
个人简介:Java领域新星创作者;阿里云技术博主、星级博主、专家博主;正在Java学习的路上摸爬滚打,记录学习的过程~
个人主页:.29.的博客
学习社区:进去逛一逛~

Maven >>> 下载、安装、配置
一、下载Maven核心程序
- 通过官方渠道,下载Maven压缩包,官网🔗:maven.apache.org
…
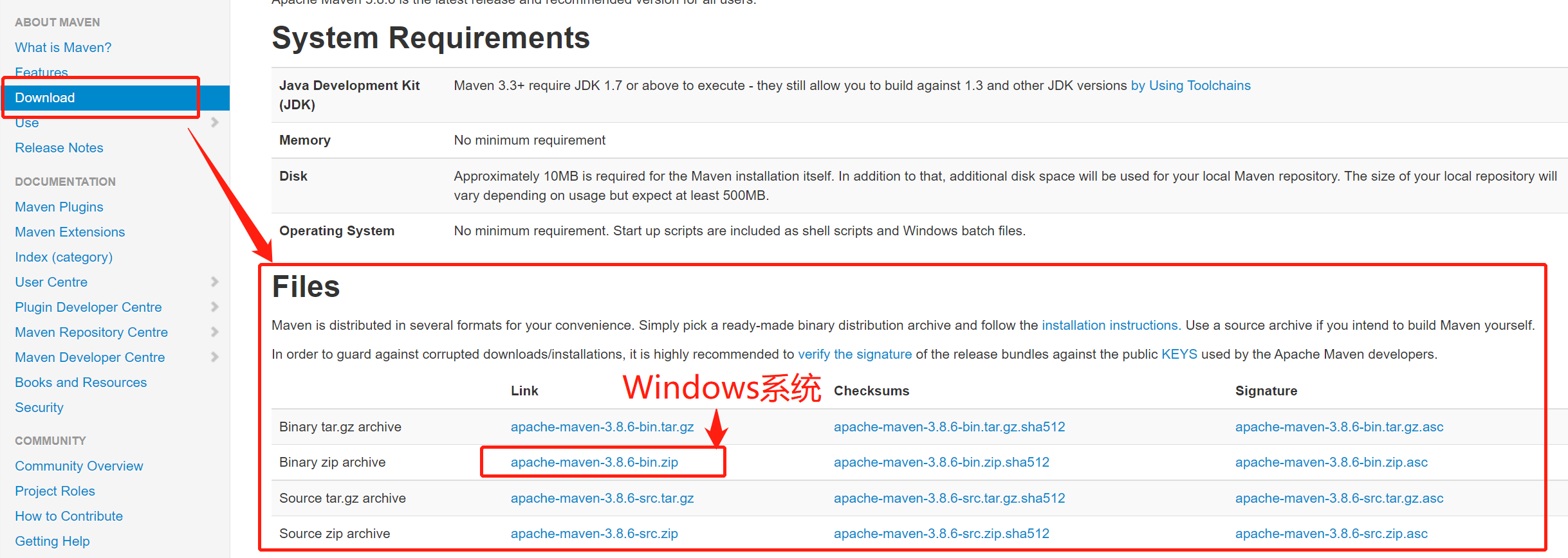
- 进入官网后,选择Download(下载)选项,安装最新版本的压缩包
…
- 将压缩包放置到自己喜欢的目录下,解压:
注意:文件夹目录要求 非中文、无空格。
👇
…
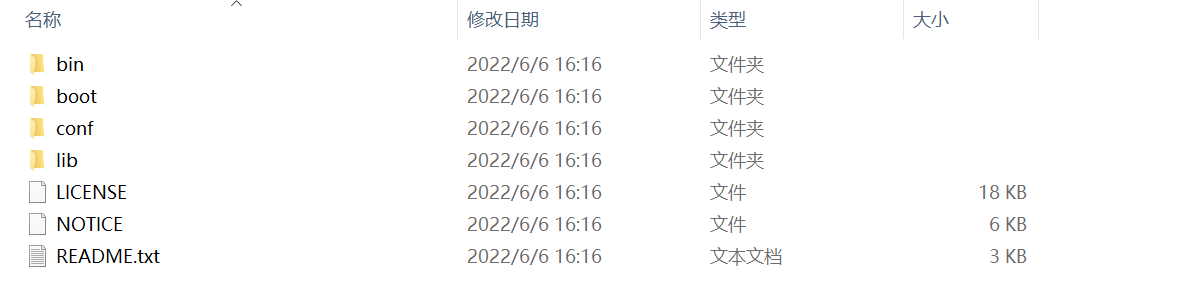
- 加压后,文件的内容目录如下:
其中,Maven核心的配置文件是conf目录下的settings.xml文件
二、设置本地仓库
⚪为什么
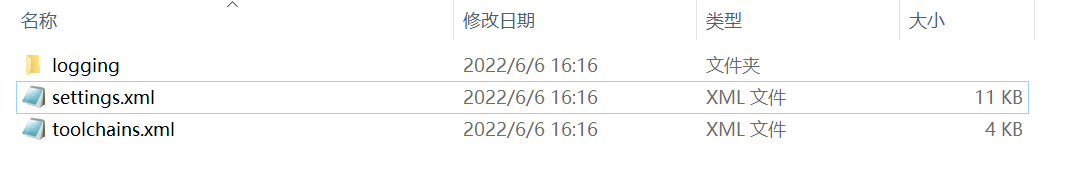
- Maven本地仓库是有默认值的,我们可以从
conf\settings.xml文件下找到关于默认本地仓库的描述:
<!-- localRepository
| The path to the local repository maven will use to store artifacts.
|
| Default: ${user.home}/.m2/repository
<localRepository>/path/to/local/repo</localRepository>
-->
我们从配置文件的这一段注释中,了解到默认仓库的存放目录是:${user.home}/.m2/repository,也就是系统的家目录中,家目录是存放在C盘(系统盘)当中的。
C盘 – 用户 – 用户名 – .m2 – repository
…
当我们累计使用的 jar包越来越多,Maven仓库的体积也将越来越大,内存过大会拖慢所在C盘的运行速度,影响系统性能。为了避免这样的结果,我们才需要设置本地仓库的路径,将Maven本地仓库放置在别的盘当中。
⚪怎么做
我们需要在配置文件中加入一行代码,来配置本地仓库:
<localRepository>d:\maven-repository</localRepository>
localRepository标签中的内容就填写我们自己配置的本地仓库路径,我们只需要手动创建一个空文件夹,将此文件夹的路径复制到标签中即可;
当然不创建也没问题,在标签中设置好路径后,当我们使用本地仓库时,Maven会帮我们创建的~
需要注意的是:本地仓库的目录也要求不包含中文、空格。
三、配置阿里云镜像仓库
⚪为什么
Maven在下载jar包时,默认会访问境外的中央仓库去进行下载,但是访问国外网站的速度较慢。为了提高访问速度从而提升效率,我们需要将Maven下载jar包时访问的仓库设置为国内阿里云提供的镜像仓库。
