2.1 namaspace命名空间
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?><!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="com.xa.mapper.UserMapper"> </mapper>
- mapper中的namespace是用来绑定dao接口的,即面向接口编程。
- 当你的namespace绑定接口后,你可以不用写接口实现类,mybatis会通过该绑定自动帮你找到对应要执行的SQL语句
- 在同一次请求中不允许出现相同名称的方法、类和常量,但是在某些特殊的应用中必须要使用相同名称的方法、类和常量,需要把他们放到不同的空间里,这个空间就是命名空间。
- 命名空间主要是为了解决命名冲突问题
- 确保方法名称的唯一性,如果两个xml文件中的方法名一样,那么就用namespace区分。
2.2 参数映射
接口方法中的映射怎么映射到mapper.xml中参数呢?
1.单个简单参数的引用
如果方法中只有一个参数可通过任意名称进行引用
UserMapper
public interface UserMapper {
UserInfo selectUserById(Long id);
}
UserMapper.xml
<select id="selectUserById" parameterType="long" resultType="UserInfo">
select * from t_user where id = #{id} <!-- 此时id可以用任意名称代替 -->
</select>
2.多个参数引用
通过参数下标引用#{arg0}#{arg1} 或者 #{param1},#{param2}
UserMapper
Integer insertUser(String userName, String sex, Date birthday, String address);
UserMapper.xml
<insert id="insertUser">
INSERT INTO t_user(user_name,sex,birthday,address ) VALUES
(#{userName},#{sex},#{birthday},#{address});
</insert>
在select标签后就不再使用parameterType,因为这个标签只能指定一个参数,而两个参数及以上的,则不用再使用
我们先测试这个方法:
public class UserTest {
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
@Before
public void init(){
// 从 XML 中构建 SqlSessionFactory
String resource = "mybatis/mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = null;
try {
inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream,"mysql_jdbc2");
}
@Test
public void insertUser(){
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
try{
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
Integer count = mapper.insertUser("tom","0",new Date(),"北京市");
sqlSession.commit();
if(count > 0){
System.out.println("插入成功.....");
}
}finally{
sqlSession.close();
}
}
}
此时测试会报错,错误信息如下:
org.apache.ibatis.exceptions.PersistenceException:
### Error updating database. Cause: org.apache.ibatis.binding.BindingException: Parameter 'userName' not found. Available parameters are [arg3, arg2, arg1, arg0, param3, param4, param1, param2]
### The error may involve defaultParameterMap
### The error occurred while setting parameters
### SQL: INSERT INTO t_user(user_name,sex,birthday,address ) VALUES (?,?,?,?);
### Cause: org.apache.ibatis.binding.BindingException: Parameter 'userName' not found. Available parameters are [arg3, arg2, arg1, arg0, param3, param4, param1, param2]
提示userName参数没有找到,只能使用 arg0,arg1…或者 param1,param2 等参数,
<insert id="insertUser">
INSERT INTO t_user(user_name,sex,birthday,address ) VALUES
(#{arg0},#{arg1},#{arg2},#{arg3});
</insert>
<insert id="insertUser">
INSERT INTO t_user(user_name,sex,birthday,address ) VALUES
(#{param1},#{param2},#{param3},#{param4});
</insert>
那么怎么使用方法名呢?
