1.simple模式

消息生产者p将消息放入队列
消费者监听队列,如果队列中有消息,就消费掉,消息被拿走后,自动从队列删除
(隐患,消息可能没有被消费者正确处理,已经消失了,无法恢复)
应用场景:聊天室
案例:
1>.首先准备依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>public class SimpleTest {
//模拟生产者将消息放入队列
@Test
public void send() throws Exception{
/*1 创建连接工厂
* 2 配置共创config
* 3 获取连接
* 4获取信道
* 5 从信道声明queue
* 6 发送消息
* 7 释放资源
*/
ConnectionFactory factory=new ConnectionFactory();
factory.setHost("106.23.34.56");
factory.setPort(5672);
factory.setVirtualHost("/tb");
factory.setUsername("admin");
factory.setPassword("123456");
//从工厂获取连接
Connection conn=factory.newConnection();
//从连接获取信道
Channel chan=conn.createChannel();
//利用channel声明第一个队列
chan.queueDeclare("simple", false, false, false, null);
//queue String类型,表示声明的queue对列的名字
//durable Boolean类型,表示是否持久化
//exclusive Boolean类型:当前声明的queue是否专注;true当前连接创建的
//任何channle都可以连接这个queue,false,新的channel不可使用
//autoDelete Boolean类型:在最后连接使用完成后,是否删除队列,false
//arguments Map类型,其他声明参数
//发送消息
String msg="helloworld,nihaoa";
chan.basicPublish("", "simple", null, msg.getBytes());
//exchange String类型,交换机名称,简单模式使用默认交换""
//routingkey String类型,当前的消息绑定的routingkey,简单模式下,与队列同名即可
//props BasicProperties类型,消息的属性字段对象,例如BasicProperties
//可以设置一个deliveryMode的值0 持久化,1 表示不持久化,durable配合使用
//body byte[] :消息字符串的byte数组
}
//模拟消费端
@Test
public void receive() throws Exception{
ConnectionFactory factory=new ConnectionFactory();
factory.setHost("106.23.34.56");
factory.setPort(5672);
factory.setVirtualHost("/tb");
factory.setUsername("admin");
factory.setPassword("123456");
//从工厂获取连接
2.work模式
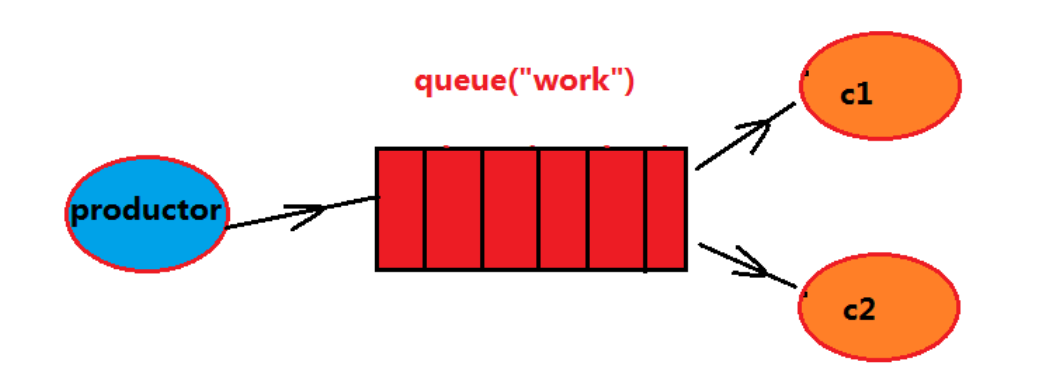
多个消费者同时监听同一个队列,消息如何被消费?