- 默认的中央仓库 - 访问国外网站 - 速度慢
- 阿里云镜像仓库 - 访问国内网站 - 速度快
⚪怎么做
依旧是打开Maven目录下,conf文件夹中的settings.xml文件,对settings.xml文件中<mirrors></mirrors>标签内的内容进行修改:
- 默认情况下的
mirrors标签内容:
<mirrors>
<!-- mirror
| Specifies a repository mirror site to use instead of a given repository. The repository that
| this mirror serves has an ID that matches the mirrorOf element of this mirror. IDs are used
| for inheritance and direct lookup purposes, and must be unique across the set of mirrors.
|
<mirror>
<id>mirrorId</id>
<mirrorOf>repositoryId</mirrorOf>
<name>Human Readable Name for this Mirror.</name>
<url>http://my.repository.com/repo/path</url>
</mirror>
-->
<mirror>
<id>maven-default-http-blocker</id>
<mirrorOf>external:http:*</mirrorOf>
<name>Pseudo repository to mirror external repositories initially using HTTP.</name>
<url>http://0.0.0.0/</url>
<blocked>true</blocked>
</mirror>
</mirrors>
——————————
- 设置完阿里云镜像仓库后的
mirrors标签内容:
改动:
- 将原本给定的例子注释掉
- 加入我们配置的镜像仓库内容(可直接复制)
<mirrors>
<!-- mirror
| Specifies a repository mirror site to use instead of a given repository. The repository that
| this mirror serves has an ID that matches the mirrorOf element of this mirror. IDs are used
| for inheritance and direct lookup purposes, and must be unique across the set of mirrors.
