#程序员自己管理的内存 X86 4G 堆区
申请内存 malloc calloc
扩容 realloc
释放内存 free
内存泄漏 检测工具 vld
* 1. 函数使用步骤
* 2. free 崩溃原因
* 1) 重复释放同一块内存 -> s=malloc free(s); s=NULL;
* 2) 释放非堆区空间 int arr[]={1,2};free(arr);
* 3) 保存 堆区空间 起始地址的变量值 发生修改
* int* p = malloc ...;
* p++;
* free(p); p=NULL;
* 3. 面试: free函数 如何知道释放内存大小?
* int*p = malloc();
* p保存的地址 前 有指针 存储大小
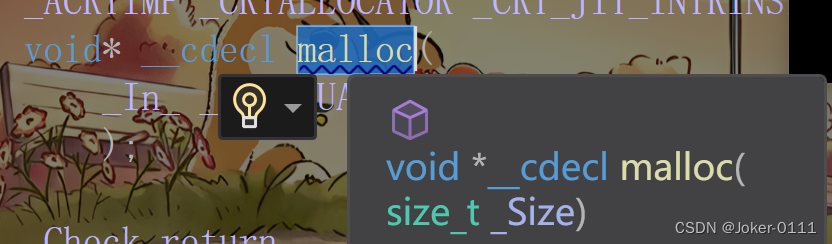
void *p=malloc(1); //无定义 1字节
(int*)malloc(1); 强转int类型
long long *
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main() { //2G
int *p=(int *)malloc(200);//申请200字节
if (p == NULL) {
printf("内存申请失败");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
//用0初始化
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
p[i] = 0;
} //用for循环
memset(p, 0, 200); //memset 函数
printf("%d", p[5]);
free(p);
return 0;
}
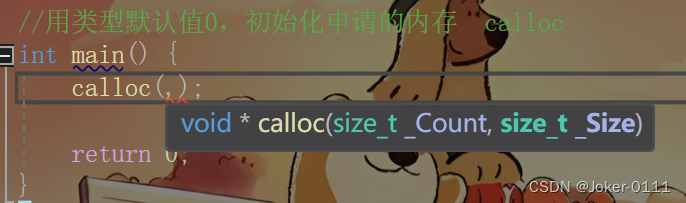
几个什么
calloc(10,sizeof(int)) 10个int类型大小
//用类型默认值0,初始化申请的内存 calloc
int main() {
int *p=(int *)calloc(10,sizeof(int)); //40字节
if (p == NULL) {
printf("内存申请失败");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("%d", p[2]);
free(p);
return 0;
}
free 释放两次什么情况
程序崩溃
//用类型默认值0,初始化申请的内存 calloc
int main() {
int *p=(int *)calloc(10,sizeof(int)); //40字节
if (p == NULL) {
printf("内存申请失败");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("%d", p[2]);
free(p); //野指针
p = NULL; //目的,防止多次释放同一块内存
free(p);
return 0;
}
// int *p=&val;
//free(p); //释放堆区空间
int main() {
int* p = (int*)malloc(100);
assert(p != NULL);
p++;
free(p);
p = NULL;
return 0;
}
free怎么知道释放多少
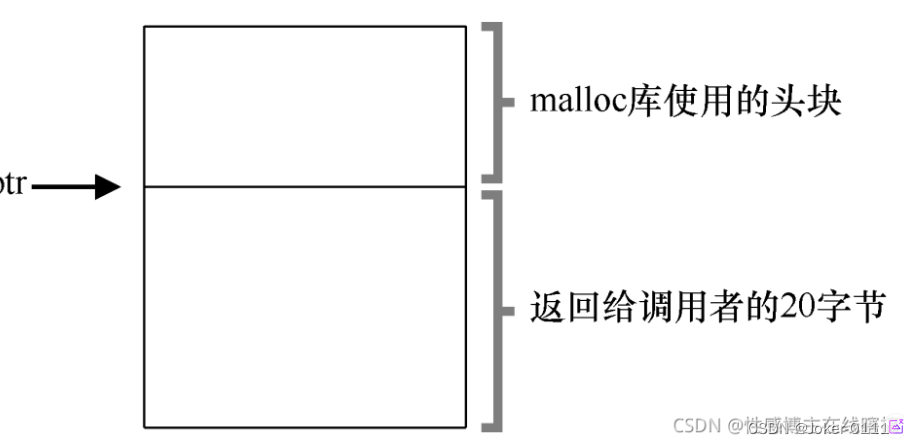
在这里你可能注意到,void free(void *ptr) 参数中只需要传入一个指针参数,就可以释放掉所分配的内存,它是如何确定指针所指向的区域分配了多大的内存空间呢?为了完成释放任务,很多内存分配函数都会在一个称之为头部指针(header,或者称之为头块)的地方保存一些额外的信息,头部指针通常在放回的内存块之前。
————————————————
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,遵循 CC 4.0 BY-SA 版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接和本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/qq_41884002/article/details/121627852
int main() {
int* p = (int*)malloc(100);
assert(p != NULL);
// [4B] p->[100字节]
free(p);
p = NULL;
return 0;
}
扩容 realloc
//realloc 扩容堆区
int main() {
int* p = (int*)malloc(10 * sizeof(int));
if (p == NULL) {
printf("内存申请失败");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
p=(int *)realloc(p, 2 * 10 * sizeof(int)); //扩容 (什么,多大)
free(p);
p = NULL;
return 0;
}
扩容底层实现
1> 100+100 在已经申请后直接加
|
100 |
2> 后边放不下 重新找一块空间 100+200
|
100(新) |
100 |
3> 返回空指针,没有合适空间























 1805
1805

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