<insert id="insertUser">
INSERT INTO t_user(user_name,sex,birthday,address ) VALUES
(#{userName},#{sex},#{birthday},#{address});
</insert>
第一种方法:
变量名称引用(需要jdk1.8支持) :通过方法中参数名称引用,需要jdk1.8支持,且在编译时必须加上 -parameters 编译命令
在idea 中添加 编译参数
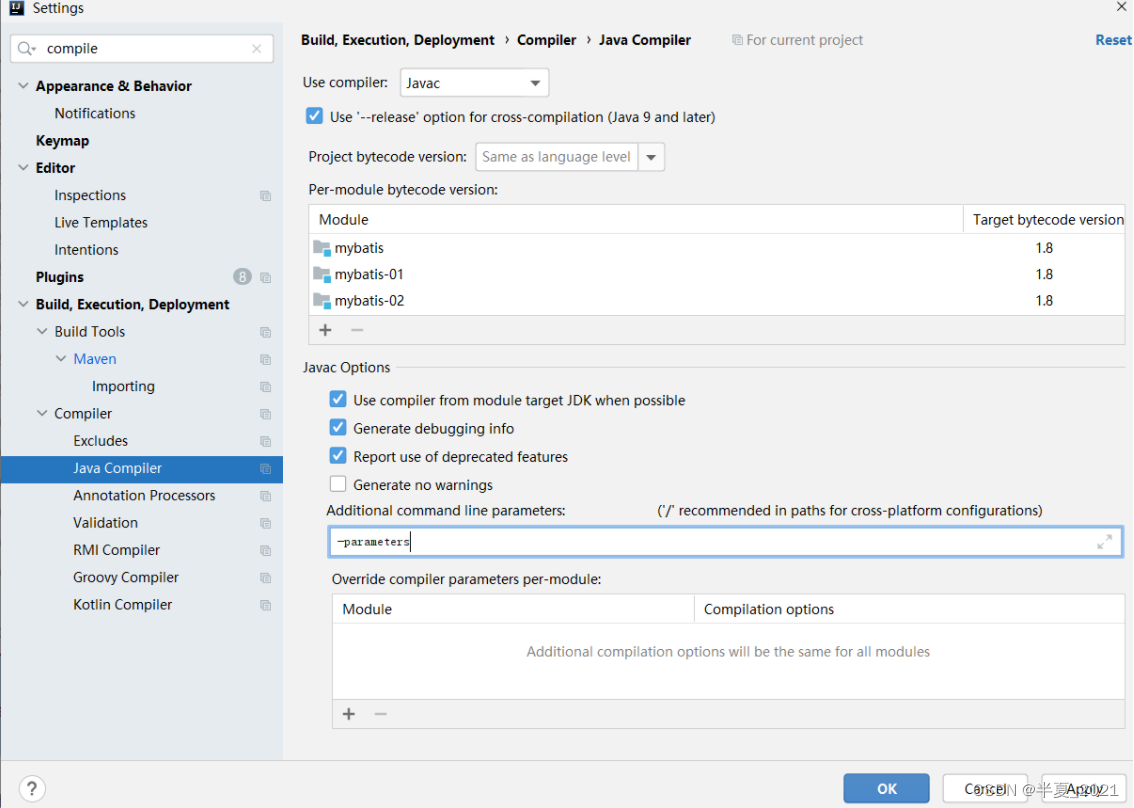
然后再 pom.xml 中添加
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.3</version>
<configuration>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
<compilerArgs>
<arg>-parameters</arg>
</compilerArgs>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
注意: 一旦通过变量名称引入将不再支持 arg0获取
第二种方法: 使用 @Param注解
修改 UserMapper insertUser 方法,使用@Param 注解
Integer insertUser( @Param("userName") String userName, @Param("sex") String sex,
@Param("birthday") Date birthday, @Param("address") String address);
3.对象属性的引用
对象属性的引用,可以直接通过对象的属性名称引用,嵌套对象通过.号进行引用
public interface UserMapper {
Integer insertUser(UserInfo userInfo);
}
<insert id="insertUser">
INSERT INTO t_user(user_name,sex,birthday,address ) VALUES
(#{userName},#{sex},#{birthday},#{address});
</insert>
如果是嵌套对象呢?
