基础View控件
View类
View类是所有界面控件类的超类;
代表屏幕上一块空白的矩形区域,用于绘画和事件处理;
在View类中定义了控件的一些共同属性(例如透明度、边距、旋转、缩放等)。
ViewGroup类
ViewGroup类是View类的一个抽象子类,是一种特殊的View;
是所有布局类和容器组件的超类,ViewGroup中可以包含View和ViewGroup对象;
ViewGroup并没有定义其包含的View布局,由其子类中定义它所包含的View的排列方式。
View和ViewGroup关系
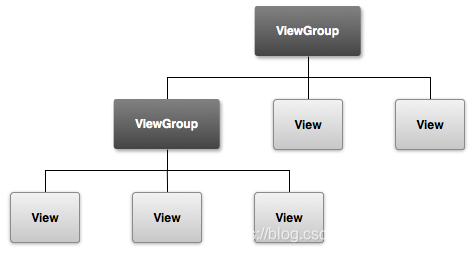
View与ViewGroup的关系类似于文件与文件夹的关系;
View与ViewGroup组合使用,形成一种界面布局的层次结构。
控制界面显示的两种方法
通过XML布局文件设置控件属性进行控制。
通过Java代码调用控件类相应的方法进行控制。
两种方式的优缺点
-完全使用Java代码来控制用户界面不仅繁琐而且界面和逻辑代码相混合,不利于软件设计人员的分工合作。
-完全使用XML布局文件虽然方便、便捷,但灵活性不好,不能动态改变属性值。
解决方案
混合使用这两种方式来控制界面,一般来说,习惯将一些变化小的、比较固定的、初始化的属性放在XML文件中管理,而对于那些需要动态变化的属性则交给Java代码控制。
文本显示框(TextView)
TextView类直接继承于View类,用于在界面上显示文本信息,与Word中“字体”的功能类似,可以设置显示文本的颜色、大小、字体、风格等信息。
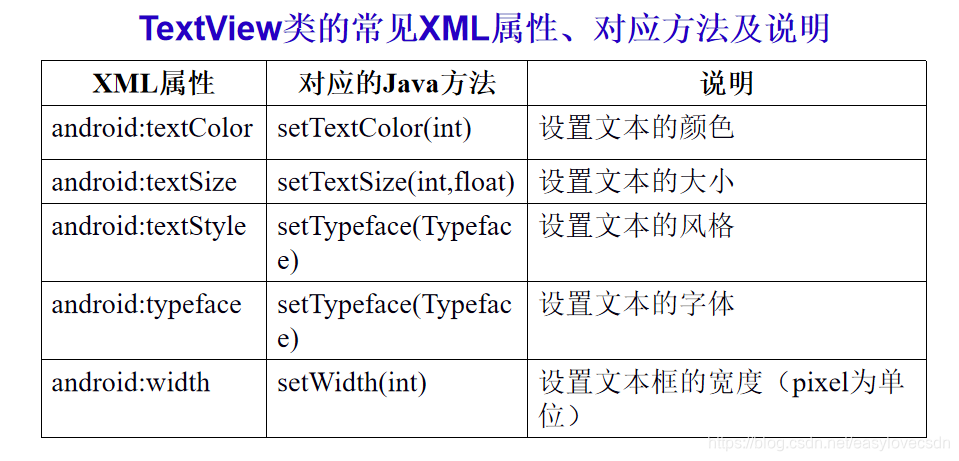
除了上述几乎所有文本显示控件都拥有的属性外,Android中的TextView还提供一些特殊功能,例如:自动识别文本中的各种链接、显示部分HTML标签定义的格式。

当匹配时,相应部分会以超链接形式显示,单击超链接,会自动运行相关程序。
在Android中经常需要设置尺寸,包括组件的宽度和高度、边距、文本大小等,这些尺寸的单位各不相同,在Android提供了多种尺寸单位,常见有:

