##1、概述##
在之前的文章中我们分析了关于Context和ContextImpl之间的关系,同时也指出了ContextImpl注册了系统中许多的服务,可直接通过getSystemService()获取相关服务的代理Android中ContextImpl源码分析(二),今天我们就来谈谈在其中的UsbManager和UsbService。
##2、源码分析##
我们还是从ContextImpl类入手,看其是如何创建UsbManager对象。
registerService(USB_SERVICE, new ServiceFetcher() {
public Object createService(ContextImpl ctx) {
//获取USBService对象
IBinder b = ServiceManager.getService(USB_SERVICE);
//创建UsbManager对象,传入USBService对象到IUsbManager.Stub.asInterface()方法中
return new UsbManager(ctx, IUsbManager.Stub.asInterface(b));
}});
这里既然可以通过ServiceManager.getService获取,那么肯定有代码将其添加到ServiceManager中,我们先看一下其处理逻辑。
//这里加载的是UsbService的内部类Lifecycle
private static final String USB_SERVICE_CLASS =
"com.android.server.usb.UsbService$Lifecycle";
mSystemServiceManager.startService(USB_SERVICE_CLASS);
在之前的文章中我们说到SystemServiceManager.startService方法其最终还是通过ServiceManager.addService来注册服务的,如果大家不是很明白可以看一下另外一篇文章ServiceManager源码分析,既然这里已经看到了如何注册UsbService,我们顺便再看一下UsbService的内部类Lifecycle。
public static class Lifecycle extends SystemService {
private UsbService mUsbService;
public Lifecycle(Context context) {
super(context);
}
@Override
public void onStart() {
//创建UsbService对象
mUsbService = new UsbService(getContext());
publishBinderService(Context.USB_SERVICE, mUsbService);
}
@Override
public void onBootPhase(int phase) {
if (phase == SystemService.PHASE_ACTIVITY_MANAGER_READY) {
mUsbService.systemReady();
}
}
}
好啦,这里我们已经清楚了如何获取UsbService对象,接下来我们在看看UsbManager的构造器以及IUsbManager.Stub.asInterface()方法。
public class UsbManager {
private final Context mContext;
private final IUsbManager mService;
public UsbManager(Context context, IUsbManager service) {
mContext = context;
mService = service;
}
//封装UsbService的方法
//......
}
我们紧接着进入IUsbManager.Stub.asInterface()方法。
public interface IUsbManager extends android.os.IInterface
{
public static abstract class Stub extends android.os.Binder implements android.hardware.usb.IUsbManager{
//asInterface方法
public static android.hardware.usb.IUsbManager asInterface(android.os.IBinder obj)
{
if ((obj==null)) {
return null;
}
android.os.IInterface iin = obj.queryLocalInterface(DESCRIPTOR);
if (((iin!=null)&&(iin instanceof android.hardware.usb.IUsbManager))) {
return ((android.hardware.usb.IUsbManager)iin);
}
//创建USBService的代理对象
return new android.hardware.usb.IUsbManager.Stub.Proxy(obj);
}
}
}
好啦,看到这里相信大家对USBService的基本结构都了解了吧,和我们之前分析的AMS以及PKMS是一样的,我们接下来给出一张图来表示这几个类的关系。
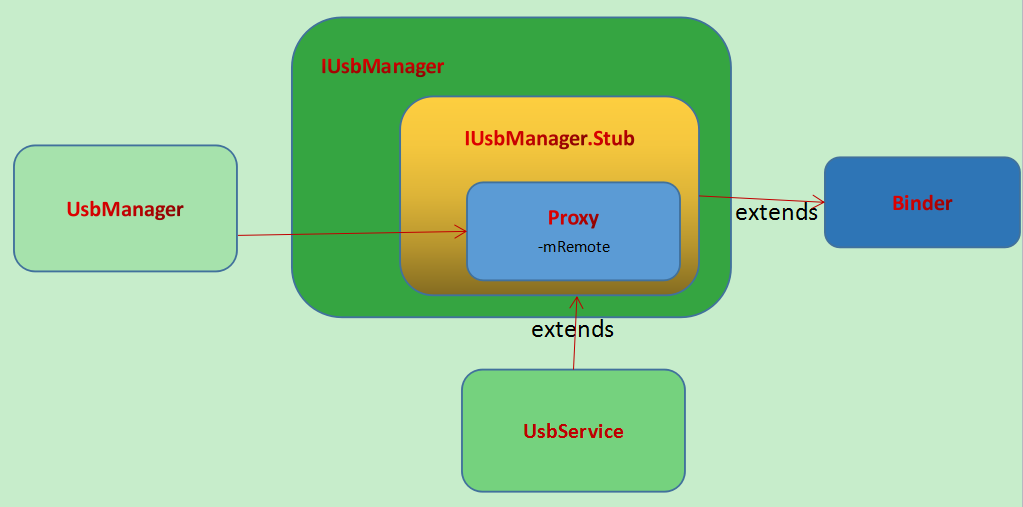
从这张图中可以直接看出几个类的相关关系,接下来我们简单的了解一下USBService的相关方法吧。
public class UsbService extends IUsbManager.Stub {
private final Context mContext;
private UsbDeviceManager mDeviceManager;
private UsbHostManager mHostManager;
public UsbService(Context context) {
mContext = context;
final PackageManager pm = mContext.getPackageManager();
if (pm.hasSystemFeature(PackageManager.FEATURE_USB_HOST)) {
//创建UsbHostManager对象
mHostManager = new UsbHostManager(context);
}
if (new File("/sys/class/android_usb").exists()) {
//创建UsbDeviceManager对象
mDeviceManager = new UsbDeviceManager(context);
}
setCurrentUser(UserHandle.USER_OWNER);
final IntentFilter userFilter = new IntentFilter();
userFilter.addAction(Intent.ACTION_USER_SWITCHED);
userFilter.addAction(Intent.ACTION_USER_STOPPED);
mContext.registerReceiver(mUserReceiver, userFilter, null, null);
}
}
由于USBService继承于IUsbManager.Stub对象,而IUsbManager.Stub却实现了IUsbManager,所以USBService最终也实现了IUsbManager接口并完成其方法的重写。
好啦,今天的USBService我们就简单的介绍到这里,下一篇文章我们在分析一下Android设备连接Usb弹出权限框问题USBService源码分析之Usb权限(二)。








 本文详细解析了Android系统中USBService与UsbManager的工作原理及其实现方式,包括两者之间的关系、UsbManager的创建过程以及USBService的内部结构。
本文详细解析了Android系统中USBService与UsbManager的工作原理及其实现方式,包括两者之间的关系、UsbManager的创建过程以及USBService的内部结构。


















 5万+
5万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