首先我们新建一个QueryVo类,包含UserInfo对象
public class QueryVo {
private UserInfo userInfo;
public UserInfo getUserInfo() {
return userInfo;
}
public void setUserInfo(UserInfo userInfo) {
this.userInfo = userInfo;
}
}
UserMapper.xml
使用包装类型查询用户时,可使用OGNL从对象中取属性值,并且如果是包装对象可以使用.操作符来取内容的属性,
<insert id="insertUser" parameterType="QueryVo">
INSERT INTO t_user(user_name,sex,birthday,address ) VALUES
(#{userInfo.userName},#{userInfo.sex},#{userInfo.birthday},#{userInfo.address});
</insert>
测试类如下:
@Test
public void insertUser(){
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
try{
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
QueryVo queryVo = new QueryVo();
UserInfo userInfo = new UserInfo("tom","1",new Date(),"guangzhou");
queryVo.setUserInfo(userInfo);
Integer count = mapper.insertUser(queryVo);
sqlSession.commit();
if(count > 0){
System.out.println("inert success.....");
}
}finally{
sqlSession.close();
}
}
4.map key值引用
Integer insertUser(Map userMap);
<insert id="insertUser" parameterType="hashmap">
INSERT INTO t_user(user_name,sex,birthday,address ) VALUES
(#{userName},#{sex},#{birthday},#{address});
</insert>
上面的userName、sex、birthday、address 就是Map中的key
@Test
public void insertUser(){
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
try{
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("userName","tom");
map.put("sex","1");
map.put("birthday",new Date());
map.put("address","wuhu");
Integer count = mapper.insertUser(map);
sqlSession.commit();
if(count > 0){
System.out.println("inert success.....");
}
}finally{
sqlSession.close();
}
}
2.3 输入映射和输出映射
2.3.1 parameterType(输入类型)
parameterType属性可以映射的输入参数类型有:
简单类型、POJO类型、Map类型、List类型(数组)。
在<insert>,<update>,<select>,<delete>标签中,可以通过parameterType指定输入参数的类型,类型可以是简单类型、hashmap、pojo的包装类型。
parameterType属性是可以省略的.MyBatis框架可以根据SqlSession接口中方法的参数
来判断输入参数的实际数据类型.
2.3.2 resultType(输出类型)
resultType属性可以映射的java类型有:
简单类型、POJO类型、Map类型。
使用resultType进行输出映射时,要求sql语句中查询的列名和要映射的pojo的属性名一致。如果查询出来的列名和pojo中的属性名全部不一致,就不会创建实体类对象.但是只要查询出来的列名和实体类中的属性有一个一致,就会创建实体类对象
2.4 resultMap
如果sql查询列名 和 pojo 的属性名不一致,可以通过resultMap 将列名和属性名做一个对应关系,最终将查询结果映射到指定的pojo 对象。
由于sql查询列名和UserInfo类属性名不一致,所以不能使用resultType进行结构映射。
需要定义一个resultMap将sql查询列名和UserInfo类的属性名对应起来,完成结果映射。
ResultMap 可以实现将查询结果映射为复杂类型的pojo, 比如在查询结果映射对象中包含的pojo 和 list 实
现一对一查询和一对多查询。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.xa02.mapper.UserMapper">
<!-- 定义resultMap:将查询的列名和映射的pojo的属性名做一个对应关系 -->
<!--
1.id 指定 resultMap的唯一表示。
2.type:指定查询结果要映射的pojo类型。
-->
<resultMap id="userResultMap" type="UserInfo">
<!--
id标签:映射查询结果的唯一列(主键列)
column:查询sql的列名
property:映射结果的属性名
-->
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<!-- result标签:映射查询结果pojo的普通列 -->
<result column="user_name" property="userName"/>
<result column="sex" property="sex"/>
<result column="birthday" property="birthday"/>
<result column="address" property="address"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectUserById" parameterType="long" resultMap="userResultMap">
select * from t_user where id = #{id}
</select>
<insert id="insertUser" parameterType="map">
INSERT INTO t_user(user_name,sex,birthday,address ) VALUES
(#{userName},#{sex},#{birthday},#{address});
</insert>
</mapper>
<id />:此属性表示查询结果集的唯一标识,非常重要。如果是多个字段为复合唯一约束则定义多个。
Property:表示UserInfo类的属性。
Column:表示sql查询出来的字段名。
Column和property放在一块儿表示将sql查询出来的字段映射到指定的pojo类属性上。
resultMap子元素的配置,在 mybatis 高级结果章节中详细介绍。
到底是使用 resultType 还是 resultMap??
- resultType
- 当使用resultType做SQL语句返回结果类型处理时,对于SQL语句查询出的字段在相应的pojo中必须有和它相同的字段对应.
