BeanDefinition资源加载
在《BeanDefinition的资源定位》中,讲到了资源的定位。Spring找到了资源后,下面就是资源的加载了:
AbstractBeanDefinitionReader.loadBeanDefinitions
public int loadBeanDefinitions(String location, Set<Resource> actualResources) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = getResourceLoader();
if (resourceLoader == null) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Cannot import bean definitions from location [" + location + "]: no ResourceLoader available");
}
if (resourceLoader instanceof ResourcePatternResolver) {
// Resource pattern matching available.
try {
//找到资源的位置
Resource[] resources = ((ResourcePatternResolver) resourceLoader).getResources(location);
//加载BeanDefinition,并记录加载的BeanDefinition的数量
int loadCount = loadBeanDefinitions(resources);
//注意这个actualResources,这个并不是来承载资源的,而是把你加载成功的资源存储起来的,意思是说,调用者传入了一个容器,然后上文加载BeanDefinition的资源,都放入到这个容器,方便以后回顾使用。所以这个actualResources在此处并不会影响BeanDefinition的加载和注册的流程,前期分析的时候可以忽略这个。
if (actualResources != null) {
for (Resource resource : resources) {
actualResources.add(resource);
}
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Loaded " + loadCount + " bean definitions from location pattern [" + location + "]");
}
//返回加载的BeanDefinition个数
return loadCount;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Could not resolve bean definition resource pattern [" + location + "]", ex);
}
}
else {
//如果resourceLoader没有实现ResourcePatternResolver接口,即没有复杂路径解析的能力,比如简单的DefaultResourceLoader,就会执行此块代码。下面的加载资源并注册BeanDefinitiion的逻辑都是一致的。
Resource resource = resourceLoader.getResource(location);
int loadCount = loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
if (actualResources != null) {
actualResources.add(resource);
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Loaded " + loadCount + " bean definitions from location [" + location + "]");
}
return loadCount;
}
}
ResourceLoader的部分继承关系,可以看出 *ApplicationContext类都实现了ResourcePatternResolver,都具有通过复杂路径表达式解析资源的能力,但是普通的资源加载器,比如DefaultResouceLoader及其子类
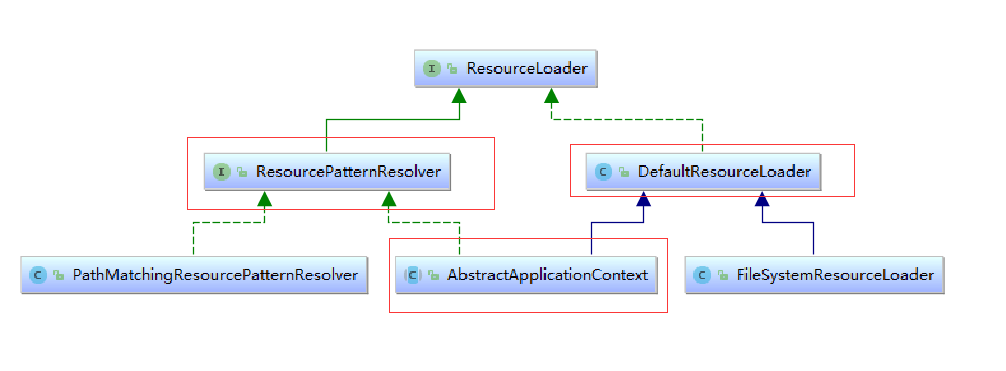
loadBeanDefinitions
AbstractBeanDefinitionReader只是简单的遍历Resource数组,然后调用子类的loadBeanDefinitions来进行资源的加载
我在此处使用的子类是XmlBeanDefinitionReader
public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource... resources) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.notNull(resources, "Resource array must not be null");
int counter = 0;
for (Resource resource : resources) {
counter += loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
}
return counter;
}
XmlBeanDefinition
public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
//将资源包装成EncodedResource,然后进行加载
//EncodedResource是一个包含字符集或编码信息的资源包装类
//但此处使用的构造函数,并没有指定编码或者字符集,所以使用的是默认的编码
return loadBeanDefinitions(new EncodedResource(resource));
}
//加载EncodedResource
public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.notNull(encodedResource, "EncodedResource must not be null");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Loading XML bean definitions from " + encodedResource.getResource());
}
//取出本线程中的资源集合
//resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded 是一个拥有name属性的ThreadLoacal,里面存储了每个线程使用此类(XmlBeanDefinitionReader)加载的资源的集合。简单点说,每个线程使用的资源都放在自己的单独小仓库中,以便后日使用。
//再结合下文的代码可以看出,此ThreadLocal的作用是,防止某个线程重复的加载同一个资源。注意是防止同一个线程多次加载同一个资源,并不会阻止不同的线程加载同一个资源。
Set<EncodedResource> currentResources = this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.get();
//如果还没有资源集合,就创建一个并放入到resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded中
if (currentResources == null) {
currentResources = new HashSet<EncodedResource>(4);
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.set(currentResources);
}
//判断此线程是否已经加载过此资源,如果有,就抛出异常
if (!currentResources.add(encodedResource)) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Detected cyclic loading of " + encodedResource + " - check your import definitions!");
}
try {
//获取资源中的输入流,
//这一行标志着资源定位的完全结束,资源加载的开始
InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream();
try {
// 包装成InputSource
InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream);
if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) {
inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding());
}
//调用真正的加载BeanDefinitiion的方法
return doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource());
}
finally {
inputStream.close();
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"IOException parsing XML document from " + encodedResource.getResource(), ex);
}
finally {
//这块有点看不明白??