|
<mirror>
<id>mirrorId</id>
<mirrorOf>repositoryId</mirrorOf>
<name>Human Readable Name for this Mirror.</name>
<url>http://my.repository.com/repo/path</url>
</mirror>
-->
<!-- <mirror>
<id>maven-default-http-blocker</id>
<mirrorOf>external:http:*</mirrorOf>
<name>Pseudo repository to mirror external repositories initially using HTTP.</name>
<url>http://0.0.0.0/</url>
<blocked>true</blocked>
</mirror>
-->
<mirror>
<id>nexus-aliyun</id>
<mirrorOf>central</mirrorOf>
<name>Nexus aliyun</name>
<url>http://maven.aliyun.com/nexus/content/groups/public</url>
</mirror>
</mirrors>
四、配置Maven的JDK版本
⚪为什么
Maven工程默认使用JDK 1.5的版本,而实际上常用的是 JDK 1.8 及以上版本。
⚪怎样做
打开Maven目录下,conf文件夹中的settings.xml文件,对settings.xml文件中<profiles></profiles>标签内的内容进行修改:
- 默认情况下的
profiles标签内容:
全都是注释
<profiles>
<!-- profile
| Specifies a set of introductions to the build process, to be activated using one or more of the
| mechanisms described above. For inheritance purposes, and to activate profiles via <activatedProfiles/>
| or the command line, profiles have to have an ID that is unique.
|
| An encouraged best practice for profile identification is to use a consistent naming convention
| for profiles, such as 'env-dev', 'env-test', 'env-production', 'user-jdcasey', 'user-brett', etc.
| This will make it more intuitive to understand what the set of introduced profiles is attempting
| to accomplish, particularly when you only have a list of profile id's for debug.
|
| This profile example uses the JDK version to trigger activation, and provides a JDK-specific repo.
<profile>
<id>jdk-1.4</id>
<activation>
<jdk>1.4</jdk>
</activation>
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>jdk14</id>
<name>Repository for JDK 1.4 builds</name>
<url>http://www.myhost.com/maven/jdk14</url>
<layout>default</layout>
<snapshotPolicy>always</snapshotPolicy>
</repository>
</repositories>
</profile>
-->
<!--
| Here is another profile, activated by the system property 'target-env' with a value of 'dev',
| which provides a specific path to the Tomcat instance. To use this, your plugin configuration
| might hypothetically look like:
|
| ...
| <plugin>
| <groupId>org.myco.myplugins</groupId>
| <artifactId>myplugin</artifactId>
|
| <configuration>
| <tomcatLocation>${tomcatPath}</tomcatLocation>
| </configuration>
| </plugin>
| ...
|
| NOTE: If you just wanted to inject this configuration whenever someone set 'target-env' to
| anything, you could just leave off the <value/> inside the activation-property.
|
<profile>
<id>env-dev</id>
<activation>
<property>
<name>target-env</name>
<value>dev</value>
</property>
</activation>
<properties>
<tomcatPath>/path/to/tomcat/instance</tomcatPath>
</properties>
</profile>
-->
</profiles>
————————————
- 配置后的
profiles标签内容:
改动:
- 添加了设置JDK版本的相关配置(配置在下述代码尾部,可直接复制)
<profiles>
<!-- profile
| Specifies a set of introductions to the build process, to be activated using one or more of the
| mechanisms described above. For inheritance purposes, and to activate profiles via <activatedProfiles/>
| or the command line, profiles have to have an ID that is unique.
|
| An encouraged best practice for profile identification is to use a consistent naming convention
| for profiles, such as 'env-dev', 'env-test', 'env-production', 'user-jdcasey', 'user-brett', etc.
| This will make it more intuitive to understand what the set of introduced profiles is attempting
| to accomplish, particularly when you only have a list of profile id's for debug.
|
| This profile example uses the JDK version to trigger activation, and provides a JDK-specific repo.