- 注意事项:
- SQL列名必须和POJO的属性是一致的
- 使用resultType,如果要使用简写配置 typeAlias(别名)
- 如果列名和JavaBean不一致,但列名符合单词下划线,java 是驼峰命名法,则需要在Mybatis全局文件中设置 mapUnderscoreToCamelCase可设置为true;
- resultMap
- 字段有自定义转化规则
- 复杂的多表查询
到底是使用resultType 还是 resultMap
强制使用resultMap, 不要用 resultType当返回参数,即使所有类属性名与数据库字段一一对应,也需要定义
2.5 传递多个参数
- 使用Map传递参数
- 使用pojo 传递参数
- 使用注解@Param方法
总结:
- 使用Map传递参数。因为Map导致业务可读性非常差,从而导致后续扩展和维护困难。不建议使用
- 使用@Param注解传递多个参数,这种方式的使用受到参数个数(n)的影响。当 n <= 5时,它是最佳的传参方式,它比用JavaBean更好,因为它更加直观;当n>5时,多个参数将给调用带来困难。
- 当参数个数多于5个时,建议使用JavaBean方式
2.6 # 和$ 的区别
#表示一个占位符号,通过#{}可以实现 prepareedStatement 向占位符中设置值,自动进行java类型和jdbc转换,#{}可以防止sql注入。
想当于 jdbc PreparedStatement
#{} 可以接收简单类型值 或 pojo 属性值。想当于JDBC SQL语句中的连接符合 + (Statement)
#{} : 进行输入映射的时候,会对参数进行类型解析(如果是String类型,那么SQL语句会自动加上’’)
${} :进行输入映射的时候,将参数原样输出到SQL语句中
#{} : 如果进行简单类型(String、Date、8种基本类型的包装类)的输入映射时,#{}中参数名称可以任意
:如果进行简单类型(String、Date、8种基本类型的包装类)的输入映射时,{} : 如果进行简单类型(String、Date、8种基本类型的包装类)的输入映射时,:如果进行简单类型(String、Date、8种基本类型的包装类)的输入映射时,{}中参数名称必须是value
UserInfo selectUserById(Long id);
<select id="selectUserById" parameterType="long" resultMap="userResultMap">
select * from t_user where id = ${value}
</select>
此时如果 使用${id} 则会报错,必须使用value
${} : 存在SQL注入问题 ,使用OR 1=1 关键字将查询条件忽略
为了能够看到两种方式的区别,需要看到MyBatis执行时输送的SQL情况.因此
需要借助Log4J日志进行观察
List<UserInfo> selectList(UserInfo userInfo);
<select id="selectList" parameterType="UserInfo" resultMap="userResultMap">
select * from t_user where sex = '${sex}' and user_name = #{userName}
</select>
日志如下:
[com.xa02.mapper.UserMapper.selectList]-==> Preparing: select * from t_user where sex = '1' and user_name = ?
[com.xa02.mapper.UserMapper.selectList]-==> Parameters: tom(String)
[com.xa02.mapper.UserMapper.selectList]-<== Total: 4
在大多数情况下,我们都是采用#{}读取参数内容.但是在一些特殊的情况下,我们还是需要使用${}读取参数的.
表名、选取的列是动态的,order by和in操作, 可以考虑使用$。
比如,当用户数据量比较大时,需要按照日期分多张表,这时表名就需要动态传入。
List<UserInfo> selectList(String tableName,UserInfo userInfo);
<select id="selectList" resultMap="userResultMap">
select * from ${arg0} where sex = '${arg1.sex}' and user_name = #{arg1.userName}
</select>
测试代码如下:
@Test
public void selectUserById(){
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
try{
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
UserInfo userInfo = new UserInfo();
userInfo.setSex("1");
userInfo.setUserName("tom");
List<UserInfo> userList = mapper.selectList("t_user2020",userInfo);
System.out.println(userList);
}finally{
sqlSession.close();
}
}
再比如.需要动态的指定查询中的排序字段,此时也只能使用${}
<select id="selectList" resultMap="userResultMap">
select * from ${arg0} where sex = '${arg1.sex}' and user_name = #{arg1.userName} order by ${arg2}
</select>
简单来说,在JDBC不支持使用占位符的地方,都可以使用${}
2.7 select/insert/update/delete
