线程池的作用:
- 减少线程的创建和销毁带来的开销
- 实现异步解耦的问题
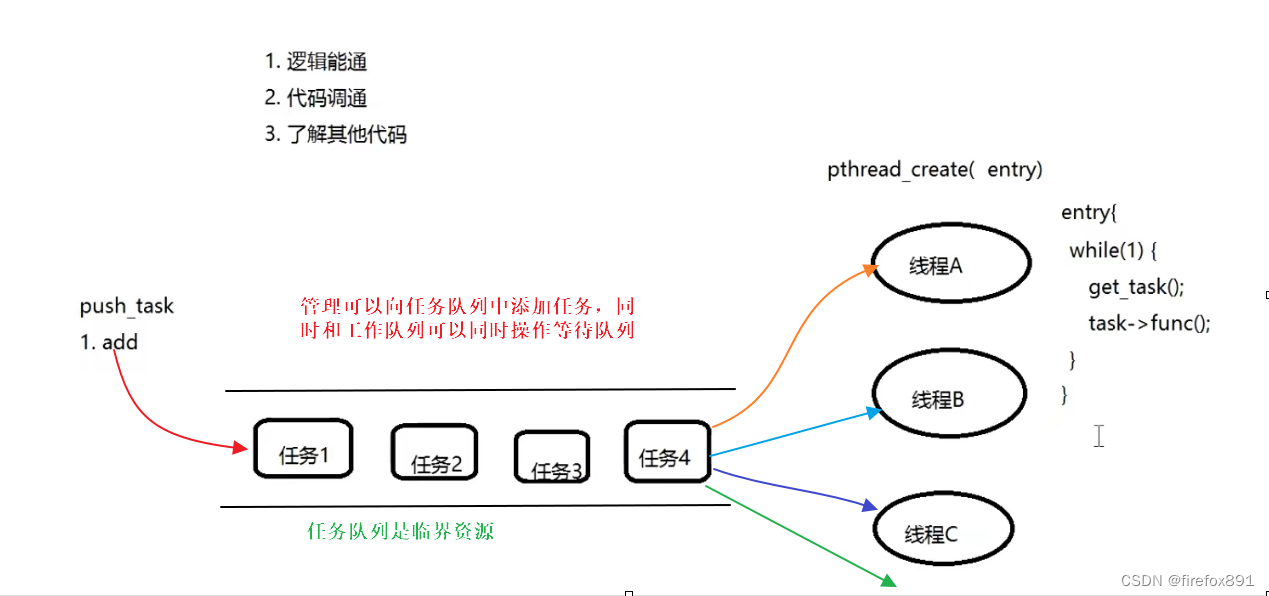
线程池的工作原理
线程池必须具备的接口:
1. 线程池的创建: create/init
2. 忘线程池中添加任务: push task
3. 线程池的销毁: delinit/destroy
线程池的实现:
typedef struct _threadpool threadpool_t;
typedef struct _worker {
pthread_t id;//id
int terminate;//线程是否正常工作
threadpool_t *pool;
struct _worker *prev;
struct _worker *next;
} worker_t;
typedef struct _job {
void *user_data;
int (*callback)(void *data);
struct _job *prev;
struct _job *next;
} job_t;
struct _threadpool
{
worker_t *workers;
job_t *wait_jobs;
pthread_cond_t cond;
pthread_mutex_t mtx;
} ;
#define LIST_ADD(item, list) \
do { \
item->prev = NULL; \
item->next = list; \
list = item; \
} while (0)
#define LIST_REMOVE(item, list) \
do { \
if (item->prev != NULL) item->prev->next = item->next; \
if (item->next != NULL) item->next->prev = item->prev; \
if (list == item) list = item->next; \
item->prev = item->next = NULL; \
} while (0)
#define THREAD_DEFAULT_COUNT 100
#define JOBS_DEFAULT_COUNT 10000
void *worker_callback(void *arg)
{
worker_t *worker = (worker_t *)arg;
while (1) {
//wait
pthread_mutex_lock(&worker->pool->mtx);
while (worker->pool->wait_jobs == NULL) {
if (worker->terminate) {
//pthread_mutex_unlock(&worker->pool->mtx);
break;
}
pthread_cond_wait(&worker->pool->cond, &worker->pool->mtx);
}
if (worker->terminate) {
pthread_mutex_unlock(&worker->pool->mtx);
break;
}
//1. get job
job_t *job = worker->pool->wait_jobs;
if (job != NULL) {
LIST_REMOVE(job, worker->pool->wait_jobs);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&worker->pool->mtx);
if (job == NULL) {
perror("get job is null.");
break;
}
//2. call job
job->callback(job->user_data);
}
free(worker);
worker = NULL;
}
int threadpool_create(threadpool_t *pool, int count)
{
//1. 检查
if (pool == NULL) {
perror("pointer is null.");
return -1;
}
if (count <= 0) {
count = 1;
}
//2. cond init
pthread_cond_t cond = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;
memcpy(&pool->cond, &cond, sizeof(pthread_cond_t));
//3. mutex init
pthread_mutex_t mtx = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
memcpy(&pool->mtx, &mtx, sizeof(pthread_mutex_t));
//4. 创建工作线程, (thread, worker)
int idx = 0;
for (idx = 0; idx < count; idx++) {
worker_t *worker = (worker_t *)malloc(sizeof(worker_t));
if (worker == NULL) {
perror("calloc worker fail.");
return idx;
}
memset(worker, 0x00, sizeof(worker_t));
worker->terminate = 0;
worker->pool = pool;
