Description
Mathematically some problems look hard. But with the help of the computer, some problems can be easily solvable.
In this problem, you will be given two integers a and b. You have to find the summation of the scores of the numbers from a to b (inclusive).
The score of a number is defined as the following function.score (x) = n2, where n is the number of relatively prime numbers with x, which are smaller than x
For example,
For 6, the relatively prime numbers with 6 are 1 and 5. So, score (6) = 22 = 4.
For 8, the relatively prime numbers with 8 are 1, 3, 5 and 7. So, score (8) = 42 = 16.
Now you have to solve this task.
Input
Input starts with an integer T (≤ 105), denoting the number of test cases.Each case will contain two integers a and b (2 ≤ a ≤ b ≤ 5 * 106).
Output
For each case, print the case number and the summation of all the scores from a to b.
Sample Input
3
6 6
8 8
2 20
Sample Output
Case 1: 4
Case 2: 16
Case 3: 1237
Note
Euler's totient function applied to a positive integer ø(n) is defined to be the number of positive integers less than or equal to ø(n) that
are relatively prime to ø(n). is read "phi of n."Given the general prime factorization of 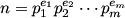 , one can compute ø(n)using the formula
, one can compute ø(n)using the formula
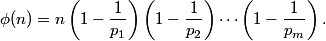
在数论中,对正整数n,欧拉函数  是小于或等于n的正整数中与n互质的数的数目,对欧拉函数打表;
是小于或等于n的正整数中与n互质的数的数目,对欧拉函数打表;
注意 :long long 需要用无符号型;
代码如下:
#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> using namespace std; typedef unsigned long long ll; const int maxx=5001000; ll a[maxx]; void init() { for(int i=0; i<maxx; i++) a[i]=i; for(int i=2; i<maxx; i++) { if(a[i]==i) { for(int j=i; j<maxx; j+=i) a[j]=a[j]/i*(i-1); } } for(int i=2; i<maxx; i++) a[i]=a[i]*a[i]+a[i-1]; } int main() { init(); int t,Case=0; cin>>t; while(t--) { int n,m; cin>>n>>m; printf("Case %d: ",++Case); cout<<a[m]-a[n-1]<<endl; } return 0; }




 本文探讨了看似复杂的数学问题如何通过计算机变得易于解决。特别地,介绍了一个具体问题,即计算从a到b(包括a和b)的所有数字的分数之和。分数定义为一个小于x且与x互质的相对质数的数量的平方。文章提供了使用欧拉φ函数的解决方案,并附带了C++代码实现。
本文探讨了看似复杂的数学问题如何通过计算机变得易于解决。特别地,介绍了一个具体问题,即计算从a到b(包括a和b)的所有数字的分数之和。分数定义为一个小于x且与x互质的相对质数的数量的平方。文章提供了使用欧拉φ函数的解决方案,并附带了C++代码实现。
















 1787
1787

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








