1.安装SVN
yum install subversion
2.验证SVN是否安装成功
[root@iZbp14w0b2rs7i1400bjjmZ ~]# svnserve --version
svnserve, version 1.6.11 (r934486)
compiled Aug 17 2015, 08:37:43
Copyright (C) 2000-2009 CollabNet.
Subversion is open source software, see http://subversion.tigris.org/
This product includes software developed by CollabNet (http://www.Collab.Net/).
The following repository back-end (FS) modules are available:
* fs_base : Module for working with a Berkeley DB repository.
* fs_fs : Module for working with a plain file (FSFS) repository.
Cyrus SASL authentication is available.
3.建立SVN仓库
#使用隐藏目录,防止被删除
mkdir /home/.svn
svnadmin create /home/.svn/CloudPayment
执行完毕后有svnadmin创建的目录和文件
db目录:就是所有版本控制的数据存放文件。
hooks目录:放置hook脚本文件的目录。
locks目录:用来放置subversion见艰苦锁定数据的目录,用来追踪存取文件库的客户端。
format文件:是一个文本文件,里面只放了一个整数,表示当前文件库配置的版本号。
conf目录:是这个仓库的配置文件(仓库的用户访问账号、权限等)。
authz文件是权限控制文件
passwd是帐号密码文件svnserve.conf SVN服务配置文件vim passwd
在[users]块中添加用户和密码,格式:帐号=密码
[root@iZbp14w0b2rs7i1400bjjmZ conf]# cat passwd
### This file is an example password file for svnserve.
### Its format is similar to that of svnserve.conf. As shown in the
### example below it contains one section labelled [users].
### The name and password for each user follow, one account per line.
[users]
# harry = harryssecret
# sally = sallyssecret
fly = 123456
设置权限
vim authz
在末尾添加如下代码:
[/]
账号=rw 说明: (r:读,w:写)
[root@iZbp14w0b2rs7i1400bjjmZ conf]# cat authz
### This file is an example authorization file for svnserve.
### Its format is identical to that of mod_authz_svn authorization
### files.
### As shown below each section defines authorizations for the path and
### (optional) repository specified by the section name.
### The authorizations follow. An authorization line can refer to:
### - a single user,
### - a group of users defined in a special [groups] section,
### - an alias defined in a special [aliases] section,
### - all authenticated users, using the '$authenticated' token,
### - only anonymous users, using the '$anonymous' token,
### - anyone, using the '*' wildcard.
###
### A match can be inverted by prefixing the rule with '~'. Rules can
### grant read ('r') access, read-write ('rw') access, or no access
### ('').
[aliases]
# joe = /C=XZ/ST=Dessert/L=Snake City/O=Snake Oil, Ltd./OU=Research Institute/CN=Joe Average
[groups]
# harry_and_sally = harry,sally
# harry_sally_and_joe = harry,sally,&joe
# [/foo/bar]
# harry = rw
# &joe = r
# * =
# [repository:/baz/fuz]
# @harry_and_sally = rw
# * = r
[/]
fly = rw
[CloudPayment:/]
fly = rw
注意
用户如果不是一个组,去掉@ ,
否则会报错:svn:unable to connect to repository invalid authz configuration
修改svnserve.conf文件
vim svnserve.conf
打开下面的几个注释:
