDL events.
Specify FOR EACH ROW to designate the trigger as a row trigger. Oracle Database fires a row trigger once for each row that is affected by the triggering statement and meets the optional trigger constraint defined in theWHEN condition.
Except for INSTEAD OF triggers, if you omit this clause, then the trigger is a statement trigger. Oracle Database fires a statement trigger only once when the triggering statement is issued if the optional trigger constraint is met.
INSTEAD OF trigger statements are implicitly activated for each row.
Restriction on Row Triggers This clause is valid only for DML event triggers, not for DDL or database event triggers.
Specify the trigger condition, which is a SQL condition that must be satisfied for the database to fire the trigger. See the syntax description of condition in Chapter 7, "Conditions". This condition must contain correlation names and cannot contain a query.
The NEW and OLD keywords, when specified in the WHEN clause, are not considered bind variables, so are not preceded by a colon (:). However, you must precede NEW and OLD with a colon in all references other than theWHEN clause.
Restrictions on Trigger Conditions Trigger conditions are subject to the following restrictions:
-
If you specify this clause for a DML event trigger, then you must also specify
FOREACHROW. Oracle Database evaluates this condition for each row affected by the triggering statement. -
You cannot specify trigger conditions for
INSTEADOFtrigger statements. -
You can reference object columns or their attributes, or varray, nested table, or LOB columns. You cannot invoke PL/SQL functions or methods in the trigger condition.
Specify the PL/SQL block that Oracle Database executes to fire the trigger.
The PL/SQL block of a database trigger can contain one of a series of built-in functions in the SYS schema designed solely to extract system event attributes. These functions can be used only in the PL/SQL block of a database trigger.
Restrictions on Trigger Implementation The implementation of a trigger is subject to the following restrictions:
-
The PL/SQL block of a trigger cannot contain transaction control SQL statements (
COMMIT,ROLLBACK,SAVEPOINT, andSETCONSTRAINT) if the block is executed within the same transaction. -
You can reference and use LOB columns in the trigger action inside the PL/SQL block. You can modify the :
NEWvalues but not the :OLDvalues of LOB columns within the trigger action.
See Also:
-
PL/SQL User's Guide and Reference for information on PL/SQL, including how to write PL/SQL blocks
-
Oracle Database Application Developer's Guide - Fundamentals for information on these functions
The call_procedure_statement lets you call a stored procedure rather than specifying the trigger code inline as a PL/SQL block. The syntax of this statement is the same as that for CALL, with the following exceptions:
-
You cannot specify the
INTOclause ofCALL, because it applies only to functions. -
You cannot specify bind variables in
expr. -
To reference columns of tables on which the trigger is being defined, you must specify :
NEWand :OLD.
Creating a DML Trigger: Examples This example shows the basic syntax for a BEFORE statement trigger. You would write such a trigger to place restrictions on DML statements issued on a table, for example, when such statements could be issued.
CREATE TRIGGER schema.trigger_name BEFORE DELETE OR INSERT OR UPDATE ON schema.table_name pl/sql_block
Oracle Database fires such a trigger whenever a DML statement affects the table. This trigger is a BEFORE statement trigger, so the database fires it once before executing the triggering statement.
The next example shows a partial BEFORE row trigger. The PL/SQL block might specify, for example, that an employee's salary must fall within the established salary range for the employee's job:
CREATE TRIGGER hr.salary_check
BEFORE INSERT OR UPDATE OF salary, job_id ON hr.employees
FOR EACH ROW
WHEN (new.job_id <> 'AD_VP')
pl/sql_block
Oracle Database fires this trigger whenever one of the following statements is issued:
-
An
INSERTstatement that adds rows to theemployeestable -
An
UPDATEstatement that changes values of thesalaryorjob_idcolumns of theemployeestable
salary_check is a BEFORE row trigger, so the database fires it before changing each row that is updated by the UPDATE statement or before adding each row that is inserted by the INSERT statement.
salary_check has a trigger condition that prevents it from checking the salary of the administrative vice president (AD_VP).
Creating a DDL Trigger: Example This example creates an AFTER statement trigger on any DDL statement CREATE. Such a trigger can be used to audit the creation of new data dictionary objects in your schema.
CREATE TRIGGER audit_db_object AFTER CREATE
ON SCHEMA
pl/sql_block
Calling a Procedure in a Trigger Body: Example You could create the salary_check trigger described in the preceding example by calling a procedure instead of providing the trigger body in a PL/SQL block. Assume you have defined a procedure check_sal in the hrschema, which verifies that an employee's salary is in an appropriate range. Then you could create the trigger salary_check as follows:
CREATE TRIGGER salary_check BEFORE INSERT OR UPDATE OF salary, job_id ON employees FOR EACH ROW WHEN (new.job_id <> 'AD_VP') CALL check_sal(:new.job_id, :new.salary, :new.last_name)
The procedure check_sal could be implemented in PL/SQL, C, or Java. Also, you can specify :OLD values in the CALL clause instead of :NEW values.
Creating a Database Event Trigger: Example This example shows the basic syntax for a trigger to log all errors. The hypothetical PL/SQL block does some special processing for a particular error (invalid logon, error number 1017). This trigger is an AFTERstatement trigger, so it is fired after an unsuccessful statement execution, such as unsuccessful logon.