currentResources.remove(encodedResource);
if (currentResources.isEmpty()) {
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.remove();
}
}
}
protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
try {
//获取XML的验证模式
//扩展XML的文件目前有2种验证方式,或者说是约束方式,一种是DTD文件,另一种是XSD文件
//这里getValidationModeForResource就是要查询使用哪一种验证模式,
int validationMode = getValidationModeForResource(resource);
//将上面的inputSource解析成xml种的Document
//Spring在解析Xml时,没有使用外部的依赖,而是使用了java本身库中的解析xml的库。使用DOM的方式解析xml。
//一篇参考链接:https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/xml/x-jaxpval.html
//这里的documentLoader是一个DefaultDocumentLoader,详解见下文 DefaultDocumentLoader.loadDocument
Document doc = this.documentLoader.loadDocument(
inputSource, getEntityResolver(), this.errorHandler, validationMode, isNamespaceAware());
//解析成Document,至此xml的加载也完成了,下面就是注册BeanDefinition的内容了!
return registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (SAXParseException ex) {
throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Line " + ex.getLineNumber() + " in XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex);
}
catch (SAXException ex) {
throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex);
}
catch (ParserConfigurationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Parser configuration exception parsing XML from " + resource, ex);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"IOException parsing XML document from " + resource, ex);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Unexpected exception parsing XML document from " + resource, ex);
}
}
getValidationModeForResource
获取Xml的验证模式,Spring对这些基本模式常量进行了简单的封装,如下