2.7.1 select
模糊查询
<select id="selectList" parameterType="UserInfo" resultMap="userResultMap">
select * from t_user where address like '%' #{address} '%'
# select * from t_user where address like concat('%',#{address},'%')
# select * from t_user where address like '%${value}%'
</select>
<select
-
id=“selectList”
-
parameterType=“UserInfo”
-
resultType=“UserInfo”
-
resultMap=“userResultMap”
-
lushCache=“false”
-
useCache=“true”
-
timeout=“10”
-
statementType= PREPARED">
2.7.2 insert/update/delete
<insert id="insertUser" parameterType="map">
INSERT INTO t_user(user_name,sex,birthday,address ) VALUES
(#{userName},#{sex},#{birthday},#{address});
</insert>
<insert
id=“addUser”
parameterType=“User”
flushCache=“true”
statementType=“PREPARED” <执行类型>
keyProperty=“”
keyColumn=“”
useGeneratedKeys=“” <!–插入成功后将 将值回设至 原参数->
timeout=“20”>
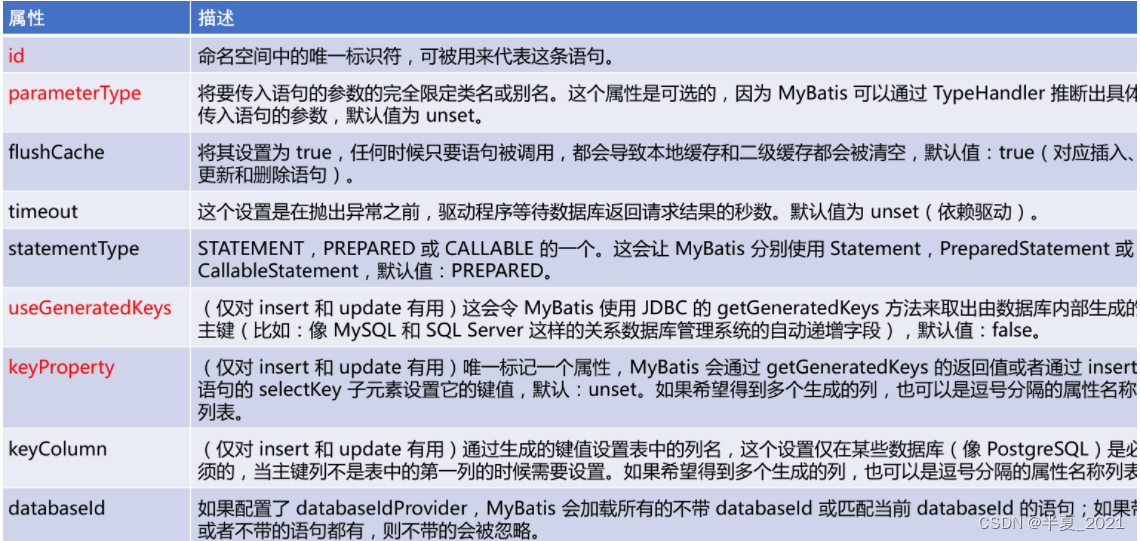
2.9 自定义主键返回
当前表支持主键自动增长
通过修改sql映射文件,可以将mysql自增主键返回:
<insert id="insertUser" parameterType="UserInfo" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id">
INSERT INTO t_user(user_name,sex,birthday,address ) VALUES
(#{userName},#{sex},#{birthday},#{address});
</insert>
- userGeneratedKeys = “true” 表示Mybatis可以通过getGeneratedKeys 方法获得本次增长的主键值
- keyProperty = “id” 表示Mybatis 将获得自动增长值赋给当前实体类对象哪个属性,比如上面用户的Id
@Test
public void insertUser(){
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
try{
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
UserInfo userInfo = new UserInfo("jack","1",new Date(),"shenzhen");
Integer count = mapper.insertUser(userInfo);
sqlSession.commit();
if(count > 0){
System.out.println("inert success....."+userInfo);
}
}finally{
sqlSession.close();
}
}
结果将返回的ID 自动赋值到UserInfo中。
[com.xa02.mapper.UserMapper.insertUser]-==> Preparing: INSERT INTO t_user(user_name,sex,birthday,address ) VALUES (?,?,?,?);
[com.xa02.mapper.UserMapper.insertUser]-==> Parameters: jack(String), 1(String), 2022-09-06 22:58:31.418(Timestamp), shenzhen(String)
[com.xa02.mapper.UserMapper.insertUser]-<== Updates: 1
[org.apache.ibatis.transaction.jdbc.JdbcTransaction]-Committing JDBC Connection [com.mysql.jdbc.JDBC4Connection@6483f5ae]
inert success.....UserInfo{id=15, userName='jack', sex='1', birthday=Tue Sep 06 22:58:31 CST 2022, address='shenzhen'}
<insert id="insertUser" parameterType="cn.edu360.mybatis.po.User">
<!-- selectKey将主键返回,需要再返回 -->
<selectKey keyProperty="id" order="AFTER" resultType="java.lang.Integer">
select LAST_INSERT_ID()
</selectKey>
insert into user(username,birthday,sex,address)
values(#{username},#{birthday},#{sex},#{address});
</insert>
当前表不支持主键自动增长
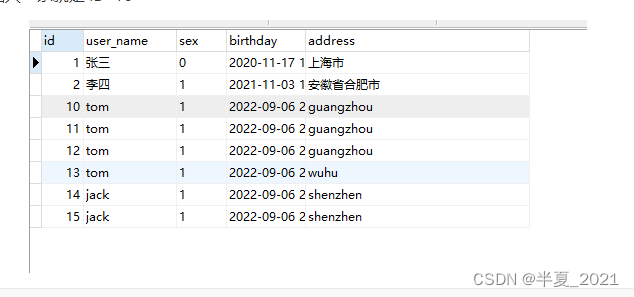
在Mysql数据库中,可以通过max函数获得当前表中最后一条插入数据id.