CREATE TRIGGER log_errors AFTER SERVERERROR ON DATABASE BEGIN IF (IS_SERVERERROR (1017)) THEN <special processing of logon error> ELSE <log error number> END IF; END;
Creating an INSTEAD OF Trigger: Example In this example, an oe.order_info view is created to display information about customers and their orders:
CREATE VIEW order_info AS
SELECT c.customer_id, c.cust_last_name, c.cust_first_name,
o.order_id, o.order_date, o.order_status
FROM customers c, orders o
WHERE c.customer_id = o.customer_id;
Normally this view would not be updatable, because the primary key of the orders table (order_id) is not unique in the result set of the join view. To make this view updatable, create an INSTEAD OF trigger on the view to process INSERT statements directed to the view. The PL/SQL trigger implementation is shown in italics.
CREATE OR REPLACE TRIGGER order_info_insert INSTEAD OF INSERT ON order_info DECLARE duplicate_info EXCEPTION; PRAGMA EXCEPTION_INIT (duplicate_info, -00001); BEGIN INSERT INTO customers (customer_id, cust_last_name, cust_first_name) VALUES ( :new.customer_id, :new.cust_last_name, :new.cust_first_name); INSERT INTO orders (order_id, order_date, customer_id) VALUES ( :new.order_id, :new.order_date, :new.customer_id); EXCEPTION WHEN duplicate_info THEN RAISE_APPLICATION_ERROR ( num=> -20107, msg=> 'Duplicate customer or order ID'); END order_info_insert; /
You can now insert into both base tables through the view (as long as all NOT NULL columns receive values):
INSERT INTO order_info VALUES (999, 'Smith', 'John', 2500, '13-MAR-2001', 0);
Creating a SCHEMA Trigger: Example The following example creates a BEFORE statement trigger on the sample schema hr. When a user connected as hr attempts to drop a database object, the database fires the trigger before dropping the object:
CREATE OR REPLACE TRIGGER drop_trigger
BEFORE DROP ON hr.SCHEMA
BEGIN
RAISE_APPLICATION_ERROR (
num => -20000,
msg => 'Cannot drop object');
END;
/
############################################################################################
####################另 一 篇####################
############################################################################################
【转自】http://heisetoufa.javaeye.com/blog/367314
oracle 触发器的种类和触发事件,DML触发器,DDL事件触发器,替代触发器,查看触发器,
关键字: oracle 触发器 种类 触发 事件 dml ddl 事件 替代 查看触发器的种类和触发事件
触发器必须由事件才能触发。触发器的触发事件分可为3类,分别是DML事件、DDL事件和数据库事件。
每类事件包含若干个事件,如下所示。数据库的事件是具体的,在创建触发器时要指明触发的事件。
种 类 关 键 字 含 义
- DML事件(3种) INSERT 在表或视图中插入数据时触发
- UPDATE 修改表或视图中的数据时触发
- DELETE 在删除表或视图中的数据时触发
- DDL事件(3种) CREATE 在创建新对象时触发
- ALTER 修改数据库或数据库对象时触发
- DROP 删除对象时触发
- 数据库事件(5种) STARTUP 数据打开时触发
- SHUTDOWN 在使用NORMAL或IMMEDIATE选项关闭数据库时触发
- LOGON 当用户连接到数据库并建立会话时触发
- LOGOFF 当一个会话从数据库中断开时触发
- SERVERERROR 发生服务器错误时触发
触发器的类型可划分为4种:数据操纵语言(DML)触发器、替代(INSTEAD OF)触发器、数据定义语言(DDL)触发器和数据库事件触发器。
各类触发器的作用如下所示。
- 种 类 简 称 作 用
- 数据操纵语言触发器 DML触发器 创建在表上,由DML事件引发的触发器
- 替代触发器 INSTEAD OF触发器 创建在视图上,用来替换对视图进行的插入、删除和修改操作
- 数据定义语言触发器 DDL触发器 定义在模式上,触发事件是数据库对象的创建和修改
- 数据库事件触发器 — 定义在整个数据库或模式上,触发事件是数据库事件
DML触发器的要点
DML触发器是定义在表上的触发器,由DML事件引发。编写DML触发器的要素是:
* 确定触发的表,即在其上定义触发器的表。
* 确定触发的事件,DML触发器的触发事件有INSERT、UPDATE和DELETE三种,说明见下。
* 确定触发时间。触发的时间有BEFORE和AFTER两种,分别表示触发动作发生在DML语句执行之前和语句执行之后。
* 确定触发级别,有语句级触发器和行级触发器两种。语句级触发器表示SQL语句只触发一次触发器,行级触发器表示SQL语句影响的每一行都要触发一次。
由于在同一个表上可以定义多个DML触发器,因此触发器本身和引发触发器的SQL语句在执行的顺序上有先后的关系。它们的顺序是:
* 如果存在语句级BEFORE触发器,则先执行一次语句级BEFORE触发器。
* 在SQL语句的执行过程中,如果存在行级BEFORE触发器,则SQL语句在对每一行操作之前,都要先执行一次行级BEFORE触发器,然后才对行进行操作。如果存在行级AFTER触发器,则SQL语句在对每一行操作之后,都要再执行一次行级AFTER触发器。
* 如果存在语句级AFTER触发器,则在SQL语句执行完毕后,要最后执行一次语句级AFTER触发器。
DML触发器还有一些具体的问题,说明如下:
* 如果有多个触发器被定义成为相同时间、相同事件触发,且最后定义的触发器是有效的,则最后定义的触发器被触发,其他触发器不执行。
* 一个触发器可由多个不同的DML操作触发。在触发器中,可用INSERTING、DELETING、UPDATING谓词来区别不同的DML操作。这些谓词可以在IF分支条件语句中作为判断条件来使用。
* 在行级触发器中,用:new 和:old(称为伪记录)来访问数据变更前后的值。但要注意,INSERT语句插入一条新记录,所以没有:old记录,而DELETE语句删除掉一条已经存在的记录,所以没有:new记录。UPDATE语句既有:old记录,也有:new记录,分别代表修改前后的记录。引用具体的某一列的值的方法是:
ld.字段名或:new.字段名
* 触发器体内禁止使用COMMIT、ROLLBACK、SAVEPOINT语句,也禁止直接或间接地调用含有上述语句的存储过程。
定义一个触发器时要考虑上述多种情况,并根据具体的需要来决定触发器的种类。
DML触发器的创建
创建DML触发器需要CREATE TRIGGER系统权限。创建DML触发器的语法如下:
CREATE [OR REPLACE] TRIGGER 触发器名
{BEFORE|AFTER|INSTEAD OF} 触发事件1 [OR 触发事件2...]