<profile>
<id>jdk-1.4</id>
<activation>
<jdk>1.4</jdk>
</activation>
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>jdk14</id>
<name>Repository for JDK 1.4 builds</name>
<url>http://www.myhost.com/maven/jdk14</url>
<layout>default</layout>
<snapshotPolicy>always</snapshotPolicy>
</repository>
</repositories>
</profile>
-->
<!--
| Here is another profile, activated by the system property 'target-env' with a value of 'dev',
| which provides a specific path to the Tomcat instance. To use this, your plugin configuration
| might hypothetically look like:
|
| ...
| <plugin>
| <groupId>org.myco.myplugins</groupId>
| <artifactId>myplugin</artifactId>
|
| <configuration>
| <tomcatLocation>${tomcatPath}</tomcatLocation>
| </configuration>
| </plugin>
| ...
|
| NOTE: If you just wanted to inject this configuration whenever someone set 'target-env' to
| anything, you could just leave off the <value/> inside the activation-property.
|
<profile>
<id>env-dev</id>
<activation>
<property>
<name>target-env</name>
<value>dev</value>
</property>
</activation>
<properties>
<tomcatPath>/path/to/tomcat/instance</tomcatPath>
</properties>
</profile>
-->
<profile>
<id>jdk-1.8</id>
<activation>
<activeByDefault>true</activeByDefault>
<jdk>1.8</jdk>
