语法:
http://docs.oracle.com/cd/B28359_01/appdev.111/b28370/executeimmediate_statement.htm
EXECUTE IMMEDIATE Statement
The EXECUTE IMMEDIATE statement builds and executes a dynamic SQL statement in a single operation. It is the means by which native dynamic SQL processes most dynamic SQL statements.
execute_immediate_statement ::=
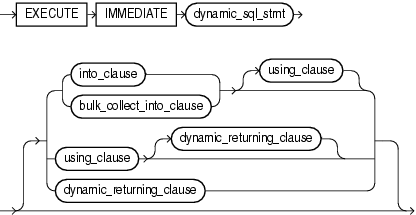
Description of the illustration execute_immediate_statement.gif
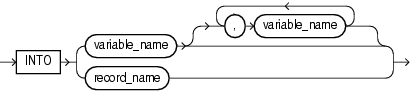
Description of the illustration into_clause.gif
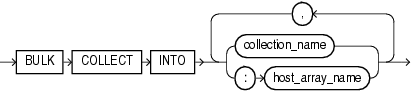
Description of the illustration bulk_collect_into_clause.gif
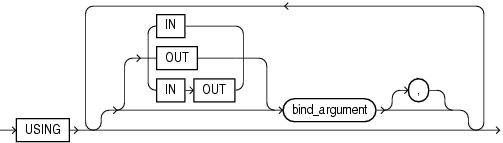
Description of the illustration using_clause.gif
Keyword and Parameter Descriptions
Either an expression whose value is passed to the dynamic SQL statement (an in bind), or a variable in which a value returned by the dynamic SQL statement is stored (an out bind).
Used if and only if dynamic_sql_stmt can return multiple rows, this clause specifies one or more collections in which to store the returned rows. This clause must have a corresponding, type-compatible collection_item or :host_array_name for each select_item in dynamic_sql_stmt.
The name of a declared collection, in which to store rows returned by dynamic_sql_stmt.
Used if and only if dynamic_sql_stmt has a RETURNING INTO clause, this clause returns the column values of the rows affected by dynamic_sql_stmt, in either individual variables or records (eliminating the need to select the rows first). This clause can include OUT bind arguments. For details, see RETURNING INTO Clause.
A string literal, string variable, or string expression that represents any SQL statement. It must be of type CHAR, VARCHAR2, or CLOB.
An array into which returned rows are stored. The array must be declared in a PL/SQL host environment and passed to PL/SQL as a bind argument (hence the colon (:) prefix).
Parameter modes of bind arguments. An IN bind argument passes its value to the dynamic SQL statement. An OUT bind argument stores a value that the dynamic SQL statement returns. An IN OUT bind argument passes its initial value to the dynamic SQL statement and stores a value that the dynamic SQL statement returns. The default parameter mode for bind_argument is IN.
Used if and only if dynamic_sql_stmt is a SELECT statement that can return at most one row, this clause specifies the variables or record into which the column values of the returned row are stored. For each select_item in dynamic_sql_stmt, this clause must have either a corresponding, type-compatibledefine_variable or a type-compatible record.
A user-defined or %ROWTYPE record into which a returned row is stored.
Used only if dynamic_sql_stmt includes placeholders, this clause specifies a list of bind arguments.
The name of a define variable in which to store a column value of the row returned by dynamic_sql_stmt.
只有DDL
begin
execute immediate 'CREATE TABLE TB_EXECUTE (ID INTEGER PRIMARY KEY, USER_NAME VARCHAR2(20) NOT NULL)';
end;使用using
begin
execute immediate 'insert into TB_EXECUTE values (:1, :2)' using 1, 'exe1';
execute immediate 'insert into TB_EXECUTE values (:1, :2)' using 2, 'exe2';
commit;
end;
使用into
declare
v_count integer;
begin
execute immediate 'select count(1) from tb_execute' into v_count;
dbms_output.put_line(v_count);
end;使用into和using
declare
p_id integer := 1;
v_name varchar2(20);
begin
execute immediate 'select USER_NAME from tb_execute where id=:1' into v_name using p_id;
dbms_output.put_line(v_name);
end;使用open for
declare
p_id integer := 1;
type sp_cursor is ref cursor;
v_cursor sp_cursor;
r_execute tb_execute%rowtype;
begin
open v_cursor for 'select * from tb_execute where id=:1' using p_id;
loop
fetch v_cursor into r_execute;
exit when v_cursor%notfound;
dbms_output.put_line(r_execute.user_name);
end loop;
close v_cursor;
end;declare
p_id integer := 1;
type sp_cursor is ref cursor;
v_cursor sp_cursor;
v_name tb_execute.USER_NAME%type;
begin
open v_cursor for 'select user_name from tb_execute';
loop
fetch v_cursor into v_name;
exit when v_cursor%notfound;
dbms_output.put_line(v_name);
end loop;
close v_cursor;
end;























 156
156

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