ON 表名
WHEN 触发条件
[FOR EACH ROW]
DECLARE
声明部分
BEGIN
主体部分
END;
其中:
OR REPLACE:表示如果存在同名触发器,则覆盖原有同名触发器。
BEFORE、AFTER和INSTEAD OF:说明触发器的类型。
WHEN 触发条件:表示当该条件满足时,触发器才能执行。
触发事件:指INSERT、DELETE或UPDATE事件,事件可以并行出现,中间用OR连接。
对于UPDATE事件,还可以用以下形式表示对某些列的修改会引起触发器的动作:
UPDATE OF 列名1,列名2...
ON 表名:表示为哪一个表创建触发器。
FOR EACH ROW:表示触发器为行级触发器,省略则为语句级触发器。
触发器的创建者或具有DROP ANY TIRGGER系统权限的人才能删除触发器。删除触发器的语法如下:
DROP TIRGGER 触发器名
可以通过命令设置触发器的可用状态,使其暂时关闭或重新打开,即当触发器暂时不用时,可以将其置成无效状态,在使用时重新打开。该命令语法如下:
ALTER TRIGGER 触发器名 {DISABLE|ENABLE}
其中,DISABLE表示使触发器失效,ENABLE表示使触发器生效。
同存储过程类似,触发器可以用SHOW ERRORS 检查编译错误。
行级触发器的应用
在行级触发器中,SQL语句影响的每一行都会触发一次触发器,所以行级触发器往往用在对表的每一行的操作进行控制的场合。若在触发器定义中出现FOR EACH ROW子句,则为语句级触发器。
【训练1】 创建包含插入、删除、修改多种触发事件的触发器DML_LOG,对EMP表的操作进行记录。用INSERTING、DELETING、UPDATING谓词来区别不同的DML操作。
在创建触发器之前,需要先创建事件记录表LOGS,该表用来对操作进行记录。该表的字段含义解释如下:
LOG_ID:操作记录的编号,数值型,它是该表的主键,由序列自动生成。
LOG_TABLE:进行操作的表名,字符型,非空,该表设计成可以由多个触发器共享使用。比如我们可以为dept表创建类似的触发器,同样将操作记录到该表。
LOG_DML:操作的动作,即INSERT、DELETE或UPDATE三种之一。
LOG_KEY_ID:操作时表的主键值,数值型。之所以记录表的主键,是因为主键是表的记录的惟一标识,可以识别是对哪一条记录进行了操作。对于emp表,主键是empno。
LOG_DATE:操作的日期,日期型,取当前的系统时间。
LOG_USER:操作者,字符型,取当时的操作者账户名。比如登录SCOTT账户进行操作,在该字段中,记录账户名为SCOTT。
步骤1:在SQL*Plus中登录STUDENT账户,创建如下的记录表LOGS:
- CREATE TABLE logs(
- LOG_ID NUMBER(10) PRIMARY KEY,
- LOG_TABLE VARCHAR2(10) NOT NULL,
- LOG_DML VARCHAR2(10),
- LOG_KEY_ID NUMBER(10),
- LOG_DATE DATE,
- LOG_USER VARCHAR2(15)
- );
执行结果:
- 表已创建。
步骤2:创建一个LOGS表的主键序列LOGS_ID_SEQ:
- CREATE SEQUENCE logs_id_squ INCREMENT BY 1
- START WITH 1 MAXVALUE 9999999 NOCYCLE NOCACHE;
执行结果:
- 序列已创建。
步骤3:创建和编译以下触发器:
- CREATE OR REPLACE TRIGGER DML_LOG
- BEFORE --触发时间为操作前
- DELETE OR INSERT OR UPDATE -- 由三种事件触发
- ON emp
- FOR EACH ROW -- 行级触发器
- BEGIN
- IF INSERTING THEN
- INSERT INTO logs VALUES(logs_id_squ.NEXTVAL,'EMP','INSERT',:new.empno,SYSDATE,USER);
- ELSIF DELETING THEN
- INSERT INTO logs VALUES(logs_id_squ.NEXTVAL,'EMP','DELETE',:old.empno,SYSDATE,USER);
- ELSE
- INSERT INTO logs VALUES(logs_id_squ.NEXTVAL,'EMP','UPDATE',:new.empno,SYSDATE,USER);
- END IF;
- END;
执行结果:
触发器已创建
步骤4:在EMP表中插入记录:
- INSERT INTO emp(empno,ename,job,sal) VALUES(8001,'MARY','CLERK',1000);
- COMMIT;
执行结果:
- 已创建1行。
- 提交完成。
步骤5:检查LOGS表中记录的信息:
- SELECT * FROM LOGS;
执行结果为:
- LOG_ID LOG_TABLE LOG_DML LOG_KEY_ID LOG_DATE LOG_USER
- ----------------- ----------------- ------------------ ----------------------- ---------------- -------------------
- 1 EMP INSERT 8001 29-3月 -04 STUDENT
- 已选择 1 行。
