关于model.train()和model.eval():
https://discuss.pytorch.org/t/model-train-and-model-eval-vs-model-and-model-eval/5744/2
- Variable 中的volatile: 在0.4.0版本中已经舍弃
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/49837638/what-is-volatile-variable-in-pytorch
max, argmax等函数中的keepdim参数:
从以下的例子中很容易看出keepdim=True保存data的dim维度的维数,
比如a在第1维(行数)为4,即[4, 4], 而在 keepdim=True后的输出为[4, 1].
a = torch.randn(4, 4)
torch.argmax(a, dim=1)
'''out:
tensor([2, 2, 1, 0])
'''
torch.argmax(a, dim=1, keepdim=True)
'''out:
tensor([[2],
[2],
[1],
[0]])
'''
a.max(dim=1, keepdim=True)
'''out
(tensor([[2.6665],
[1.7574],
[0.4446],
[1.9416]]), tensor([[2],
[2],
[1],
[0]]))
'''
- view_as 和view: 改变数据的size形状的
data1.view_as(data) 等效于data1.view(datd.size())
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/qq_37385726/article/details/81738518
cpu()
实现将GPU上的tensor转化为cpu上从而进行一些只能在cpu上进行的运算。
https://discuss.pytorch.org/t/what-is-the-cpu-in-pytorch/15007
hook pytorch
提供一种手段可以接触中间过程的梯度
class LayerActivations():
features=None
def __init__(self,model,layer_num):
self.hook = model[layer_num].register_forward_hook(self.hook_fn)
def hook_fn(self,module,input,output):
self.features = output.cpu().data.numpy()
def remove(self):
self.hook.remove()
conv_out = LayerActivations(vgg.features,5)
o = vgg(Variable(img.cuda()))
# remove handle
conv_out.remove()
act = conv_out.features
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(20,50))
fig.subplots_adjust(left=0,right=1,bottom=0,top=0.8,hspace=0,wspace=0.2)
for i in range(30):
ax = fig.add_subplot(12,5,i+1,xticks=[],yticks=[])
ax.imshow(act[0][i])
在这里插入图片描述
以上代码解析:
register_forward_hook函数能够输出中间层的梯度,
在forward之前完成register_forward_hook(hook)的注册
将梯度存在self.features中
__init__函数有两个参数:
- model
- layer_num
这两个参数将被outputs解析为参数,在__init__中,在该层上调用register_forward_hook函数,并传递给一个函数参数完成hook注册。
在图像在层之间传递时(在做前向传播时),Pytorch将调用传递给register_forward_hook的函数, 该方法返回一个handle句柄,可以解析掉的哦
hook函数有三个参数(model, input, output)
- model: 可以使用model本身
- input: 在层之间传递的数据
- output: 转换过的输入或激活, 或者是更新的梯度值
获得网络层的weight
通过state_dict 给函数返回一个字典,键是网络层,值是该层的weights.
以下是可视化vgg16的第一层的权重:
vgg.state_dict().keys()
cnn_weights = vgg.state_dict()['features.0.weight'].cpu()
'''
odict_keys(['features.0.weight', 'features.0.bias', 'features.2.weight',
'features.2.bias', 'features.5.weight', 'features.5.bias',
'features.7.weight', 'features.7.bias', 'features.10.weight',
'features.10.bias', 'features.12.weight', 'features.12.bias',
'features.14.weight', 'features.14.bias', 'features.17.weight',
'features.17.bias', 'features.19.weight', 'features.19.bias',
'features.21.weight', 'features.21.bias', 'features.24.weight',
'features.24.bias', 'features.26.weight', 'features.26.bias',
'features.28.weight', 'features.28.bias', 'classifier.0.weight',
'classifier.0.bias', 'classifier.3.weight', 'classifier.3.bias',
'classifier.6.weight', 'classifier.6.bias'])
'''
cnn_weight.shape
# [64, 3, 3, 3]
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(30,30))
fig.subplots_adjust(left=0,right=1,bottom=0,top=0.8,hspace=0,wspace=0.2)
for i in range(30):
ax = fig.add_subplot(12,6,i+1,xticks=[],yticks=[])
ax.imshow(cnn_weights[i])
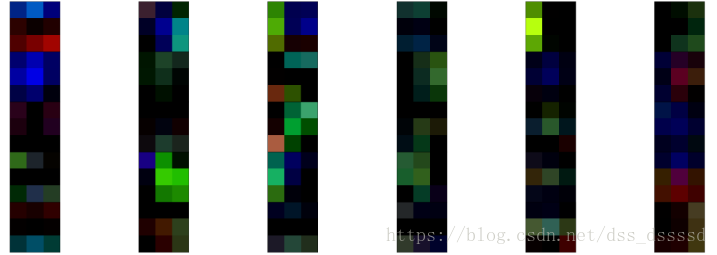





 本文介绍了PyTorch中model.train()和model.eval()的用途,讨论了Variable的volatile属性的弃用,解释了view和view_as在调整数据尺寸的作用,详细阐述了如何利用cpu()将张量转移到CPU以及运用hook来获取网络层的梯度。此外,还展示了如何获取并可视化网络层的权重,特别是VGG16模型第一层的权重。
本文介绍了PyTorch中model.train()和model.eval()的用途,讨论了Variable的volatile属性的弃用,解释了view和view_as在调整数据尺寸的作用,详细阐述了如何利用cpu()将张量转移到CPU以及运用hook来获取网络层的梯度。此外,还展示了如何获取并可视化网络层的权重,特别是VGG16模型第一层的权重。

















 8万+
8万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