为了适应不同分辨率、不同的屏幕密度的设备,推荐使用dip,文字大小使用sp。
显示部分HTML标签定义的格式,需要Android中Html类的辅助,该类提供了一个fromHtml()方法,该方法可以识别字符串中的HTML标签,返回值为Spanned类型,该类实现了CharSequence接口,可以作为参数传入setText()方法。
首先为该文本框添加一个id属性,然后在onCreate()方法中,通过findViewById(R.id.***),获取该文本框,最后设置通过setText()方法来设置显示的内容。
TextView tv=((TextView)findViewById(R.id.myText);
tv.setText(Html.fromHtml (“欢迎参加<font color=‘blue’>手机软件设计赛</font>”));
可以把TextView看成是一个文本编辑器的基类,但其本身不提供编辑功能,TextView有一个子类EditText,该控件允许用户输入,并且可设置输入的类型。

按钮(Button)
按钮是人机交互中一个关键的控件,主要用于发送请求、提交数据等,例如登录、注册等。 Android中Button是TextView的子类,也可以显示文本信息,相对于普通的TextView而言,Button的特殊之处在于可以接收事件,并对相应事件进行处理。例如单击事件、双击事件、触摸事件等。具体的事件处理将在后面进行讲解。
注意:Button是TextView的子类,是一个特殊的文本。
应用举例
在activity_main.xml中编写如下代码
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:gravity="center_horizontal"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_title"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="欢迎参加手机软件设计赛"
android:textColor="#0000ff"
android:textSize="24sp"
/>
<EditText
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="请在此输入用户名"
/>
<EditText
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="请在此输入用户名"
android:inputType="textPassword"
/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="登陆"
/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="注册"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:autoLink="all"
android:text="如有疑问请联系我们\n联系电话:+8618406587454\nE-mail:2511384642@qq.com\n网址:https://me.nuc.ink/"
android:textColor="#0000ff"
android:textSize="20sp" />
</LinearLayout>
同时在ActivityMain.java中编写
package com.example.login;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.text.Html;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private TextView tv_title = null;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
tv_title = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.tv_title);
tv_title.setText(Html.fromHtml("欢迎参加<font color=red>手机软件设计赛</font>"));
}
}
即可产生如下界面
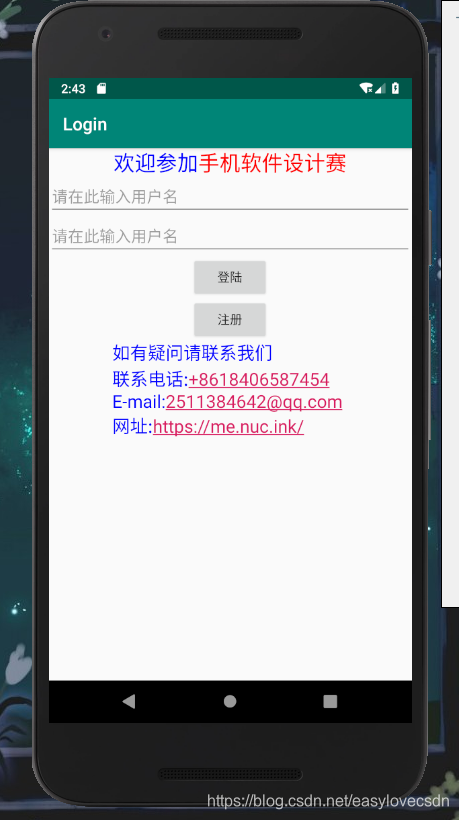




 本文详细介绍了Android中基础View控件的概念,包括View和ViewGroup类的区别,以及如何通过XML布局文件和Java代码控制界面显示。深入解析了文本显示框(TextView)、按钮(Button)的功能与使用方法,展示了如何设置文本颜色、大小、链接识别,以及按钮的事件处理。
本文详细介绍了Android中基础View控件的概念,包括View和ViewGroup类的区别,以及如何通过XML布局文件和Java代码控制界面显示。深入解析了文本显示框(TextView)、按钮(Button)的功能与使用方法,展示了如何设置文本颜色、大小、链接识别,以及按钮的事件处理。

















 3415
3415

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