说明:本例中在emp表上创建了一个由INSERT或DELETE或UPDATE事件触发的行级触发器,触发器的名称是LOG_EMP。对于不同的操作,记录的内容不同。本例中只插入了一条记录,如果用一条不带WHERE条件的UPDATE语句来修改所有雇员的工资,则将逐行触发触发器。
INSERT、DELETE和UPDATE都能引发触发器动作,在分支语句中使用INSERTING、DELETING和UPDATING来区别是由哪种操作引发的触发器动作。
在本例的插入动作中,LOG_ID字段由序列LOG_ID_SQU自动填充为1;LOGS表LOG_KEY_ID字段记录的是新插入记录的主键8001;LOD_DML字段记录的是插入动作INSERT;LOG_TABLE字段记录当前表名EMP;LOG_DATE字段记录插入的时间04年3月1日;LOG_USER字段记录插入者STUDENT。
【练习1】修改、删除刚刚插入的雇员记录,提交后检查LOGS表的结果。
【练习2】为DEPT表创建同样的触发器,使用LOGS表进行记录,并检验结果。
【训练2】 创建一个行级触发器LOG_SAL,记录对职务为CLERK的雇员工资的修改,且当修改幅度超过200时才进行记录。用WHEN条件限定触发器。
在创建触发器之前,需要先创建事件记录表LOGERR,该表用来对操作进行记录。该表的字段含义解释如下:
NUM:数值型,用于记录序号。
MESSAGE:字符型,用于记录错误信息。
步骤1:在SQL*Plus中登录STUDENT账户,创建如下的记录表LOGERR:
- CREATE TABLE logerr(
- NUM NUMBER(10) NOT NULL,
- MESSAGE VARCHAR2(50) NOT NULL
- );
执行结果:
- 表已创建。
步骤2:创建和编译以下触发器:
- CREATE OR REPLACE TRIGGER log_sal
- BEFORE
- UPDATE OF sal
- ON emp
- FOR EACH ROW
- WHEN (new.job='CLERK' AND (ABS(new.sal-old.sal)>200))
- DECLARE
- v_no NUMBER;
- BEGIN
- SELECT COUNT(*) INTO v_no FROM logerr;
- INSERT INTO logerr VALUES(v_no+1,'雇员'||:new.ename||'的原工资:'||:old.sal||'新工资:'||:new.sal);
- END;
执行结果:
- 触发器已创建。
步骤3:在EMP表中更新记录:
- UPDATE emp SET sal=sal+550 WHERE empno=7788;
- UPDATE emp SET sal=sal+500 WHERE empno=7369;
- UPDATE emp SET sal=sal+50 WHERE empno=7876;
- COMMIT;
执行结果:
- 已更新 1 行。
- 已更新 1 行。
- 已更新 1 行。
- 提交完成。
步骤4:检查LOGSAL表中记录的信息:
- SELECT * FROM logerr;
执行结果为:
- NUM MESSAGE
- ------------------ --------------------------------------------------------
- 1 雇员SMITH的原工资:800新工资:1300
- 已选择 1 行。
说明:本例中,在emp表的sal列上创建了一个由UPDATE事件触发的行级触发器,触发器的名称是LOG_SAL。该触发器由WHEN语句限定,只有当被修改工资的雇员职务为CLERK,且修改的工资超过200时才进行触发,否则不进行触发。
所以在验证过程中,虽然修改了3条记录,但通过查询语句发现:第一条修改语句修改编号为7788的SCOTT记录,因为SCOTT的职务是ANALYST,不符合WHEN条件,没有引起触发器动作;第二条修改语句修改编号为7369的SMITH的记录,职务为CLERK,因为增加的工资(500)超过了200,所以引起触发器动作,并在LOGERR表中进行了记录;第三条修改语句修改编号为7876的雇员ADAMS的记录,虽然ADAMS的职务为CLERK,但修改的工资(50)没有超过200,所以没有引起触发器动作。
注意:在WHEN条件中引用new和old不需要在前面加“: ”。
在以上实例中,记录了对工资的修改超出范围的信息,但没有限制对工资的修改。那么当对雇员工资的修改幅度不满足条件时,能否直接限制对工资的修改呢?答案是肯定的。
【训练3】 创建触发器CHECK_SAL,当对职务为CLERK的雇员的工资修改超出500至2000的范围时,进行限制。
步骤1:创建和编译以下触发器:
- CREATE OR REPLACE TRIGGER CHECK_SAL
- BEFORE
- UPDATE
- ON emp
- FOR EACH ROW
- BEGIN
- IF :new.job='CLERK' AND (:new.sal<500 OR :new.sal>2000) THEN
- RAISE_APPLICATION_ERROR(-20001, '工资修改超出范围,操作取消!');
- END IF;
- END;
执行结果:
- 触发器已创建。
步骤2:在EMP表中插入记录:
- UPDATE emp SET sal=800 WHERE empno=7876;
- UPDATE emp SET sal=450 WHERE empno=7876;
- COMMIT;
执行结果:
- UPDATE emp SET sal=450 WHERE empno=7876
- *
- ERROR 位于第 1 行:
- ORA-20001: 工资修改超出范围,操作取消!