在MyBatis中,也可以通过这种方式来获得主键值
比如当前用户信息最大ID 为 15,再插入一条就是 ID=16
<insert id="insertUser" parameterType="UserInfo" >
<selectKey resultType="long" keyProperty="id" order="BEFORE">
select max(id)+1 from t_user
</selectKey>
INSERT INTO t_user(id,user_name,sex,birthday,address ) VALUES
(#{id},#{userName},#{sex},#{birthday},#{address});
</insert>
- selectKey 标签: 用于声明查询当前表主键的SQL语句。
- keyProperty: 表示将查询结果赋值给当前实体类对象中的id属性。
- resultType=“long” 表示将查询结果转换为 long 类型。
- order = “BEFORE” 表示当前查询语句要在insert语句之前执行。

测试类
@Test
public void insertUser(){
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
try{
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
UserInfo userInfo = new UserInfo("jame","1",new Date(),"shenzhen");
Integer count = mapper.insertUser(userInfo);
sqlSession.commit();
if(count > 0){
System.out.println("inert success....."+userInfo);
}
}finally{
sqlSession.close();
}
}
结果:
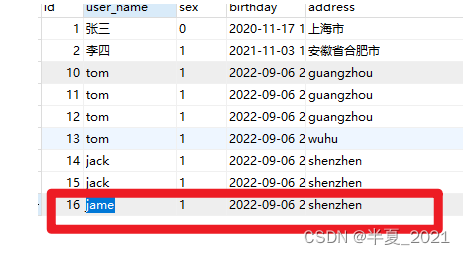
2.10 mysql中使用uuid实现主键
需要增加通过select uuid()得到uuid值
<insert id="insertUser" parameterType="UserInfo" >
<selectKey resultType="string" keyProperty="id" order="BEFORE">
select uuid()
</selectKey>
INSERT INTO t_user(id,user_name,sex,birthday,address ) VALUES
(#{id},#{userName},#{sex},#{birthday},#{address});
</insert>
注意这里使用的order是“BEFORE”
2.11 sql 标签
在同一个mapper 多个statement 存在多个相同的sql 片段时,可以通过元素声明,在通过 元素进行引用
声明sql 段
id ,name ,createTime
在映射文件中可使用sql标签将重复的sql提取出来,然后使用include标签引用即可,最终达到sql重用的目的,具体实现如下:
使用include引用
<!-- 使用包装类型查询用户 使用ognl从对象中取属性值,如果是包装对象可以使用.操作符来取内容部的属性 -->
<sql id="selectAllColumn">
user_name,sex,birthday,address
</sql>
<select id="selectList" parameterType="UserInfo" resultMap="userResultMap">
select <include refid="selectAllColumn"></include>
from t_user where address like '%' #{address} '%'
</select>
注意:
1、如果引用其它mapper.xml的sql片段,则在引用时需要加上namespace,如下:****<include refid=*"*namespace.sql片段”/>
2.12 mybatis 动态SQL
根据用户提供的参数,动态决定查询语句依赖的查询条件或者SQL语句的内容
2.12.1 IF 使用
<select id="selectList" parameterType="UserInfo" resultMap="userResultMap">
select <include refid="selectAllColumn"></include>
from t_user
where 1=1
<if test="userName !=null and userName !=''">
and user_name = #{userName}
</if>
<if test="address !=null and address !=''">
and address like '%' #{userName} '%'
</if>
</select>
- 判断条件property != null 或 property = == null 适用于任何类型的字段,用于判断属性值是否为空
- 判断条件 property !=‘’ 或 Pro二批任天野== ‘’ 仅适用于 String 类型的字段,用于判断是否为空字符串
- and 和 or : 当有多个判断条件时,适用 and 或 or 进行连接,嵌套的判断可以使用小括号分组。
2.12.2 choose、when、otherwise
按顺序判断其内部when标签中的test条件出否成立,如果有一个成立,则 choose 结束。当 choose 中所有 when 的条件都不满则时,
则执行 otherwise 中的sql。类似于Java 的 switch 语句,choose 为 switch,when 为 case,otherwise 则为 default。
<select id="selectList" parameterType="UserInfo" resultMap="userResultMap">
select <include refid="selectAllColumn"></include>
from t_user
where 1=1
<choose>