//不验证 0 public static final int VALIDATION_NONE = XmlValidationModeDetector.VALIDATION_NONE; //自动选择验证模式 1 public static final int VALIDATION_AUTO = XmlValidationModeDetector.VALIDATION_AUTO; //DTD验证模式 2 public static final int VALIDATION_DTD = XmlValidationModeDetector.VALIDATION_DTD; //Scheme验证模式 3 public static final int VALIDATION_XSD = XmlValidationModeDetector.VALIDATION_XSD;也许有些同学不太明白XML的验证模式,这里我简单的扩展下:
XML的语法是比html要严格的,但是xml本身并没有规定标签名必须是什么,标签的属性是什么,标签内的值是什么类型。所以产生了XML的验证模式,用于校验XML的内部的标签名、标签关系(顺序、个数、嵌套等关系)、属性、值等有没有符合自定义的规则。
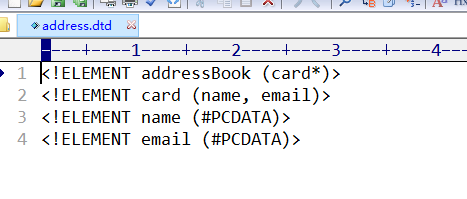
最早是DTD模式,即Document Type Definition模式,使用一个*.dtd文件来校验xml
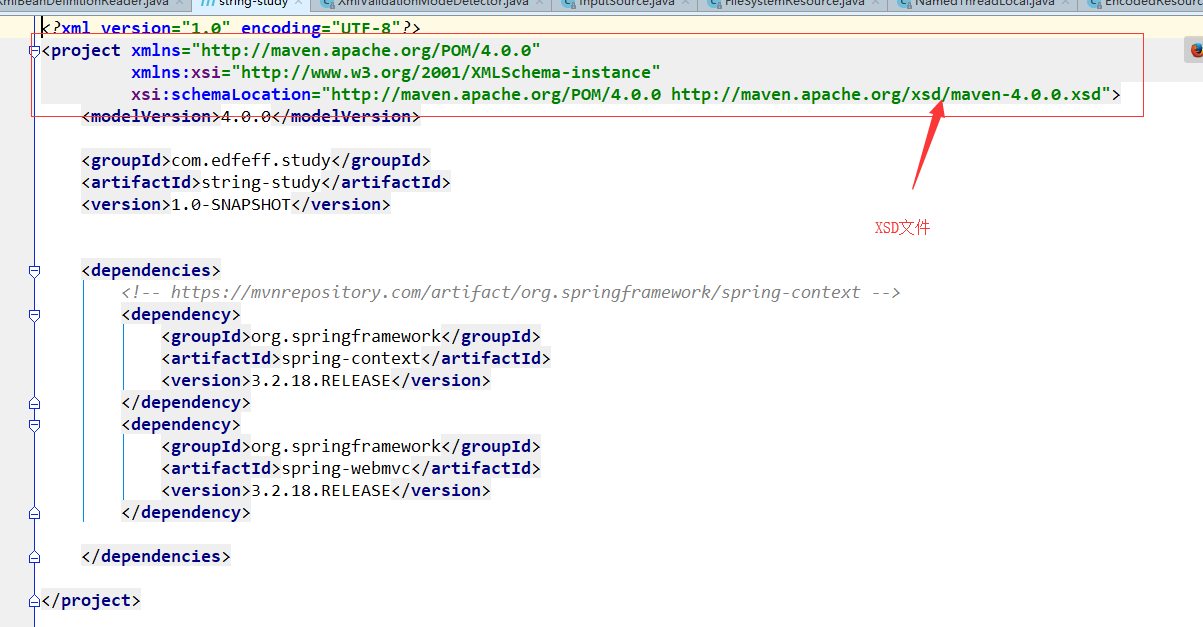
但是由于DTD模式不够灵活,不能校验复杂的场景,且DTD文件本身的语法规则不是xml形式的,所以又出现了一种XSD(XML Schemas Definition)类型的验证模式,XSD本身的就是一个XML文件,并且非常灵活。
附图
DTD模式的xml和DTD文件
XSD模式的xml和XSD文件
参考链接:
protected int getValidationModeForResource(Resource resource) {
// 首先,尝试获取配置的验证模式,默认的配置的模式是AUTO
int validationModeToUse = getValidationMode();
//如果不是AUTO,就直接返回,是AUTO的话,就需要推断具体的类型了,(Spring常用的套路,detect模式,spring再推测一个App是不是web应用时也有类似的方法)
if (validationModeToUse != VALIDATION_AUTO) {
return validationModeToUse;
}
//推断XML验证类型,简单点讲就是看下XML的头几行,到底是引用的DTD文件,还是XSD文件,从而决定验证类型
//详细分析见下《 推断Xml验证模式》
int detectedMode = detectValidationMode(resource);
if (detectedMode != VALIDATION_AUTO) {
return detectedMode;
}
//这里是Spring有点意思的地方,也是有点模糊的地方,
//如果Spring没有看出XML的验证模式到底是啥时,它采用了XSD的验证模式
//大家看下下面的注释,大意是在xml中没有找到DTD的声明,就假设为XSD模式了
// Hmm, we didn't get a clear indication... Let's assume XSD,
// since apparently no DTD declaration has been found up until
// detection stopped (before finding the document's root tag).