- ORA-06512: 在"STUDENT.CHECK_SAL", line 3
- ORA-04088: 触发器 'STUDENT.CHECK_SAL' 执行过程中出错提交完成。
步骤3:检查工资的修改结果:
- SELECT empno,ename,job,sal FROM emp WHERE empno=7876;
执行结果为:
- EMPNO ENAME JOB SAL
- ----------------- ------------- ------------- ------------------------
- 7876 ADAMS CLERK 800
说明:在触发器中,当IF语句的条件满足时,即对职务为CLERK的雇员工资的修改超出指定范围时,用RAISE_APPLICATION_ERROR语句来定义一个临时定义的异常,并立即引发异常。由于触发器是BEFORE类型,因此触发器先执行,触发器因异常而终止,SQL语句的执行就会取消。
通过步骤2的执行信息可以看到,第一条语句修改编号为7876的雇员ADAMS的工资为800,成功执行。第二条语句修改雇员ADAMS的工资为450,发生异常,执行失败。这样就阻止了不符合条件的工资的修改。通过步骤3的查询可以看到,雇员ADAMS最后的工资是800,即发生异常之前的修改结果。
【练习3】限定对emp表的修改,只能修改部门10的雇员工资。
【训练4】 创建一个行级触发器CASCADE_UPDATE,当修改部门编号时,EMP表的相关行的部门编号也自动修改。该触发器称为级联修改触发器。
步骤1:创建和编译以下触发器:
- CREATE TRIGGER CASCADE_UPDATE
- AFTER
- UPDATE OF deptno
- ON DEPT
- FOR EACH ROW
- BEGIN
- UPDATEEMP SET EMP.DEPTNO=:NEW.DEPTNO
- WHERE EMP.DEPTNO=:OLD.DEPTNO;
- END;
执行结果:
- 触发器已创建
步骤2:验证触发器:
- UPDATE dept SET deptno=11 WHERE deptno=10;
- COMMIT;
执行结果:
- 已更新 1 行。
执行查询:
- SELECT empno,ename,deptno FROM emp;
执行结果:
- EMPNO ENAME DEPTNO
- ----------------- ----------- -------------------------
- 7369 SMITH 20
- 7499 ALLEN 30
- 7521 WARD 30
- 7566 JONES 20
- 7654 MARTIN 30
- 7698 BLAKE 30
- 7782 CLARK 11
- 7839 KING 11
- 7844 TURNER 30
- 7876 ADAMS 20
- 7900 JAMES 30
- 7902 FORD 20
- 7934 MILLER 11
- 7788 SCOTT 20
说明:通过检查雇员的部门编号,发现原来编号为10的部门编号被修改为11。
本例中的UPDATE OF deptno表示只有在修改表的DEPTNO列时才引发触发器,对其他列的修改不会引起触发器的动作。在触发器中,对雇员表的部门编号与修改之前的部门编号一样的雇员,修改其部门编号为新的部门编号。注意,在语句中同时用到了:new和:old来引用修改部门编号前后的部门编号。
【练习4】建立级联删除触发器CASCADE_DELETE,当删除部门时,级联删除EMP表的雇员记录。
利用触发器还可以修改数据。
【训练5】 将插入的雇员的名字变成以大写字母开头。
步骤1:创建和编译以下触发器:
- CREATE OR REPLACE TRIGGER INITCAP
- BEFORE INSERT
- ON EMP
- FOR EACH ROW
- BEGIN
- :new.ename:=INITCAP(:new.ename);
- END;
执行结果:
- 触发器已创建。
步骤2:验证运行结果:
- INSERT INTO emp(empno,ename,job,sal) VALUES(1000,'BILL','CLERK',1500);
执行结果:
- 已创建 1 行。
执行查询:
- SELECT ename,job,sal FROM emp WHERE empno=1000;
执行结果:
- ENAME JOB SAL
- ------------- ------------- ------------------------
- Bill CLERK 1500
说明:在本例中,通过直接为:new.ename进行赋值,修改了插入的值,但是这种用法只能在BEFORE型触发器中使用。验证结果为,在插入语句中雇员名称为大写的BILL,查询结果中雇员名称已经转换成以大写开头的Bill。
【练习5】限定一次对雇员的工资修改不超过原工资的10%。
语句级触发器的应用
同行级触发器不同,语句级触发器的每个操作语句不管操作的行数是多少,只触发一次触发器,所以语句级触发器适合于对整个表的操作权限等进行控制。在触发器定义中若省略FOR EACH ROW子句,则为语句级触发器。
【训练1】 创建一个语句级触发器CHECK_TIME,限定对表EMP的修改时间为周一至周五的早8点至晚5点。
步骤1:创建和编译以下触发器:
- CREATE OR REPLACE TRIGGER CHECK_TIME
- BEFORE
- UPDATE OR INSERT OR DELETE
- ON EMP
- BEGIN
- IF (TO_CHAR(SYSDATE,'DY') IN ('SAT','SUN'))
- OR TO_CHAR(SYSDATE,'HH24')< '08'
- OR TO_CHAR(SYSDATE,'HH24')>='17' THEN
- RAISE_APPLICATION_ERROR(-20500,'非法时间修改表错误!');
- END IF;
- END;
执行结果:
- 触发器已创建。
步骤2:当前时间为18点50分,在EMP表中插入记录:
- UPDATE EMP SET SAL=3000 WHERE EMPNO=7369;
显示结果为:
- UPDATE EMP SET SAL=3000 WHERE EMPNO=7369
- *
- ERROR 位于第 1 行:
- ORA-20500: 非法时间修改表错误!