<when test="userName !=null and userName !=''">
and user_name = #{userName}
</when>
<when test="sex !=null and sex !=''">
and sex = #{sex}
</when>
<otherwise>
and address like '%' #{address} '%'
</otherwise>
</choose>
</select>
测试代码如下:
@Test
public void selectUserById(){
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
try{
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
UserInfo userInfo = new UserInfo();
userInfo.setUserName("zhangsan");
userInfo.setSex("1");
userInfo.setAddress("guangzhou");
List<UserInfo> userList = mapper.selectList(userInfo);
System.out.println(userList);
}finally{
sqlSession.close();
}
}
测试日志:
[com.xa02.mapper.UserMapper.selectList]-==> Preparing: select user_name,sex,birthday,address from t_user where 1=1 and user_name = ?
[com.xa02.mapper.UserMapper.selectList]-==> Parameters: zhangsan(String)
[com.xa02.mapper.UserMapper.selectList]-<== Total: 1
从上面日志看,choose 遇到第一个when 满足条件就结束了。
2.12.3 where
可以自动的将第一个条件前面的逻辑运算符(or ,and)去掉
在where 包裹的SQL前会自动添加 where 字符 并去掉首尾多佘的 and|or 字符 相
<select id="selectList" parameterType="UserInfo" resultMap="userResultMap">
select <include refid="selectAllColumn"></include>
from t_user
<where>
<if test="userName !=null and userName !=''">
and user_name = #{userName}
</if>
<if test="sex !=null and sex !=''">
and sex = #{sex}
</if>
</where>
</select>
2.13.4 set
会在成功拼接的条件前加上SET单词且最后一个”,”号会被无视掉
在set包裹的SQL前会自动添加 set 字符并去掉首尾多佘的 , 字符。
<update id="updateUser" parameterType="UserInfo">
update t_user
<set>
<if test="userName !=null and userName !=''">
user_name = #{userName},
</if>
<if test="sex !=null and sex !=''">
sex = #{sex},
</if>
<if test="birthday !=null">
birthday = #{birthday},
</if>
<if test="address !=null and address !=''">
address = #{address},
</if>
</set>
where id = #{id}
</update>
2.13.5 trim
格式:
<trim prefix="" suffix="" suffixOverrides="" prefixOverrides=""></trim>
-
prefix:
-
- 表示在trim包裹的SQL语句前面添加的指定内容。
-
suffix:
-
- 表示在trim包裹的SQL末尾添加指定内容
-
prefixOverrides:
-
- 表示去掉(覆盖)trim包裹的SQL的指定首部内容
-
suffixOverrides:
-
- 表示去掉(覆盖)trim包裹的SQL的指定尾部内容
<select id="selectList" parameterType="UserInfo" resultMap="userResultMap">
select <include refid="selectAllColumn"></include>
from t_user
<trim prefix="where" prefixOverrides="and | or" suffix="" suffixOverrides="">
<if test="userName != null and userName != ''">
and user_name = #{userName}
</if>
<if test="sex != null and sex != ''">
and sex = #{sex}
</if>
<if test="address != null and address != ''">
and address like '%' #{address} '%'
</if>
</trim>
</select>
-
prefix=“where” // 前缀, 上面sql 会自动在t_user后加上where
-
prefixOverrides=“and|or” // 前缀要替换的词 ,如果userName 为null, 则会执行sex,这样sex前就会有and,使用 prefixOverrides可以去掉trim包裹的指定首部内容。
-
suffix=“” // 添加后缀
-
suffixOverrides=“” // 后缀要替换的词
2.13.6 foreach
foreach标签用于对集合内容进行遍历,将得到内容作为SQL语句的一部分.