return VALIDATION_XSD;
}
✈ 推断Xml验证模式
//推测XML的验证类型
protected int detectValidationMode(Resource resource) {
if (resource.isOpen()) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Passed-in Resource [" + resource + "] contains an open stream: " +
"cannot determine validation mode automatically. Either pass in a Resource " +
"that is able to create fresh streams, or explicitly specify the validationMode " +
"on your XmlBeanDefinitionReader instance.");
}
InputStream inputStream;
try {
inputStream = resource.getInputStream();
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Unable to determine validation mode for [" + resource + "]: cannot open InputStream. " +
"Did you attempt to load directly from a SAX InputSource without specifying the " +
"validationMode on your XmlBeanDefinitionReader instance?", ex);
}
try {
//使用一个模式推断器来探测XML的验证模式,这个validationModeDetector是XmlValidationModeDetector
return this.validationModeDetector.detectValidationMode(inputStream);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("Unable to determine validation mode for [" +
resource + "]: an error occurred whilst reading from the InputStream.", ex);
}
}
//XmlValidationModeDetector的验证方法detectValidationMode
//Spring的这个推断方法是比较有意思的,也是效率比较高的
//大致的逻辑,看Xml的头几行中有没有 DCOTYPE 的字符出现,如果出现了就认为是DTD,否则是XSD
public int detectValidationMode(InputStream inputStream) throws IOException {
// Peek into the file to look for DOCTYPE.
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(inputStream));
try {
//DTD文件标志位,默认为false
boolean isDtdValidated = false;
String content;
//读取一行
while ((content = reader.readLine()) != null) {
//获取不在注释中的字符
content = consumeCommentTokens(content);
if (this.inComment || !StringUtils.hasText(content)) {
continue;
}
//判断字符中有没有 DOCTYPE 字样
if (hasDoctype(content)) {
isDtdValidated = true;
break;
}
//遇到第一个开放标签,意味着xml的头部声明已经结束了,不用继续解析了
if (hasOpeningTag(content)) {
// End of meaningful data...
break;
}
}
return (isDtdValidated ? VALIDATION_DTD : VALIDATION_XSD);
}
catch (CharConversionException ex) {
// Choked on some character encoding...
// Leave the decision up to the caller.
return VALIDATION_AUTO;
}
finally {
reader.close();
}
}
//注释符号处理
//总体的处理逻辑
//1.如果是在注释中,就返回null,
//2.如果不在注释中,返回原来的字符
//这块我的解析大家大致看下,一定要结合debug来看下,因为这里Spring的处理非常巧妙,我不够完全清晰的解释出其中的意思
//如果今后大家要解析 开闭符号 之类的需求,可以借鉴这里的处理,非常的nb
private String consumeCommentTokens(String line) {
//如果没有 <!-- 符号 并且没有 --> 符号,就直接返回该line
if (!line.contains(START_COMMENT) && !line.contains(END_COMMENT)) {
return line;
}
//对于注释的处理
//有上述其中注释的符号,这里的每一行的具体解析,四月我讲解下大致的原理
//这个XmlValidationModeDetector有一个标识位inComment,用于标识当前读出的这一行是不是在注释状态,然后XmlValidationModeDetector来通过维护这个标识位,来决定怎么处理这一行
// 1. <!--1
// 2. 2
// 3. 3-->
//对于注释上面的3中情况,这里会返回null回去
//这个while很关键
while ((line = consume(line)) != null) {
if (!this.inComment && !line.trim().startsWith(START_COMMENT)) {
return line;
}
}
return line;
}
private boolean hasDoctype(String content) {
return content.contains(DOCTYPE);
}
private boolean hasOpeningTag(String content) {
if (this.inComment) {
return false;
}
int openTagIndex = content.indexOf('<');
return (openTagIndex > -1 && (content.length() > openTagIndex + 1) &&
Character.isLetter(content.charAt(openTagIndex + 1)));
}
//消费一行
private String consume(String line) {
//如果inComment==true,进入endComment,否则进入startComment
//从line中确定index的值
int index = (this.inComment ? endComment(line) : startComment(line));
//如果
return (index == -1 ? null : line.substring(index));
}
//startComment和endComment都调用了同一个方法commentToken,但是传入的参数不同
private int startComment(String line) {
//查找 <!-- ,
//如果有 <!-- ,将inComment设置为true,标识注释结束,同时返回
//如果没有,返回-1
return commentToken(line, START_COMMENT, true);
}
private int endComment(String line) {