- ORA-06512: 在"STUDENT.CHECK_TIME", line 5
- ORA-04088: 触发器 'STUDENT.CHECK_TIME' 执行过程中出错
说明:通过引发异常限制对数据库进行的插入、删除和修改操作的时间。SYSDATE用来获取系统当前时间,并按不同的格式字符串进行转换。“DY”表示获取英文表示的星期简写,“HH24”表示获取24小时制时间的小时。
当在18点50分修改表中的数据时,由于时间在8点至17点(晚5点)之外,所以产生“非法时间修改表错误”的用户自定义错误,修改操作终止。
【练习1】设计一个语句级触发器,限定只能对数据库进行修改操作,不能对数据库进行插入和删除操作。在需要进行插入和删除时,将触发器设置为无效状态,完成后重新设置为生效状态。
数据库事件触发器
数据库事件触发器有数据库级和模式级两种。前者定义在整个数据库上,触发事件是数据库事件,如数据库的启动、关闭,对数据库的登录或退出。后者定义在模式上,触发事件包括模式用户的登录或退出,或对数据库对象的创建和修改(DDL事件)。
数据库事件触发器的触发事件的种类和级别如表9-3所示。
- 种 类 关 键 字 说 明
- 模式级 CREATE 在创建新对象时触发
- ALTER 修改数据库或数据库对象时触发
- DROP 删除对象时触发
- 数据库级 STARTUP 数据库打开时触发
- SHUTDOWN 在使用NORMAL或IMMEDIATE选项关闭数据库时触发
- SERVERERROR 发生服务器错误时触发
- 数据库级与模式级 LOGON 当用户连接到数据库,建立会话时触发
- LOGOFF 当会话从数据库中断开时触发
定义数据库事件和模式事件触发器
创建数据库级触发器需要ADMINISTER DATABASE TRIGGER系统权限,一般只有系统管理员拥有该权限。
对于模式级触发器,为自己的模式创建触发器需要CREATE TRIGGER权限,如果是为其他模式创建触发器,需要CREATE ANY TRIGGER权限。
数据库事件和模式事件触发器的创建语法与DML触发器的创建语法类似。数据库事件或模式事件触发器的创建语法如下:
CREATE [OR REPLACE] TRIGGER 触发器名
{BEFORE|AFTER }
{DDL事件1 [DDL事件2...]| 数据库事件1 [数据库事件2...]}
ON {DATABASE| [模式名.]SCHEMA }
[WHEN (条件)]
DECLARE
声明部分
BEGIN
主体部分
END;
其中:DATABASE表示创建数据库级触发器,数据库级要给出数据库事件;SCHEMA表示创建模式级触发器,模式级要给出模式事件或DDL事件。
在数据库事件触发器中,可以使用如表9-4所示的一些事件属性。不同类型的触发器可以使用的事件属性有所不同。
- 属 性 适用触发器类型 说 明
- Sys.sysevent 所有类型 返回触发器触发事件字符串
- Sys.instance_num 所有类型 返回Oracle实例号
- Sys.database_name 所有类型 返回数据库名字
- Sys.server_error(stack_position) SERVERERROR 从错误堆栈指定位置返回错误号,参数为1表示最近的错误
- Is_servererror(error_number) SERVERERROR 判断堆栈中是否有参数指定的错误号
- Sys.login_user 所有类型 返回导致触发器触发的用户名
- Sys.dictionary_obj_type CREATE、ALTER、DROP 返回DDL触发器触发时涉及的对象类型
- Sys. dictionary_obj_name CREATE、ALTER、DROP 返回DDL触发器触发时涉及的对象名称
- Sys.des_encrypted_password CREATE、ALTER、DROP 创建或修改用户时,返回加密后的用户密码
数据库事件触发器
下面是一个综合的数据库事件触发器练习。先为STUDENT账户授予创建数据库事件触发器的权限,ADMINISTER DATABASE TRIGGER,然后创建有关的表和触发器,最后予以验证。
【训练1】 创建触发器,对本次数据库启动以来的用户登录时间进行记录,每次数据库启动后,先清空该表。
步骤1:创建登录事件记录表:
- CREATE TABLE userlog (
- USERNAME VARCHAR2(20),
- LOGON_TIME DATE);
执行结果:
- 表已创建。
步骤2:创建数据库STARTUP事件触发器:
- CREATE OR REPLACE TRIGGER INIT_LOGON
- AFTER
- STARTUP
- ON DATABASE
- BEGIN
- DELETE FROM userlog;
- END;
执行结果:
- 触发器已创建。
步骤3:创建数据库LOGON事件触发器:
- CREATE OR REPLACE TRIGGER DATABASE_LOGON
- AFTER
- LOGON
- ON DATABASE
- BEGIN
- INSERT INTO userlog
- VALUES(sys.login_user,sysdate);
- END;
执行结果:
- 触发器已创建。
步骤4:验证DATABASE_LOGON触发器:
- CONNECT SCOTT/TIGER@MYDB;
- CONNECT STUDENT/STUDENT@MYDB;
执行结果:
- 已连接。
- 已连接。
