文章目录
一、Java ACM 基础
转到
JAVA ACM 基础
ACM中java的使用(各种比赛中)
Scanner是一个扫描器,它扫描数据都是去内存中一块缓冲区中进行扫描并读入数据的,而我们在控制台中输入的数据也都是被先存入缓冲区中等待扫描器的扫描读取。这个扫描器在扫描过程中判断停止的依据就是“结束符”,空格,回车,tab 都算做是结束符
而坑点在于 next 系列的,也就是下面这些函数:
- next
- nextInt
- nextDouble
- nextFloat
这些函数与 nextLine 连用都会有坑:
坑点就是 next 系列的函数返回了数据后,会把回车符(\r)留在缓冲区,因此我们下一次使用 nextLine 的时候会碰到读取空字符串的情况
解决方案:
- 输入都用 nextLine ,做格式转换
- 输入 next 系列函数调用后,中间调用一次 nextLine 调用去掉了回车符后,再调用一次 nextLine 调用真正输入我们的数据
读取有限个字符串
都使用 nextLine:
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.lang.System;
import java.lang.String;
import java.lang.Integer;
class ScannerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int num = Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
String[] str = new String[num];
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
str[i] = sc.nextLine();
}
sc.close();
}
}
使用 next、nextLine 去临时回车符、nextLine 读入真正数据:
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.lang.System;
import java.lang.String;
class ScannerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int num = sc.nextInt();
String[] str = new String[num];
sc.nextLine();
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
str[i] = sc.nextLine();
}
sc.close();
}
}
这两种方式都能解决可读入带空格的字符串,并且不会读异常空串。
易错点
- nextInt()或者next()读取完毕并回车之后其后紧跟nextLine(),就会导致nextLine()读取到空值,因为nextLine()自动读取到’\n’,意味着遇到结束符;
- 有时候将字符串转为整数时,代码没问题却提示数组越界,往往是因为字符串代表的整数超过了int的最值,需要改用long。
Scanner 性能
Scanner 是真的太慢了,一直用的是 BufferReader 写的,但今天一尝试就超时,于是改回用 BufferReader 就过了
归根结底是因为 Scanner 对输入字符实现了多样性的操作,BufferReader 就比较单一,读入的是字节流转换成字符串
实际测试,BufferReader 至少比 Scanner 输入快两倍
用 Scanner 是为了循环输入的功能,也就是 hasNext() 方法的功能
今天忽然想到了可以用死循环来代替,所以,还是继续使用BufferReader 吧!少年!Scanner 性能劝退
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.lang.System;
import java.lang.String;
import java.lang.Integer;
class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader bf = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int num = Integer.parseInt(bf.readLine());
String[] str = new String[num];
int i = 0;
while (true) {
if (i >= num) {
bf.close();
break;
} else {
str[i++] = bf.readLine();
System.out.println(str[i-1]); // 循环输入
}
}
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException{
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String str;
while((str=in.readLine())!=null){
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(str);
sb.reverse();
System.out.println(sb.toString());
}
}
}
读取连续整数
输入:包括两个正整数a,b(1 <= a, b <= 10^9),输入数据包括多组。
输出:a+b的结果。
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.lang.System;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
while(in.hasNext()){
int a=in.nextInt();
int b=in.nextInt();
System.out.println(a+b);
}
} }
读取有限整数
输入:第一行包括一个数据组数t(1 <= t <= 100),接下来每行包括两个正整数a,b(1 <= a, b <= 10^9)
输出:a+b的结果
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.lang.System;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
int n=in.nextInt();
while(n-->0){
int a=in.nextInt();
int b=in.nextInt();
System.out.println(a+b);
}
}
}
每行读取空格隔开的整数
输入:输入数据有多组, 每行表示一组输入数据。每行不定有n个整数,空格隔开。(1 <= n <= 100)。
输出:每组数据输出求和的结果
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.lang.System;
import java.lang.String;
import java.lang.Integer;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
while(in.hasNext()){