C1,C2共同争抢当前消息队列的内容,谁先拿到消息,谁来负责消费
应用场景:红包;大型项目中的资源调度过程(直接由最空闲的系统争抢到资源处理任务)
案例:
1>首先写一个工具类
public class ConnectionUtil {
public static Connection getConn(){
try{
ConnectionFactory factory=new ConnectionFactory();
factory.setHost("106.33.44.179");
factory.setPort(5672);
factory.setVirtualHost("/tb");
factory.setUsername("admin");
factory.setPassword("123456");
//从工厂获取连接
Connection conn=factory.newConnection();
return conn;
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
return null;
}
}
}2>写test类
public class WorkTest {
@Test
public void send() throws Exception{
//获取连接
Connection conn = ConnectionUtil.getConn();
Channel chan = conn.createChannel();
//声明队列
chan.queueDeclare("work", false, false, false, null);
for(int i=0;i<100;i++){
String msg="1712,hello:"+i+"message";
chan.basicPublish("", "work", null, msg.getBytes());
System.out.println("第"+i+"条信息已经发送");
}
chan.close();
conn.close();
}
@Test
public void receive1() throws Exception{
//获取连接,获取信道
Connection conn = ConnectionUtil.getConn();
Channel chan = conn.createChannel();
chan.queueDeclare("work", false, false, false, null);
//同一时刻服务器只发送一条消息给同一消费者,消费者空闲,才发送一条
chan.basicQos(1);
//定义消费者
QueueingConsumer consumer=new QueueingConsumer(chan);
//绑定队列和消费者的关系
//queue
//autoAck:消息被消费后,是否自动确认回执,如果false,不自动需要手动在
//完成消息消费后进行回执确认,channel.ack,channel.nack
//callback
//chan.basicConsume(queue, autoAck, callback)
chan.basicConsume("work", false, consumer);
//监听
while(true){
Delivery delivery=consumer.nextDelivery();
byte[] result = delivery.getBody();
String msg=new String(result);
System.out.println("接受到:"+msg);
Thread.sleep(50);
//返回服务器,回执
chan.basicAck(delivery.getEnvelope().getDeliveryTag(), false);
}
}
@Test
public void receive2() throws Exception{
//获取连接,获取信道
Connection conn = ConnectionUtil.getConn();
Channel chan = conn.createChannel();
chan.queueDeclare("work", false, false, false, null);
