1.栈与队列
栈与队列是程序设计中广泛使用的两种重要的线性数据结构。
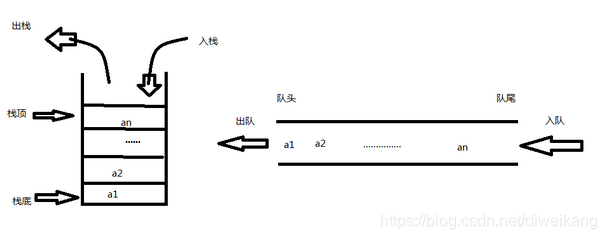
栈是LIFO(Last In First Out),先存进去的数据只能最后被取出来,进出顺序逆序,即先进后出,后进先出。
队列是FIFO(First In First Out),它保持进出顺序一致,即先进先出,后进后出。
4.如何使用两个栈模拟队列操作
public class TwoStackForQueue<E> {
/*
* 用法两个stack 实现队列操作 队列是先进先出的
* 思想:设置两个stack A,B, stackA为入队的栈,stackB为出队的栈
* 入队直接进栈A,出栈需要判断栈B是否为空,如果为空,需要将栈A中的元素放入栈B中
* 如果不为空 直接获取栈B的栈顶元素
*/
Stack<E> A = new Stack<>();
Stack<E> B = new Stack<>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
TwoStackForQueue<Integer> queue = new TwoStackForQueue<>();
queue.put(1);
queue.put(2);
queue.put(3);
// int i = queue.pop();
// System.out.println(i);
// i = queue.pop();
// System.out.println(i);
// i = queue.pop();
// System.out.println(i);
while(!queue.empty()){
int i = queue.pop();
System.out.println(i);
}
}
//判断是否队空
public boolean empty(){
return A.isEmpty() && B.isEmpty();
}
//出队
public synchronized E pop(){
if(B.isEmpty()){
while(!A.isEmpty())
{
B.push(A.pop());
}
}
return B.pop();
}
//入队
public synchronized void put(E e){
A.push(e);
}
}
5.如果使用两个队列模拟栈操作
public class TwoQueueForStack<E> {
/*
* 使用两个队列实现栈 栈的特点是先进后出,后进先出
* 思路:两个Queue 使用LinkedList实例化 LinkedList实际上是一个双向链表
* q1作为入栈的队列 即直接将入栈的数据放入q1
* q2作为出栈的队列 即需要出栈时,如果q1只有一个元素 直接出栈
* 如果q1不止一个元素,即可以将q1队列中的数据依次放入q2,最后一个不放入,最后一个元素输出
* 再将q2中的元素依次放回q1
*/
private Queue<E> q1 = new LinkedList<E>();
private Queue<E> q2 = new LinkedList<E>();;
public static void main(String[] args) {
TwoQueueForStack<Integer> stack = new TwoQueueForStack<>();
stack.put(1);
stack.put(2);
stack.put(3);
while(!stack.empty()){
int i = stack.pop();
System.out.println(i);
}
}
//判断是否栈空
public boolean empty(){
return q1.isEmpty() && q2.isEmpty();
}
//出栈
public synchronized E pop(){
int size = q1.size();
if(size==1)
return q1.poll();
int i=1;
while(!(i==size)){
q2.add(q1.poll());
i++;
}
E e = q1.poll();
while(!q2.isEmpty()){
q1.add(q2.poll());
}
return e;
}
//入栈
public synchronized void put(E e){
q1.add(e);
}
}




 本文深入探讨了栈与队列这两种基本数据结构,详细解析了它们的工作原理及特性,栈遵循LIFO原则,而队列则遵循FIFO原则。文章进一步介绍了如何通过两个栈来模拟队列的操作,以及如何利用两个队列实现栈的功能,提供了具体的代码示例,帮助读者理解并掌握数据结构转换的技巧。
本文深入探讨了栈与队列这两种基本数据结构,详细解析了它们的工作原理及特性,栈遵循LIFO原则,而队列则遵循FIFO原则。文章进一步介绍了如何通过两个栈来模拟队列的操作,以及如何利用两个队列实现栈的功能,提供了具体的代码示例,帮助读者理解并掌握数据结构转换的技巧。
















 1029
1029

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