String[] temp=in.nextLine().split(" ");
int sum=0;
for(String s:temp)
sum+=Integer.valueOf(s);
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
}
二、Collection


单列集合框架结构
Collection接口:单列集合,用来存储一个一个的对象
- List接口:存储有序的、可重复的数据。 -->“动态”数组
- ArrayList、LinkedList、Vector
- Set接口:存储无序的、不可重复的数据 -->高中讲的“集合”
- HashSet、LinkedHashSet、TreeSet
Collection接口常用方法:
add(Object obj), addAll(Collection coll), size(), isEmpty(), clear(),
contains(Object obj), containsAll(Collection coll), remove(Object obj),
removeAll(Collection coll), retainsAll(Collection coll), equals(Object obj);
hasCode(), toArray(), iterator();
Collection集合与数组间的转换
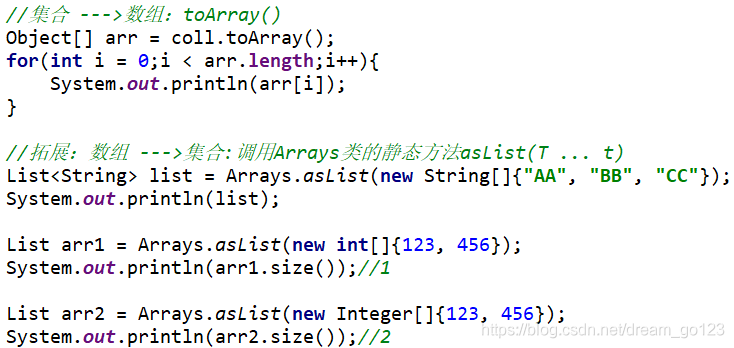
遍历Collection的两种方式
- ① 使用迭代器Iterator (java.utils包下定义的迭代器接口:Iterator )
- ② foreach循环(或增强for循环)
import java.util.*;
public class CollectionMapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection coll = new ArrayList();
coll.add(123);
coll.add("asd");
coll.add(false);
// Iterator 迭代器
Iterator iterator = coll.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
// for each 增强循环
for (Object obj : coll) {
System.out.println(obj);
}
}
}
List
常用方法
- 增:add(Object obj)
- 删:remove(int index) / remove(Object obj)
- 改:set(int index, Object ele)
- 查:get(int index)
- 插:add(int index, Object ele)
- 长度:size()
- 遍历:
- ① Iterator迭代器方式
- ② 增强for循环
- ③ 普通的循环
List接口:存储有序的、可重复的数据。 -->“动态”数组
- 常用实现类:ArrayList、LinkedList、Vector
import java.util.*;
public class CollectionMapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> l1 = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<String> l2 = new ArrayList<>();
List<Character> l3 = new LinkedList<>();
LinkedList<Object> l4 = new LinkedList<>();
List<Object> l5 = new Vector<>();
List<Object> l6 = new Stack<>();
Vector<Object> l7 = new Stack<>();
}
}
java8List.sort()排序功能
//按照List中对象的id属性升序
list.sort(Comparator.comparing(Stu::getId)) //Stu:指待排序的类;getId: 待排序属性的get方法
//按照List中对象的id属性降序
list.sort(Comparator.comparing(Stu::getId).reversed());
//多条件升序
list.sort(Comparator.comparing(Stu::getId).thenComparing(Stu::getSid));
//id升序,sid降序
list.sort(Comparator.comparing(Stu::getId).reversed().thenComparing(Stu::getSid));
//集合升序排序
Collections.sort(student, new Comparator(){
public int compare(StudentVo p1, StudentVo p2) {
return Integer.parseInt(p1.getStudentCode()) - Integer.parseInt(p2.getStudentCode());
}
});
//key值重复的map
MultiValueMap<Integer, String> timeMap = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
详解:
在java中对LIst集合的两种排序方法(即sort的使用方法)
java的list的几种排序写法整理(sort的用法)
List集合的常见实现类
1、ArrayList集合: List接口大小可变数组的实现。(查询快,增删慢。)此实现不是同步的(多线程问题)。
2、LinkedList集合: List接口的链表实现。此实现不是同步的。
java.util.LinkedList集合 implements List接口
特点:
①、底层是一个链表结构:查询慢,增删快。
②、里边包含了大量操作首尾元素的方法。
注意:使用LinkedList集合特有的方法,不能使用多态。
—public void addFirst(E e):将指定元素插入此列表的开头。
—public void addLast(E e):将指定元素添加到此列表的结尾。
—public E getFirst():返回此列表的第一个元素。
—public E getLast():返回此列表的最后一个元素。
—public E removeFirst():移除并返回此列表的第一个元素。
—public E removeLast():移除并返回此列表的最后一个元素。
—public E pop():从此列表所表示的堆栈处弹出一个元素。等效于removeFirst()。
—public void push(E e):将元素推入此列表所表示的堆栈。等效于addFirst(E e)。
—public boolean isEmpty():如果列表不包含元素,则返回true。
—clear(); //清空集合中的元素,再获取集合中的元素会抛出NoSuchElementException。
3、Vector集合: 可以实现可增长的对象数组。此实现是同步的。JDK1.0最早期的集合,底层也是数组,但是是单线程的,速度比较慢。
Java双端队列Deque实现 堆栈

队列的实现
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