//同一时刻服务器只发送一条消息给同一消费者,消费者空闲,才发送一条
chan.basicQos(1);
//定义消费者
QueueingConsumer consumer=new QueueingConsumer(chan);
//绑定队列和消费者的关系
//queue
//autoAck:消息被消费后,是否自动确认回执,如果false,不自动需要手动在
//完成消息消费后进行回执确认,channel.ack,channel.nack
//callback
//chan.basicConsume(queue, autoAck, callback)
chan.basicConsume("work", false, consumer);
//监听
while(true){
Delivery delivery=consumer.nextDelivery();
byte[] result = delivery.getBody();
String msg=new String(result);
System.out.println("接受到:"+msg);
Thread.sleep(150);
//返回服务器,回执
chan.basicAck(delivery.getEnvelope().getDeliveryTag(), false);
}
}
}
3 publish/fanout发布订阅
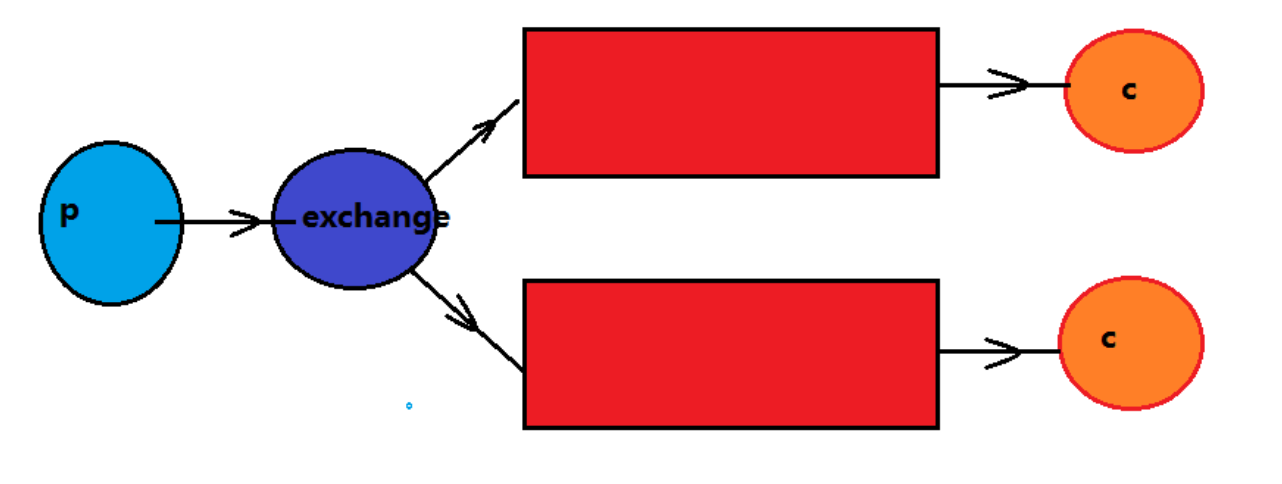
生产者将消息交给交换机
有交换机根据发布订阅的模式设定将消息同步到所有的绑定队列中;
后端的消费者都能拿到消息
应用场景:邮件群发,群聊天,广告
案例:
public class FanoutTest {
//交换机,有类型,发布订阅:fanout
//路由模式:direct
//主题模式:topic
@Test
public void send() throws Exception {
//获取连接
Connection conn = ConnectionUtil.getConn();
Channel chan = conn.createChannel();
//声明交换机
//参数意义,1 交换机名称,2 类型:fanout,direct,topic
chan.exchangeDeclare("fanoutEx", "fanout");
//发送消息
for(int i=0;i<100;i++){
String msg="1712 hello:"+i+"msg";
chan.basicPublish("fanoutEx", "", null, msg.getBytes());
System.out.println("第"+i+"条信息已经发送");
}
}
@Test
public void receiv01() throws Exception{
//获取连接
Connection conn = ConnectionUtil.getConn();
Channel chan = conn.createChannel();
//生命队列
chan.queueDeclare("fanout01", false, false, false, null);
//声明交换机
chan.exchangeDeclare("fanoutEx", "fanout");
//绑定队列到交换机
//参数 1 队列名称,2 交换机名称 3 路由key
chan.queueBind("fanout01", "fanoutEx", "");
chan.basicQos(1);
//定义消费者
QueueingConsumer consumer=new QueueingConsumer(chan);
//消费者与队列绑定
chan.basicConsume("fanout01",false, consumer);
while(true){
Delivery delivery= consumer.nextDelivery();
System.out.println("一号消费者接收到"+
new String(delivery.getBody()));
chan.basicAck(delivery.getEnvelope().
getDeliveryTag(), false);