if (pthread_create(&worker->id, NULL, worker_callback, (void *)worker) != 0) {
perror("pthread_create() fail.");
free(worker);
worker = NULL;
return idx;
}
LIST_ADD(worker, pool->workers);
}
return idx;
}
int threadpool_push_data(threadpool_t *pool, job_t *job)
{
//检查
if (pool == NULL) {
perror("pointer is null.");
return -1;
}
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mtx);
LIST_ADD(job, pool->wait_jobs);
pthread_cond_signal(&pool->cond);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mtx);
return 0;
}
void threadpool_destroy(threadpool_t *pool)
{
worker_t *worker = NULL;
for (worker = pool->workers; worker != NULL; worker = worker->next) {
worker->terminate = 1;
}
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mtx);
pthread_cond_broadcast(&pool->cond);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mtx);
return ;
}
int print_user(void *arg)
{
int idx = *(int *)arg;
printf("user idx:%d, threadid: %ld\n", idx, pthread_self());
//用户申请,用户释放内存
free(arg);
arg = NULL;
return 0;
}
int main()
{
int retv = 0;
threadpool_t pool = {0};
//创建线程池
retv = threadpool_create(&pool, THREAD_DEFAULT_COUNT);
if (retv < 0) {
perror("threadpool_create() fail.");
return -1;
}
//创建任务并调用
for (int i = 0; i < JOBS_DEFAULT_COUNT; i++) {
job_t *job = (job_t *)calloc(1, sizeof(job_t));
if (job == NULL) {
perror("calloc fail.");
return -1;
}
job->callback = print_user;
job->user_data = calloc(1, sizeof(int));
*(int *)(job->user_data) = i;
//push job
threadpool_push_data(&pool, job);
}
threadpool_destroy(&pool);
return 0;
}
nigix中的线程池
typedef struct {
ngx_array_t pools;
} ngx_thread_pool_conf_t;
typedef struct {
ngx_thread_task_t *first;
ngx_thread_task_t **last;
} ngx_thread_pool_queue_t;
#define ngx_thread_pool_queue_init(q) \
(q)->first = NULL; \
(q)->last = &(q)->first
struct ngx_thread_pool_s {
ngx_thread_mutex_t mtx;
ngx_thread_pool_queue_t queue;
ngx_int_t waiting;
ngx_thread_cond_t cond;
ngx_log_t *log;
ngx_str_t name;
ngx_uint_t threads;
ngx_int_t max_queue;
u_char *file;
ngx_uint_t line;
};
线程池的应用场景
1. 在工作中的日志落地的工作
2. nginx的快速连接问题
3. 工作中常用比较耗时的数据库的操作
4. 网络IO的处理







 文章介绍了线程池的作用,如减少线程创建和销毁的成本,解决异步解耦问题,列举了应用场景如日志处理、nginx连接、数据库操作和网络IO。接着,文章详细阐述了线程池的工作原理,包括线程的等待和执行,并给出了线程池创建、添加任务和销毁的接口。最后,文章提供了一个简单的线程池实现示例。
文章介绍了线程池的作用,如减少线程创建和销毁的成本,解决异步解耦问题,列举了应用场景如日志处理、nginx连接、数据库操作和网络IO。接着,文章详细阐述了线程池的工作原理,包括线程的等待和执行,并给出了线程池创建、添加任务和销毁的接口。最后,文章提供了一个简单的线程池实现示例。
















 254
254

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