</activation>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target>
<maven.compiler.compilerVersion>1.8</maven.compiler.compilerVersion>
</properties>
</profile>
</profiles>
五、配置环境变量
——————————————
⚪配置Java环境变量
Maven 是一个用 Java 语言开发的程序,它必须基于 JDK 来运行,学习过Java的同学应该都配置过Java环境变量,可以直接跳过这一步。
如果还未下载JDK,配置Java环境变量,可以参考这篇文章:JDK安装+配置环境变量
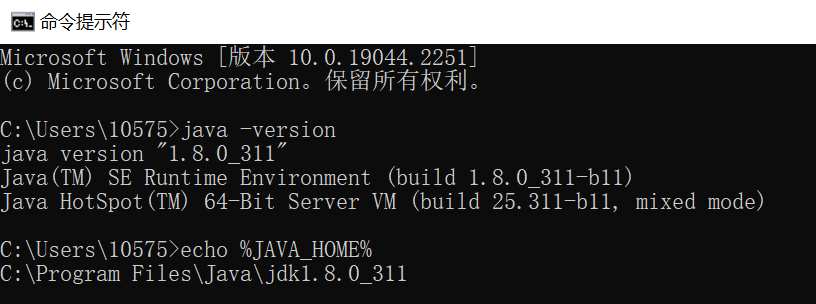
检查:
Win+R 输入 cmd 进入命令指示符界面,使用以下指令检查:
java -version
echo %JAVA_HOME%
⚪配置Maven环境变量
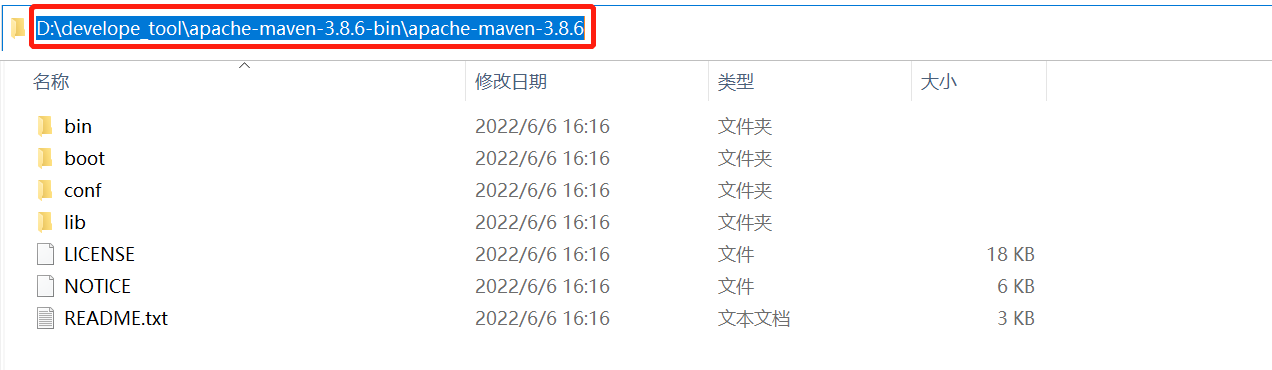
- 打开之间下载解压好的Maven文件目录,复制路径进行备用:
👇
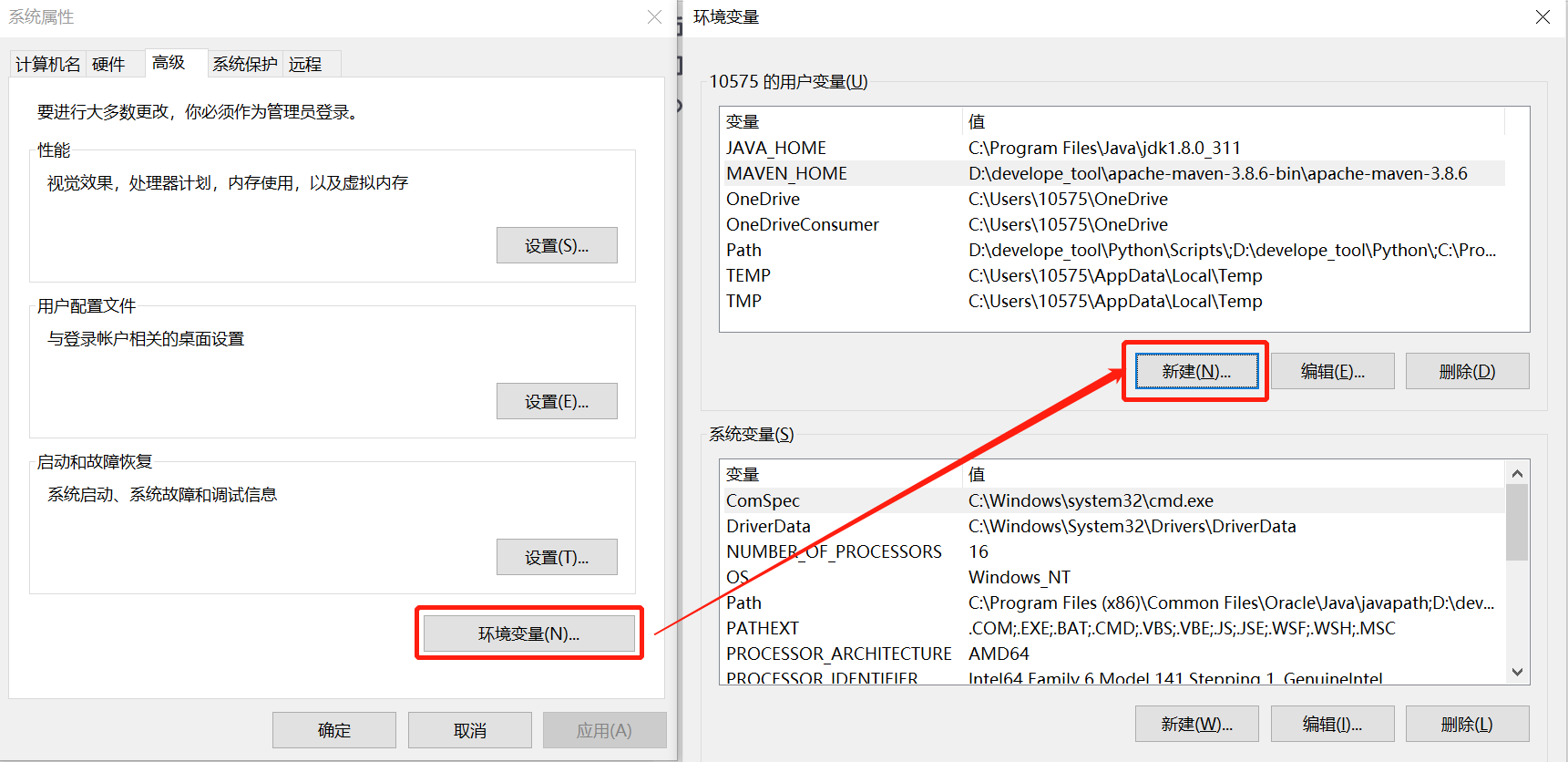
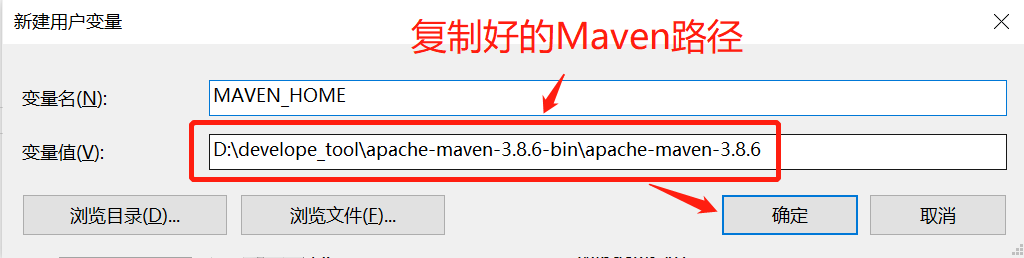
- 打开计算机高级系统设置,选择环境变量,新建MAVEN_HOME:
AND
👇
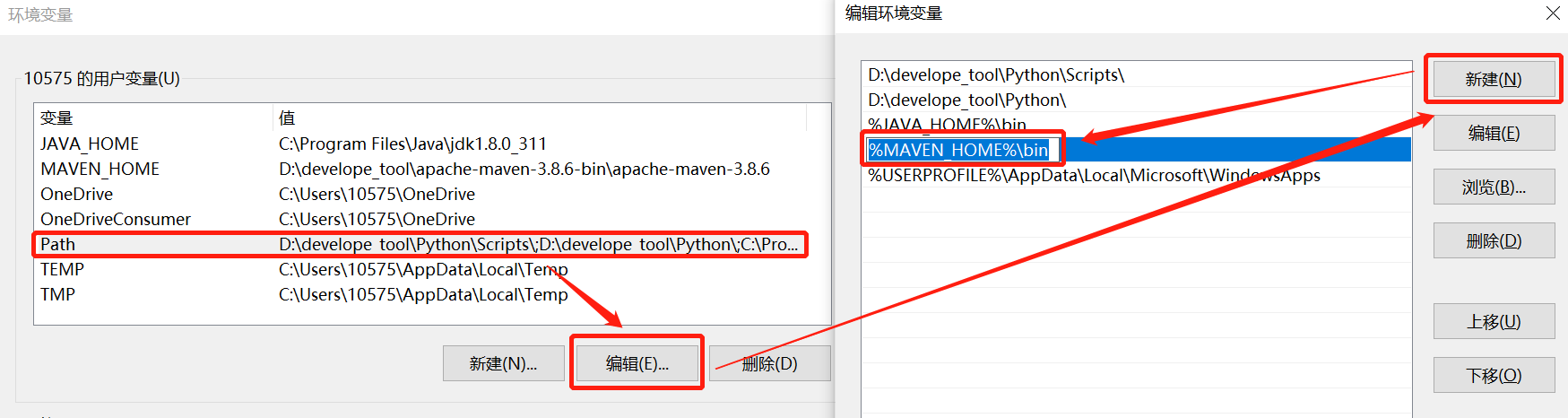