Queue<Node> queue1 = new LinkedList<>();
// add(), offer(); remove(), poll(); element(), peek()
LinkedList<Node> queue1 = new LinkedList<>();
// addLast(), offerLast(); removeFirst(), pollFirst(); element(), peekFirst()
offer,add 区别: (???看源码发现是一样的)
一些队列有大小限制,因此如果想在一个满的队列中加入一个新项,多出的项就会被拒绝。这时新的 offer 方法就可以起作用了。它不是对调用 add() 方法抛出一个 unchecked 异常,而只是得到由 offer() 返回的 false。
poll,remove 区别:
remove() 和 poll() 方法都是从队列中删除第一个元素。remove() 的行为与 Collection 接口的版本相似, 但是新的 poll() 方法在用空集合调用时不是抛出异常,只是返回 null。因此新的方法更适合容易出现异常条件的情况。
peek,element区别:
element() 和 peek() 用于在队列的头部查询元素。与 remove() 方法类似,在队列为空时, element() 抛出一个异常,而 peek() 返回 null。
栈的实现
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Deque;
import java.util.Stack;
Deque deque = new LinkedList()
Stack<Integer> s = new Stack<>();
优先级队列
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
Queue<Integer> A, B;
A = new PriorityQueue<>(); // 小顶堆
B = new PriorityQueue<>((x, y) -> (y - x)); // 大顶堆
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
PriorityQueue<Integer> maxHeap = new PriorityQueue<Integer>(new MaxHeapComparator());
PriorityQueue<Integer> minHeap = new PriorityQueue<Integer>(new MinHeapComparator());
public static class MaxHeapComparator implements Comparator<Integer> {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
if (o2 > o1) {
return 1;
} else {
return -1;
}
}
}
public static class MinHeapComparator implements Comparator<Integer> {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
if (o2 < o1) {
return 1;
} else {
return -1;
}
}
}
class MedianFinde {
PriorityQueue<Integer> min_priorityQueue;
PriorityQueue<Integer> max_priorityQueue;
/**
* initialize your data structure here.
*/
public MedianFinder() {
max_priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o2 - o1;
}
});
min_priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o1 - o2;
}
});
}
}
Set
常用方法
Set接口中没额外定义新的方法,使用的都是Collection中声明过的方法。
Set接口:无序的、不可重复的元素 -->高中讲的“集合”
- 常用实现类:HashSet、LinkedHashSet、TreeSet
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
import java.util.TreeHashSet;
Set<String> set1 = new HashSet<String>();
Set<String> set2 = new LinkedHashSet<String>();
Set<String> set3 = new TreeSet<String>();
三、Map

双列集合框架:Map
常用实现类结构:Map:双列数据,存储key-value对的数据 —类似于高中的函数:y = f(x)
- HashMap:作为Map的主要实现类;线程不安全的,效率高;存储null的key和value
- LinkedHashMap:保证在遍历map元素时,可以照添加的顺序实现遍历。原因:在原的HashMap底层结构基础上,添加了一对指针,指向前一个和后一个元素。对于频繁的遍历操作,此类执行效率高于HashMap。
- TreeMap:保证照添加的key-value对进行排序,实现排序遍历。此时考虑key的自然排序或定制排序。底层使用红黑树
- Hashtable:作为古老的实现类;线程安全的,效率低;不能存储null的key和value
Map中的key:无序的、不可重复的,使用Set存储所的key —> key所在的类要重写equals()和hashCode() (以HashMap为例)
Map中的value:无序的、可重复的,使用Collection存储所的value —value所在的类要重写equals()
一个键值对:key-value构成了一个Entry对象。
Map中的entry:无序的、不可重复的,使用Set存储所的entry

常用方法
- 添加:put(Object key,Object value)
- 删除:remove(Object key)
- 修改:put(Object key,Object value)
- 查询:get(Object key)
- 长度:size()
- 遍历:keySet() / values() / entrySet() —— iterator()
其他方法
- void clear()
- boolean containsKey(Object key)
- boolean containsValue(Object value)
- boolean isEmpty()
四、Collections 工具类
Collections
作用:操作Collection和Map的工具类
常用方法
- reverse(List):反转 List 中元素的顺序
- shuffle(List):对 List 集合元素进行随机排序
- sort(List):根据元素的自然顺序对指定 List 集合元素升序排序
- sort(List,Comparator):根据指定的 Comparator 产生的顺序对 List 集合元素进行排序
