转自:https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/wangzhiyu1980/article/details/44227913
参考:
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/YEYUANGEN/article/details/37593533
https://www.cnblogs.com/secondtonone1/p/5580203.html
一个简单的实例程序,说明pthread_cond_wait 和 pthread_cond_broadcast 的使用方式。
函数定义:
int pthread_cond_wait(pthread_cond_t *cond, pthread_mutex_t *mutex)
int pthread_cond_broadcast(pthread_cond_t *cond)
函数说明:
pthread_cond_wait :有两个输入参数,一个是pthread_cond_t,是函数将要等待的信号,另一个是 pthread_mutex_t,一个互斥锁。用于对信号量进行保护,防止多个线程同时对其进行操作。在线程开始等待信号量前,必须由本线程对互斥锁进行锁定,然后pthread_cond_wait会更新条件等待队列,并且释放互斥量,允许其他线程进行访问;当cond 满足条件允许线程继续执行时,wait_cond也会先对mutex 进行锁定,对cond进行处理,然后再允许线程继续运行。所以pthread_cond_wait() 后的pthread_mutex_unlock()还是必要的。
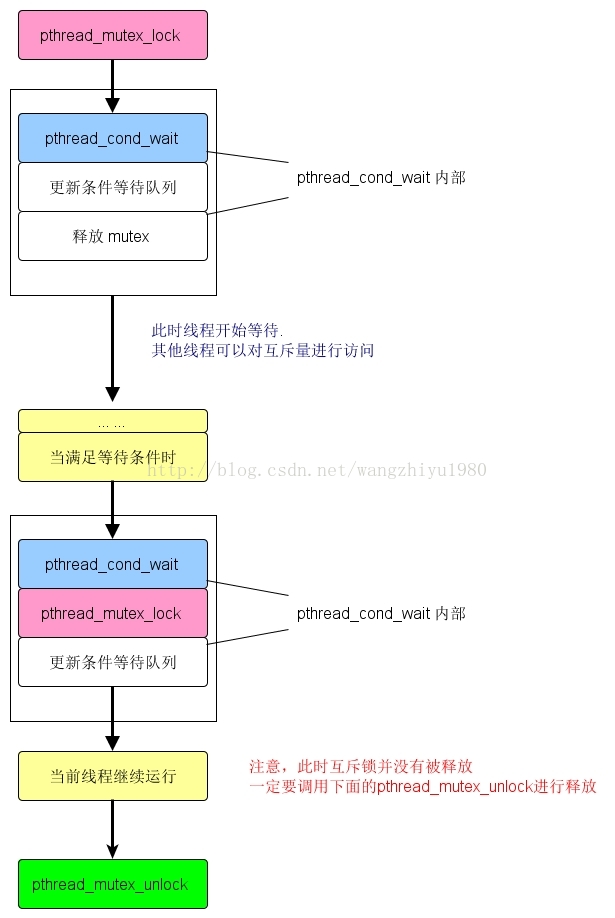
实例程序:
#include <pthread.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
static pthread_mutex_t mtx=PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
static pthread_cond_t cond=PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;
static void* func_1(void* arg)
{
cout << "func_1 start" << endl;
pthread_mutex_lock(&mtx);
cout << "func_1 lock mtx" << endl;
cout << "func_1 wait cond" << endl;
pthread_cond_wait(&cond, &mtx);
cout << "func_1 unlock mtx" << endl;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mtx);
cout << "func_1 end" << endl;
sleep(5);
return NULL;
}
static void* func_2(void* arg)
{
cout << "func_2 start" << endl;
pthread_mutex_lock(&mtx);
cout << "func_2 lock mtx" << endl;
cout << "func_2 wait cond" << endl;
pthread_cond_wait(&cond, &mtx);
cout << "func_2 unlock mtx" << endl;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mtx);
cout << "func_2 end" << endl;
sleep(5);
return NULL;
}
int main()
{
pthread_t tid1, tid2;
cout << "main create thread" << endl;
pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, func_1, NULL);
pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, func_2, NULL);
sleep(3);
cout << "main boradcast signal" << endl;
pthread_cond_broadcast(&cond);
cout << "main join thread" << endl;
pthread_join(tid1, NULL);
pthread_join(tid2, NULL);
cout << "main end" << endl;
return 0;
}
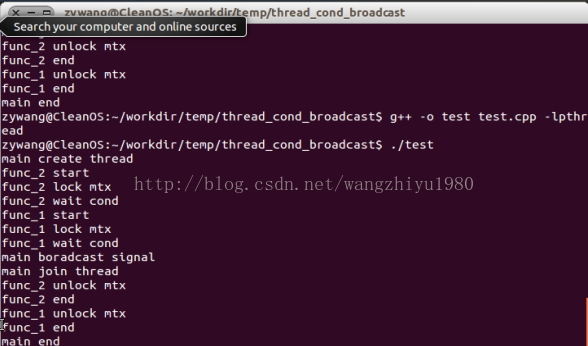
测试结果:




 本文通过一个简单实例展示了pthread_cond_wait和pthread_cond_broadcast的用法。介绍了这两个函数的基本定义及如何在多线程环境中使用它们来同步线程的执行流程。
本文通过一个简单实例展示了pthread_cond_wait和pthread_cond_broadcast的用法。介绍了这两个函数的基本定义及如何在多线程环境中使用它们来同步线程的执行流程。
















 466
466

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