执行查询:
- SELECT username,TO_CHAR(logon_time,'YYYY/MM/DD HH24:MI:SS') FROM userlog;
执行结果:
- USERNAME TO_CHAR(LOGON_TIME,
- ----------------------------- -----------------------------------------
- SCOTT 2004/03/29 22:42:20
- STUDENT 2004/03/29 22:42:20
步骤5:验证INIT_LOGON触发器。
重新启动数据库,登录STUDENT账户:
- SELECT username,TO_CHAR(logon_time,'YYYY/MM/DD HH24:MI:SS') FROM userlog;
执行结果:
- USERNAME TO_CHAR(LOGON_TIME,
- -------------------------------- ---------------------------------------
- STUDENT 2004/03/29 22:43:59
- 已选择 1 行
说明:本例中共创建了两个数据库级事件触发器。DATABASE_LOGON在用户登录时触发,向表userlog中增加一条记录,记录登录用户名和登录时间。INIT_LOGON在数据库启动时触发,清除userlog表中记录的数据。所以当数据库重新启动后,重新登录STUDENT账户,此时userlog表中只有一条记录。
【训练2】 创建STUDENT_LOGON模式级触发器,专门记录STUDENT账户的登录时间:
- CREATE OR REPLACE TRIGGER STUDENT_LOGON
- AFTER
- LOGON ON STUDENT.SCHEMA
- BEGIN
- INSERT INTO userlog
- VALUES(sys.login_user,sysdate);
- END;
执行结果:
- 触发器已创建。
说明:为当前模式创建触发器,可以省略SCHEMA前面的模式名。
【练习1】修改DATABASE_LOGON触发器和userlog表,增加对退出时间的记录。
DDL事件触发器
【训练1】 通过触发器阻止对emp表的删除。
步骤1:创建DDL触发器:
- CREATE OR REPLACE TRIGGER NODROP_EMP
- BEFORE
- DROP ON SCHEMA
- BEGIN
- IF Sys.Dictionary_obj_name='EMP' THEN
- RAISE_APPLICATION_ERROR(-20005,'错误信息:不能删除emp表!');
- END IF;
- END;
执行结果:
- 触发器已创建。
步骤2:通过删除emp表验证触发器:
- DROP TABLE emp;
执行结果:
- DROP TABLE emp
- *
- ERROR 位于第 1 行:
- ORA-00604: 递归 SQL 层 1 出现错误
- ORA-20005: 错误信息:不能删除emp表!
- ORA-06512: 在line 3
说明:该触发器阻止在当前模式下对emp表的删除,但不阻止删除其他对象。Sys.Dictionary_obj_name属性返回要删除的对象名称。
替代触发器
【训练1】 在emp表的视图上,通过触发器修改emp表。
步骤1:创建视图emp_name:
- CREATE VIEW emp_name AS SELECT ename FROM emp;
执行结果:
- 视图已建立。
步骤1:创建替代触发器:
- CREATE OR REPLACE TRIGGER change_name
- INSTEAD OF INSERT ON emp_name
- DECLARE
- V_EMPNO NUMBER(4);
- BEGIN
- SELECT MAX(EMPNO)+1 INTO V_EMPNO FROM EMP;
- INSERT INTO emp(empno,ename)
- VALUES(V_EMPNO,:new.ename);
- END;
执行结果:
- 触发器已创建。
步骤2:向emp_name视图插入记录:
- INSERT INTO emp_name VALUES('BROWN');
- COMMIT;
执行结果:
- 已创建 1 行。
- 提交完成。
说明:向视图直接插入雇员名将会发生错误,因为emp表的雇员编号列不允许为空。通过创建替代触发器,将向视图插入雇员名称转换为向emp表插入雇员编号和雇员名称,雇员编号取当前的最大雇员编号加1。试检查emp表的雇员列表。
【训练2】 在emp表的视图emp_name上,通过触发器阻止对emp表的删除。
步骤1:阻止通过视图删除雇员,并显示用户自定义错误信息:
- CREATE OR REPLACE TRIGGER delete_from_ename
- INSTEAD OF DELETE ON emp_name
- BEGIN
- RAISE_APPLICATION_ERROR(-20006,'错误信息:不能在视图中删除emp表的雇员!');
- END;
执行结果:
- 触发器已创建。
步骤2:通过对视图进行删除来验证触发器:
- DELETE FROM emp_name;
执行结果:
- DELETE FROM emp_name
- *
- ERROR 位于第 1 行:
- ORA-20006: 错误信息:不能在视图中删除emp表的雇员!