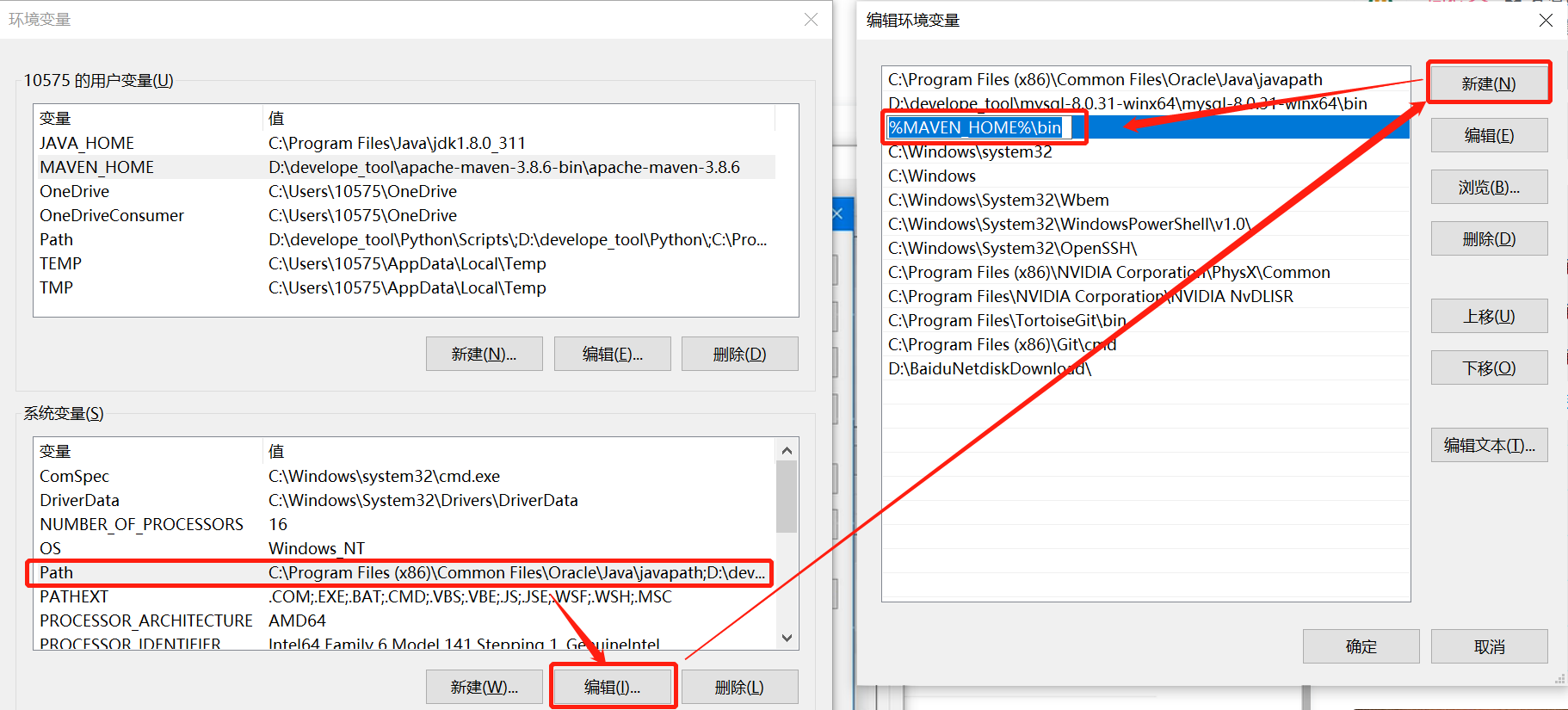
- 系统变量选择Path进行编辑,在Path环境当中增加一个MAVEN_HOME的bin目录:
%MAVEN_HOME%\bin
👇
检查:
Win+R 输入 cmd 进入命令指示符界面,使用以下指令检查:
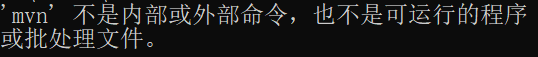
mvn -v
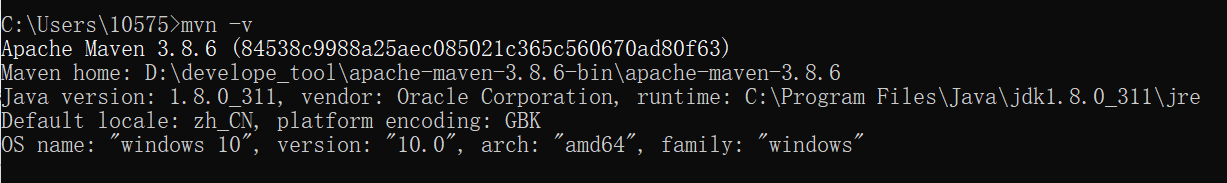
————
如果出现以下提示:
说明没有读取到环境变量
👇
- 在用户变量的Path环境变量也添加MAVEN_HOME,之后再检查一次:
%MAVEN_HOME%\bin
到了这里,我们就成功从0完成了Maven的下载,安装以及配置啦~
恭喜!






 本文详细介绍了Maven的下载、安装和配置步骤,包括设置本地仓库以避免C盘占用过大,配置阿里云镜像仓库以加速下载,调整Maven的JDK版本至1.8,以及正确配置Maven和Java的环境变量,确保Maven的顺利运行。
本文详细介绍了Maven的下载、安装和配置步骤,包括设置本地仓库以避免C盘占用过大,配置阿里云镜像仓库以加速下载,调整Maven的JDK版本至1.8,以及正确配置Maven和Java的环境变量,确保Maven的顺利运行。





















 2750
2750