- swap(List,int, int):将指定 list 集合中的 i 处元素和 j 处元素进行交换
- Object max(Collection):根据元素的自然顺序,返回给定集合中的最大元素
- Object max(Collection,Comparator):根据 Comparator 指定的顺序,返回给定集合中的最大元素
- Object min(Collection)
- Object min(Collection,Comparator)
- int frequency(Collection,Object):返回指定集合中指定元素的出现次数
- void copy(List dest,List src):将src中的内容复制到dest中
- boolean replaceAll(List list,Object oldVal,Object newVal):使用新值替换 List 对象的所旧值
- 说明:ArrayList和HashMap都是线程不安全的,如果程序要求线程安全,我们可以将ArrayList、HashMap转换为线程的。使用synchronizedList(List list) 和 synchronizedMap(Map map)
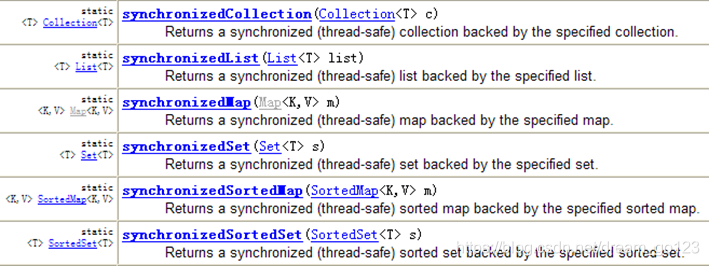
Arrays
Java中的Arrays类使用详解
Java中Arrays类的常用方法
五、基本类型和String
String
常用方法
- char[] toCharArray():
- int length():返回字符串的长度: return value.length
- char charAt(int index): 返回某索引处的字符return value[index]
- boolean isEmpty():判断是否是空字符串:return value.length == 0
- String toLowerCase():使用默认语言环境,将 String 中的所字符转换为小写
- String toUpperCase():使用默认语言环境,将 String 中的所字符转换为大写
- String trim():返回字符串的副本,忽略前导空白和尾部空白
- boolean equals(Object obj):比较字符串的内容是否相同
- boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String anotherString):与equals方法类似,忽略大小写
- String concat(String str):将指定字符串连接到此字符串的结尾。 等价于用“+”
- int compareTo(String anotherString):比较两个字符串的大小
- String substring(int beginIndex):返回一个新的字符串,它是此字符串的从beginIndex开始截取到最后的一个子字符串。
- String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex) :返回一个新字符串,它是此字符串从beginIndex开始截取到endIndex(不包含)的一个子字符串。
- boolean endsWith(String suffix):测试此字符串是否以指定的后缀结束
- boolean startsWith(String prefix):测试此字符串是否以指定的前缀开始
- boolean startsWith(String prefix, int toffset):测试此字符串从指定索引开始的子字符串是否以指定前缀开始
- boolean contains(CharSequence s):当且仅当此字符串包含指定的 char 值序列时,返回 true
- int indexOf(String str):返回指定子字符串在此字符串中第一次出现处的索引
- int indexOf(String str, int fromIndex):返回指定子字符串在此字符串中第一次出现处的索引,从指定的索引开始
- int lastIndexOf(String str):返回指定子字符串在此字符串中最右边出现处的索引
- int lastIndexOf(String str, int fromIndex):返回指定子字符串在此字符串中最后一次出现处的索引,从指定的索引开始反向搜索
注:indexOf和lastIndexOf方法如果未找到都是返回-1 - 替换
*String replace(char oldChar, char newChar):返回一个新的字符串,它是通过用 newChar 替换此字符串中出现的所 oldChar 得到的。
String replace(CharSequence target, CharSequence replacement):使用指定的字面值替换序列替换此字符串所匹配字面值目标序列的子字符串。
String replaceAll(String regex, String replacement):使用给定的 replacement 替换此字符串所匹配给定的正则表达式的子字符串。
String replaceFirst(String regex, String replacement):使用给定的 replacement 替换此字符串匹配给定的正则表达式的第一个子字符串。 - 匹配
boolean matches(String regex):告知此字符串是否匹配给定的正则表达式。
切片
String[] split(String regex):根据给定正则表达式的匹配拆分此字符串。
String[] split(String regex, int limit):根据匹配给定的正则表达式来拆分此字符串,最多不超过limit个,如果超过了,剩下的全部都放到最后一个元素中。
String与其它结构的转换
与基本数据类型、包装类之间的转换:
String --> 基本数据类型、包装类:调用包装类的静态方法:parseXxx(str)
基本数据类型、包装类 --> String:调用String重载的valueOf(xxx)
与字符数组之间的转换
String --> char[]:调用String的toCharArray()
char[] --> String:调用String的构造器
与字节数组之间的转换
编码:String --> byte[]:调用String的getBytes()
解码:byte[] --> String:调用String的构造器
编码:字符串 -->字节 (看得懂 —>看不懂的二进制数据)
解码:编码的逆过程,字节 --> 字符串 (看不懂的二进制数据 —> 看得懂
说明:解码时,要求解码使用的字符集必须与编码时使用的字符集一致,否则会出现乱码。
与StringBuffer、StringBuilder之间的转换
String -->StringBuffer、StringBuilder:调用StringBuffer、StringBuilder构造器
StringBuffer、StringBuilder -->String:①调用String构造器;②StringBuffer、StringBuilder的toString()
六、其他
向上向下取整
import java.util.Math
Math.ceil(double a)
Math.floor(double a)

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