- ORA-06512:
- 在"STUDENT.DELETE_FROM_ENAME", line 2
- ORA-04088: 触发器 'STUDENT.DELETE_FROM_ENAME' 执行过程中出错
说明:可以通过视图emp_name对雇员进行删除,比如执行DELETE FROM emp_name语句将删除雇员表的全部雇员。但是由于在emp_name视图中只能看到一部分雇员信息,所以删除可能会产生误操作。通过定义一个替代触发器,可阻止通过emp_name视图对emp表雇员进行删除,但不阻止直接对emp表进行删除。
查看触发器
【训练1】 显示触发器CHECK_TIME的体部分:
- SELECT TRIGGER_BODY FROM USER_TRIGGERS WHERE TRIGGER_NAME='CHECK_TIME';
结果为:
- TRIGGER_BODY
- ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- BEGIN
- IF (TO_CHAR(SYSDATE,'DY') IN ('SAT','SUN'))
- OR TO_CHAR(SYSDATE,'HH24')<
- TRIGGER_BODY字段为LONG类型,只显示出脚本的一部分内容。
阶段训练
【训练1】 创建触发器,进行表的同步复制。
步骤1:创建emp表的复本employee:
- CREATE TABLE employee AS SELECT * FROM emp;
执行结果:
- 表已创建。
步骤2:创建和编译以下触发器:
- CREATE OR REPLACE TRIGGER DUPLICATE_EMP
- AFTER
- UPDATE OR INSERT OR DELETE
- ON EMP
- FOR EACH ROW
- BEGIN
- IF INSERTING THEN
- INSERT INTO employee
- VALUES(:new.empno,:new.ename,:new.job,:new.mgr,
- :new.hiredate,:new.sal,:new.comm,:new.deptno);
- ELSIF DELETING THEN
- DELETE FROM employee
- WHERE empno=:old.empno;
- ELSE
- UPDATE employee SET
- empno=:new.empno,
- ename=:new.ename,
- job=:new.job,
- mgr=:new.mgr,
- hiredate=:new.hiredate,
- sal=:new.sal,
- comm=:new.comm,
- deptno=:new.deptno
- WHERE empno=:old.empno;
- END IF;
- END;
执行结果:
- 触发器已创建。
步骤3:对emp表进行插入、删除和更新:
- DELETE FROM emp WHERE empno=7934;
- INSERT INTO emp(empno,ename,job,sal) VALUES(8888,'ROBERT','ANALYST',2900);
- UPDATE emp SET sal=3900 WHERE empno=7788;
- COMMIT;
执行结果:
- 已删除 1 行。
- 已创建 1 行。
- 已更新 1 行。
- 提交完成。
步骤4:检查emp表和employee表中被插入、删除和更新的雇员。
运行结果略,请自行验证。
说明:在触发器中判断触发事件,根据不同的事件对employee表进行不同的操作。
【练习1】创建一个emp表的触发器EMP_TOTAL,每当向雇员表插入、删除或更新雇员信息时,将新的统计信息存入统计表EMPTOTAL,使统计表总能够反映最新的统计信息。
统计表是记录各部门雇员总人数、总工资的统计表,结构如下:
部门编号 number(2)
总人数 number(5)
总工资 number(10,2)
练习
1. 下列有关触发器和存储过程的描述,正确的是:
A. 两者都可以传递参数
B. 两者都可以被其他程序调用
C. 两种模块中都可以包含数据库事务语句
D. 两者创建的系统权限不同
2. 下列事件,属于DDL事件的是:
A. INSERT B. LOGON
C. DROP D. SERVERERROR
3. 假定在一个表上同时定义了行级和语句级触发器,在一次触发当中,下列说法正确的是:
A. 语句级触发器只执行一次
B. 语句级触发器先于行级触发器执行
C. 行级触发器先于语句级触发器执行
D. 行级触发器对表的每一行都会执行一次
4. 有关行级触发器的伪记录,下列说法正确的是:
A. INSERT事件触发器中,可以使用:old伪记录。
B. DELETE事件触发器中,可以使用:new伪记录。
C. UPDATA事件触发器中,只能使用:new伪记录。
D. UPDATA事件触发器中,可以使用:old伪记录。
5. 下列有关替代触发器的描述,正确的是:
A. 替代触发器创建在表上
B. 替代触发器创建在数据库上
C. 通过替代触发器可以向基表插入数据
D. 通过替代触发器可以向视图插入数据
黑色头发:http://heisetoufa.javaeye.com/###############################################################################################################自己写了个例子###############################################################################################################drop trigger c_object; drop trigger d_object;CREATE OR REPLACE TRIGGER d_object BEFORE DROP ON SCHEMA DECLARE BEGIN delete from dict_columns where table_name = lower(Sys.Dictionary_obj_name); END; /CREATE OR REPLACE TRIGGER c_object AFTER CREATE ON SCHEMA DECLARE aa VARCHAR2(64); sql_str VARCHAR2(768); BEGIN FOR curs IN (SELECT table_name, column_name, data_type, data_length, data_default FROM user_tab_columns where table_name not like '%$%' ORDER BY table_name, column_id) LOOP IF curs.data_default IS NULL THEN curs.data_default := ' '; END IF; sql_str := 'INSERT INTO dict_columns (table_name,column_name,data_type,data_length,data_default) VALUES(:1,:2,:3,:4,:6)'; EXECUTE IMMEDIATE sql_str USING curs.table_name,curs.column_name,curs.data_type,curs.data_length,curs.data_default; END LOOP; END; /










 本文详细介绍了Oracle数据库中的触发器概念,包括DML触发器、DDL触发器、替代触发器等的创建方法及应用场景,提供了丰富的示例代码。
本文详细介绍了Oracle数据库中的触发器概念,包括DML触发器、DDL触发器、替代触发器等的创建方法及应用场景,提供了丰富的示例代码。
















 3195
3195

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








