Problem Description
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm describes a set of procedures or instructions that define a procedure. The term has become increasing popular since the advent of cheap and reliable computers. Many companies now employ a single coder to write an algorithm that will replace many other employees. An added benefit to the employer is that the coder will also become redundant once their work is done.
1
You are now the signle coder, and have been assigned a new task writing code, since your boss would like to replace many other employees (and you when you become redundant once your task is complete).
Your code should be able to complete a task to replace these employees who do nothing all day but eating: make the digest sum.
By saying “digest sum” we study some properties of data. For the sake of simplicity, our data is a set of integers. Your code should give response to following operations:
1. add x – add the element x to the set;
2. del x – remove the element x from the set;
3. sum – find the digest sum of the set. The digest sum should be understood by
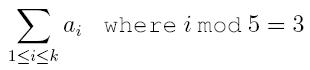
where the set S is written as {a 1, a 2, ... , a k} satisfying a 1 < a 2 < a 3 < ... < a k
Can you complete this task (and be then fired)?
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 See http://uncyclopedia.wikia.com/wiki/Algorithm
You are now the signle coder, and have been assigned a new task writing code, since your boss would like to replace many other employees (and you when you become redundant once your task is complete).
Your code should be able to complete a task to replace these employees who do nothing all day but eating: make the digest sum.
By saying “digest sum” we study some properties of data. For the sake of simplicity, our data is a set of integers. Your code should give response to following operations:
1. add x – add the element x to the set;
2. del x – remove the element x from the set;
3. sum – find the digest sum of the set. The digest sum should be understood by
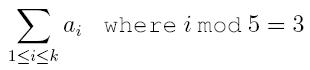
where the set S is written as {a 1, a 2, ... , a k} satisfying a 1 < a 2 < a 3 < ... < a k
Can you complete this task (and be then fired)?
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 See http://uncyclopedia.wikia.com/wiki/Algorithm
Input
There’re several test cases.
In each test case, the first line contains one integer N ( 1 <= N <= 10 5 ), the number of operations to process.
Then following is n lines, each one containing one of three operations: “add x” or “del x” or “sum”.
You may assume that 1 <= x <= 10 9.
Please see the sample for detailed format.
For any “add x” it is guaranteed that x is not currently in the set just before this operation.
For any “del x” it is guaranteed that x must currently be in the set just before this operation.
Please process until EOF (End Of File).
In each test case, the first line contains one integer N ( 1 <= N <= 10 5 ), the number of operations to process.
Then following is n lines, each one containing one of three operations: “add x” or “del x” or “sum”.
You may assume that 1 <= x <= 10 9.
Please see the sample for detailed format.
For any “add x” it is guaranteed that x is not currently in the set just before this operation.
For any “del x” it is guaranteed that x must currently be in the set just before this operation.
Please process until EOF (End Of File).
Output
For each operation “sum” please print one line containing exactly one integer denoting the digest sum of the current set. Print 0 if the set is empty.
Sample Input
9 add 1 add 2 add 3 add 4 add 5 sum add 6 del 3 sum 6 add 1 add 3 add 5 add 7 add 9 sum
Sample Output
3 4 5HintC++ maybe run faster than G++ in this problem.
Source
思路:用sum[400005][5] 来保存对应区间的 下标模5为i的数的和,剩下的就是单点更新和根据左右儿子节点的数的数量来维护sum。
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <map>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct S{
char op[5];
int x,id;
}e[100005];
bool cmpval(S a,S b)
{
if(a.x==b.x) return a.op[0]<b.op[0];
return a.x<b.x;
}
bool cmpid(S a,S b)
{
return a.id<b.id;
}
int n,cnt,val[100005],num[400005];
long long sum[400005][5];
void build(int idx,int s,int e)
{
if(s!=e)
{
int mid=(s+e)>>1;
build(idx<<1,s,mid);
build(idx<<1|1,mid+1,e);
}
num[idx]=0;
for(int i=0;i<5;i++) sum[idx][i]=0;
}
void update(int idx,int s,int e,int pos,int flag)
{
num[idx]+=flag;
if(s==e)
{
sum[idx][1]+=val[s]*flag;
return;
}
int mid=(s+e)>>1;
if(pos<=mid) update(idx<<1,s,mid,pos,flag);
else update(idx<<1|1,mid+1,e,pos,flag);
for(int i=0;i<5;i++) sum[idx][i]=sum[idx<<1][i]+sum[idx<<1|1][i-num[idx<<1]%5>=0?i-num[idx<<1]%5:i-num[idx<<1]%5+5];//更新对应区间内下标为模5等于i数的和
}
long long query(int idx,int s,int e,int mod)
{
return sum[idx<<1][mod]+sum[idx<<1|1][mod-num[idx<<1]%5>=0?mod-num[idx<<1]%5:mod-num[idx<<1]%5+5];
}
int main()
{
int i;
long long ans;
while(~scanf("%d",&n))
{
map<int,int>mp;//用于离散化过程中判重,有可能存在先add a,再del a,再 add a的情况
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%s",e[i].op);
if(e[i].op[0]=='s') e[i].x=0;
else scanf("%d",&e[i].x);
e[i].id=i;
}
sort(e,e+n,cmpval);
cnt=1;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)//离散化
{
if(e[i].op[0]=='a')
{
if(!mp[e[i].x]) mp[e[i].x]=cnt++;
val[mp[e[i].x]]=e[i].x;
e[i].x=mp[e[i].x];
}
else if(e[i].op[0]=='d')
{
e[i].x=mp[e[i].x];
}
}
sort(e,e+n,cmpid);
cnt--;
if(!cnt)//特判
{
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(e[i].op[0]=='s')
{
printf("0\n");
}
}
continue;
}
build(1,1,cnt);
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(e[i].op[0]=='a') update(1,1,cnt,e[i].x,1);
else if(e[i].op[0]=='d') update(1,1,cnt,e[i].x,-1);
else printf("%I64d\n",query(1,1,n,3));
}
}
}








 本文介绍了一种使用算法替代员工日常任务的方法,特别关注消化求和操作。通过实现添加、删除和求和操作,可以有效管理一组整数数据集,并计算其特殊性质下的总和。
本文介绍了一种使用算法替代员工日常任务的方法,特别关注消化求和操作。通过实现添加、删除和求和操作,可以有效管理一组整数数据集,并计算其特殊性质下的总和。
















 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