//查找 --> ,如果有 --> ,将inComment设置为false,标识注释结束
return commentToken(line, END_COMMENT, false);
}
//
private int commentToken(String line, String token, boolean inCommentIfPresent) {
//判断是否存在token值
int index = line.indexOf(token);
//存在token,就将inComment设置为inCommentIfPresent
if (index > - 1) {
this.inComment = inCommentIfPresent;
}
//如果存在token就返回(token的位置+token的长度)
//联系上面的逻辑,意思就是如果token存在,就取token后面的所有字符
//如果token不存在,返回-1
return (index == -1 ? index : index + token.length());
}
DefaultDocumentLoader.loadDocument
AbstractBeanDefinitionReader把xml文件加载成Docuemnt的任务交给了DefaultDocumentLoader,具体步骤如下;
Document doc = this.documentLoader.loadDocument(
inputSource, //xml文件的流
getEntityResolver(),//获取EntityResolver,这个实体解析器是上文AbstractXmlApplicationContext中的loadBeanDefinitions设置进入的,是一个 ResourceEntityResolver
this.errorHandler,//错误处理器,是一个SimpleSaxErrorHandler,解析的错误都是记录到logger中
validationMode,//验证模式
isNamespaceAware()//命令空间处理,默认是false
);
/*---
这里解释下EntityResolver,上文中提到了xml的验证需要DTD文件或者XSD文件。一般DTD的文件可以通过publicId和SystemId来从网络中下载,但是单机情况下就可用了,所以需要一个本地的DTD文件,这个EntityResolver就是根据publicId和systemId来从指定的位置加载出需要的DTD文件。
---*/
public Document loadDocument(InputSource inputSource, EntityResolver entityResolver,
ErrorHandler errorHandler, int validationMode, boolean namespaceAware) throws Exception {
// 创建一个 DocumentBuilderFactory
DocumentBuilderFactory factory = createDocumentBuilderFactory(validationMode, namespaceAware);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Using JAXP provider [" + factory.getClass().getName() + "]");
}
//创建DocumentBuilder
//设置实体解析器、错误处理器
DocumentBuilder builder = createDocumentBuilder(factory, entityResolver, errorHandler);
//将inputSource解析成Domcument,不再继续深入了,因为与Spring本身已经无关了,有可能在后续的文章探究下XML的解析源码。
return builder.parse(inputSource);
}
//创建 DocumentBuilderFactory的过程
protected DocumentBuilderFactory createDocumentBuilderFactory(int validationMode, boolean namespaceAware)
throws ParserConfigurationException {
//获取单例
DocumentBuilderFactory factory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
//设置命令空间处理
factory.setNamespaceAware(namespaceAware);
//如果xml验证模式不是none时,则设置验证模式
if (validationMode != XmlValidationModeDetector.VALIDATION_NONE) {
//开启验证模式
factory.setValidating(true);
//XSD验证模式
if (validationMode == XmlValidationModeDetector.VALIDATION_XSD) {
// Enforce namespace aware for XSD...
//设置命名空间处理
factory.setNamespaceAware(true);
try {
//设置属性,使用什么Schema语言来验证xml
//SCHEMA_LANGUAGE_ATTRIBUTE = "http://java.sun.com/xml/jaxp/properties/schemaLanguage";
// XSD_SCHEMA_LANGUAGE = "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema";
factory.setAttribute(SCHEMA_LANGUAGE_ATTRIBUTE, XSD_SCHEMA_LANGUAGE);
}
catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
ParserConfigurationException pcex = new ParserConfigurationException(
"Unable to validate using XSD: Your JAXP provider [" + factory +
"] does not support XML Schema. Are you running on Java 1.4 with Apache Crimson? " +
"Upgrade to Apache Xerces (or Java 1.5) for full XSD support.");
pcex.initCause(ex);
throw pcex;
}
}
}
return factory;
}
XmlBeanDefinitionReader.registerBeanDefinitions
Document已经加载完毕了,后面就是注册BeanDefinition,这部分是重中之重,我将在下篇文章中进行详细的讲解。
下篇预告《BeanDefinition注册》








 本文围绕Spring中BeanDefinition的资源加载展开。先介绍了AbstractBeanDefinitionReader.loadBeanDefinitions方法,以及ResourceLoader的继承关系。接着阐述了XmlBeanDefinitionReader加载资源的过程,包括获取Xml验证模式(如DTD、XSD),还提到将xml文件加载成Document的步骤,注册BeanDefinition将在下篇讲解。
本文围绕Spring中BeanDefinition的资源加载展开。先介绍了AbstractBeanDefinitionReader.loadBeanDefinitions方法,以及ResourceLoader的继承关系。接着阐述了XmlBeanDefinitionReader加载资源的过程,包括获取Xml验证模式(如DTD、XSD),还提到将xml文件加载成Document的步骤,注册BeanDefinition将在下篇讲解。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