}
}
@Test
public void receiv02() throws Exception{
//获取连接
Connection conn = ConnectionUtil.getConn();
Channel chan = conn.createChannel();
//生命队列
chan.queueDeclare("fanout02", false, false, false, null);
//声明交换机
chan.exchangeDeclare("fanoutEx", "fanout");
//绑定队列到交换机
//参数 1 队列名称,2 交换机名称 3 路由key
chan.queueBind("fanout02", "fanoutEx", "");
chan.basicQos(1);
//定义消费者
QueueingConsumer consumer=new QueueingConsumer(chan);
//消费者与队列绑定
chan.basicConsume("fanout02",false, consumer);
while(true){
Delivery delivery= consumer.nextDelivery();
System.out.println("二号消费者接收到"+new String(delivery.getBody()));
chan.basicAck(delivery.getEnvelope().getDeliveryTag(), false);
}
}
}
4 routing路由模式
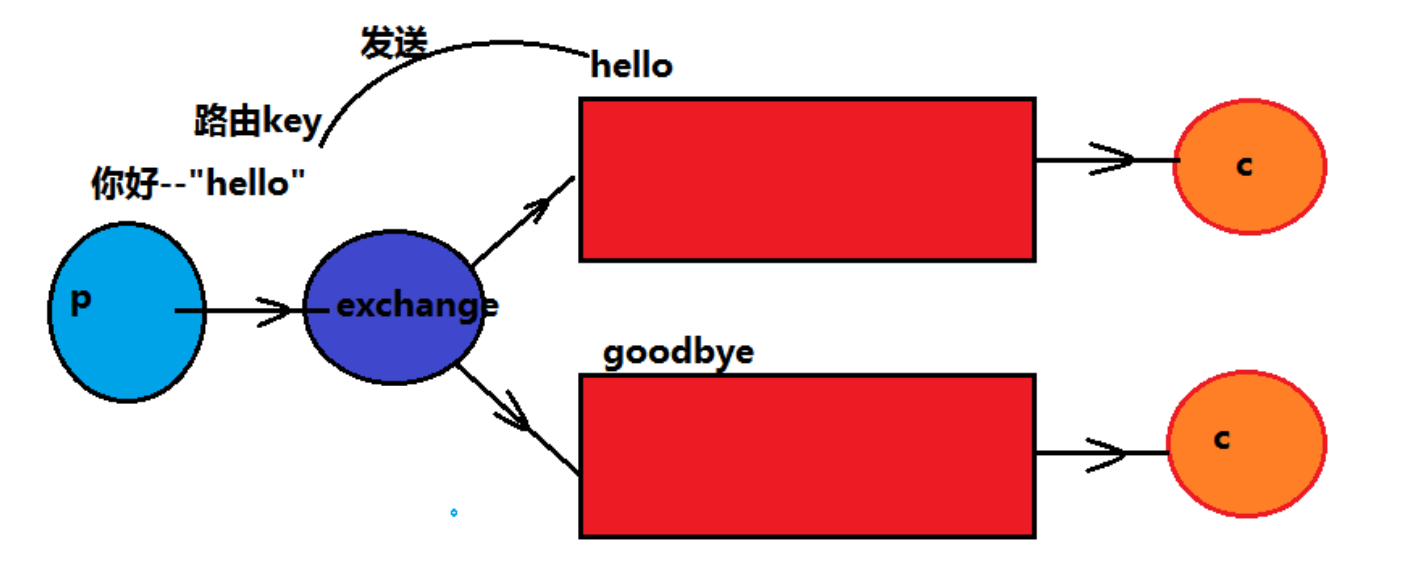
生产者发送消息到交换机,同时绑定一个路由Key,交换机根据路由key对下游绑定的队列进行路
由key的判断,满足路由key的队列才会接收到消息,消费者消费消息
应用场景: 项目中的error报错
案例:
public class RoutingTopicTest {
@Test
public void routingSend() throws Exception{
//获取连接
Connection conn = ConnectionUtil.getConn();
Channel chan = conn.createChannel();
//声明交换机
//参数意义,1 交换机名称,2 类型:fanout,direct,topic
chan.exchangeDeclare("directEx", "direct");
//发送消息
String msg="路由模式的消息";
chan.basicPublish("directEx", "jt1713",
null, msg.getBytes());
}
@Test
public void routingRec01() throws Exception{
System.out.println("一号消费者等待接收消息");
//获取连接
Connection conn = ConnectionUtil.getConn();
Channel chan = conn.createChannel();
//声明队列
chan.queueDeclare("direct01", false, false, false, null);
//声明交换机
chan.exchangeDeclare("directEx", "direct");
//绑定队列到交换机
//参数 1 队列名称,2 交换机名称 3 路由key
chan.queueBind("direct01", "directEx", "jt1712");
chan.basicQos(1);
//定义消费者
QueueingConsumer consumer=new QueueingConsumer(chan);
//消费者与队列绑定
chan.basicConsume("direct01",false, consumer);
while(true){
Delivery delivery= consumer.nextDelivery();
System.out.println("一号消费者接收到"+
new String(delivery.getBody()));
chan.basicAck(delivery.getEnvelope().