在实际开发过程中主要用于in语句的构建和批量添加操作
foreach元素的属性主要有 item,index,collection,open,separator,close。
-
表示传入的集合名称,可是 list ,array,map对象,
-
item: 表示集合中每一个元素进行迭代时的别名。
-
index 指定一个名字,用于表示在迭代过程中,每次迭代到的位置,在list/array 中,index作为索引号,但是在Map中,index 为遍历元素的key值。
-
open 表示该语句以什么开始,通常与 close = “)” 大搭配使用,使用场景为 in(), values()
-
separator 表示在每次进行迭代之间以什么符号作为分隔符,比如在IN时,separator=“,”,最终所有遍历的元素将会以设定的(,)逗号符号隔开
-
close 表示以什么结束,通常与open="("搭配使用
案例1:传入参数为List
比如 根据id查询用户信息
select * from t_user where user_name like ’tom‘ and id in (1,2,3)
UserMapper.xm 映射文件中添加如下元素
<select id="findUserByIds" parameterType="queryvo" resultType="UserInfo">
SELECT * FROM t_user
<where>
<!-- 此时 collection 可以为 collection 或者为list -->
<foreach collection="collection" item="id" open="and id in(" close=")" separator=",">
#{id}
</foreach>
</where>
</select>
如果需要使用ids变量名,则需要修改mapper接口
List<UserInfo> findUserByIds(@Param("ids") List<Long> ids);
案例2.传入参数为array
<select id="findUserByIds" parameterType="queryvo" resultType="UserInfo">
SELECT * FROM t_user
<where>
<!-- 此时 collection 可以为 array或者变量名称ids(需要在接口方法加上注解 @Param) -->
<foreach collection="array" item="id" open="and id in(" close=")" separator=",">
#{id}
</foreach>
</where>
</select>
如果要使用变量名ids,则需要在接口方法中加上 @Param注解
List<UserInfo> findUserByIds(@Param("ids") Long[] ids);
案例3.传入参数为map
<select id="findUserByIds" parameterType="queryvo" resultType="UserInfo">
SELECT * FROM t_user
<where>
<!-- 此时 collection 可以为 array或者变量名称ids(需要在接口方法加上注解 @Param) -->
<foreach collection="ids.values" item="id" open="and id in(" close=")" separator=",">
#{id}
</foreach>
</where>
</select>
接口mapper
List<UserInfo> findUserByIds(@Param("ids") Map<String,Long> ids);
- 如果要获取map的key和value,则使用 ids.entry
<select id="getUserInfoList" resultType="UserInfo">
SELECT
*
FROM user_info
where
<if test="user!= null and user.size() >0">
(user_name,sex) IN
<foreach collection="userList.entrySet()" item="value" index="key" separator="," open="(" close=")">
(#{key},#{value})
</foreach>
</if>
</select>
- 获取 key 或者 value ,使用 userList.keys 或者 userList.values








 本文详细介绍了Mybatis XML配置中的命名空间、参数映射、输入输出映射、resultMap、多参数传递、#和$的区别、SQL标签以及动态SQL等内容,强调了命名空间在解决命名冲突中的作用,参数映射的多种方式,以及如何使用resultMap处理列名与属性名不一致的情况。此外,还讨论了在何时使用#和$,以及如何在insert、update、delete、select语句中配置这些元素。
本文详细介绍了Mybatis XML配置中的命名空间、参数映射、输入输出映射、resultMap、多参数传递、#和$的区别、SQL标签以及动态SQL等内容,强调了命名空间在解决命名冲突中的作用,参数映射的多种方式,以及如何使用resultMap处理列名与属性名不一致的情况。此外,还讨论了在何时使用#和$,以及如何在insert、update、delete、select语句中配置这些元素。


















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