anon-access = read #匿名用户可读
auth-access = write #授权用户可写
password-db = passwd #使用哪个文件作为账号文件
authz-db = authz #使用哪个文件作为权限文件
realm = realm = /home/.svn # 认证空间名,版本库所在目录
[root@iZbp14w0b2rs7i1400bjjmZ conf]# cat svnserve.conf
### This file controls the configuration of the svnserve daemon, if you
### use it to allow access to this repository. (If you only allow
### access through http: and/or file: URLs, then this file is
### irrelevant.)
### Visit http://subversion.tigris.org/ for more information.
[general]
### These options control access to the repository for unauthenticated
### and authenticated users. Valid values are "write", "read",
### and "none". The sample settings below are the defaults.
anon-access = read
auth-access = write
### The password-db option controls the location of the password
### database file. Unless you specify a path starting with a /,
### the file's location is relative to the directory containing
### this configuration file.
### If SASL is enabled (see below), this file will NOT be used.
### Uncomment the line below to use the default password file.
password-db = passwd
### The authz-db option controls the location of the authorization
### rules for path-based access control. Unless you specify a path
### starting with a /, the file's location is relative to the the
### directory containing this file. If you don't specify an
### authz-db, no path-based access control is done.
### Uncomment the line below to use the default authorization file.
authz-db = authz
### This option specifies the authentication realm of the repository.
### If two repositories have the same authentication realm, they should
### have the same password database, and vice versa. The default realm
### is repository's uuid.
realm = /home/.svn
[sasl]
### This option specifies whether you want to use the Cyrus SASL
### library for authentication. Default is false.
### This section will be ignored if svnserve is not built with Cyrus
### SASL support; to check, run 'svnserve --version' and look for a line
### reading 'Cyrus SASL authentication is available.'
# use-sasl = true
### These options specify the desired strength of the security layer
### that you want SASL to provide. 0 means no encryption, 1 means
### integrity-checking only, values larger than 1 are correlated
### to the effective key length for encryption (e.g. 128 means 128-bit
### encryption). The values below are the defaults.
# min-encryption = 0
# max-encryption = 256
4.启动SVN
启动:
1. 从CloudPayment目录启动,svnserve -d -r /home/.svn/CloudPayment,
根目录(/)是CloudPayment,authz中规则的配置使用section[/]。
访问方式为: svn://ip/
2. 从.svn目录启动,svnserve -d -r /home/.svn,
根目录(/)是.svn,authz中对CloudPayment的配置使用section[CloudPayment:/] 。
访问方式为: svn://ip/CloudPayment
如果需要svn自启动,把命令加入/etc/rc.local中
检查svn服务器是否已经启动(svn默认使用3690端口)
netstat -an | grep 3690
停止
killall svnserve
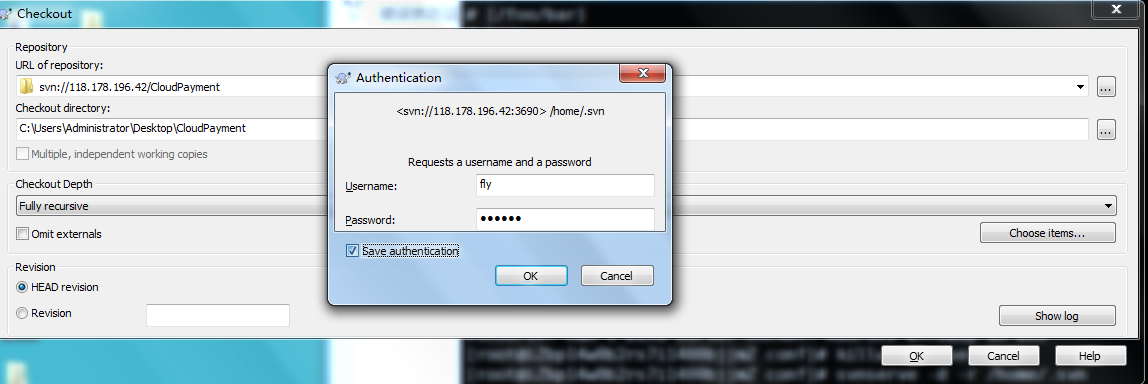
5.客户端连接测试






 本文详细介绍如何在Linux环境下安装Subversion (SVN),并进行仓库创建、权限配置及服务启动等步骤。通过实例演示了如何设置用户权限,确保版本库的安全访问。
本文详细介绍如何在Linux环境下安装Subversion (SVN),并进行仓库创建、权限配置及服务启动等步骤。通过实例演示了如何设置用户权限,确保版本库的安全访问。

















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