getDeliveryTag(), false);
}
}
@Test
public void routingRec02() throws Exception{
System.out.println("二号消费者等待接收消息");
//获取连接
Connection conn = ConnectionUtil.getConn();
Channel chan = conn.createChannel();
//声明队列
chan.queueDeclare("direct02", false, false, false, null);
//声明交换机
chan.exchangeDeclare("directEx", "direct");
//绑定队列到交换机
//参数 1 队列名称,2 交换机名称 3 路由key
chan.queueBind("direct02", "directEx", "jt1711");
chan.basicQos(1);
//定义消费者
QueueingConsumer consumer=new QueueingConsumer(chan);
//消费者与队列绑定
chan.basicConsume("direct02",false, consumer);
while(true){
Delivery delivery= consumer.nextDelivery();
System.out.println("二号消费者接收到"+
new String(delivery.getBody()));
chan.basicAck(delivery.getEnvelope().
getDeliveryTag(), false);
}
}
}5 topic主题模式
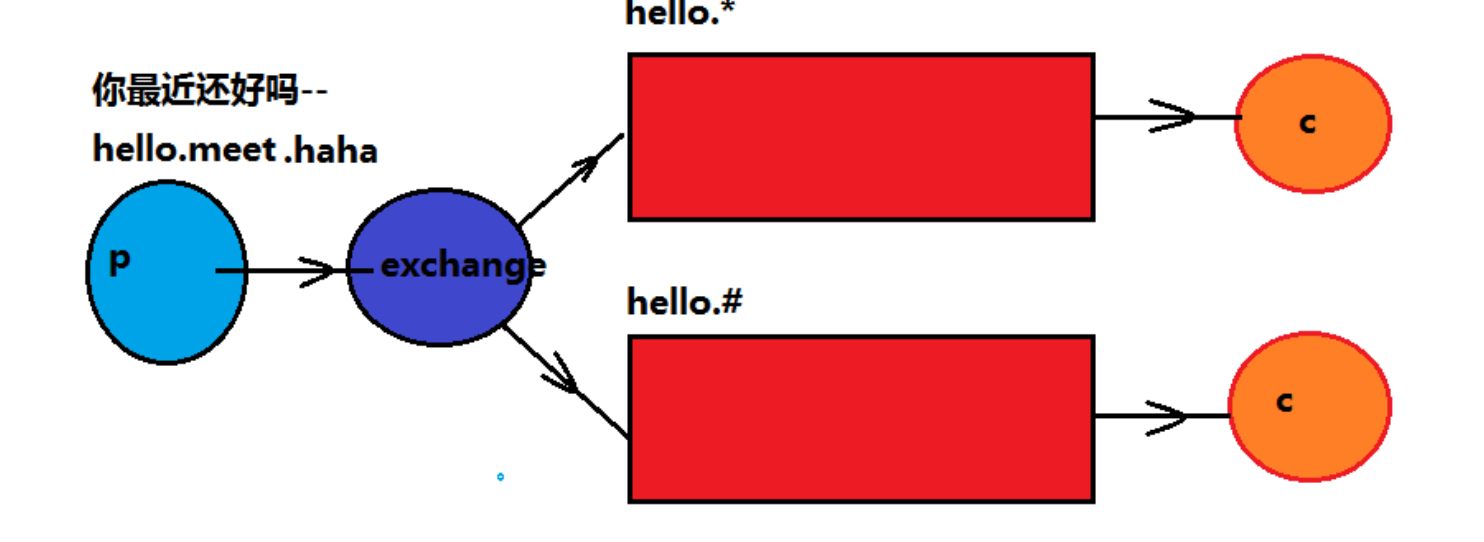
*号代表单个词语
#代表多个词语
其他的内容与routing路由模式一致
案例:
public class RoutingTopicTest {
@Test
public void routingRec02() throws Exception{
System.out.println("二号消费者等待接收消息");
//获取连接
Connection conn = ConnectionUtil.getConn();
Channel chan = conn.createChannel();
//声明队列
chan.queueDeclare("direct02", false, false, false, null);
//声明交换机
chan.exchangeDeclare("directEx", "direct");
//绑定队列到交换机
//参数 1 队列名称,2 交换机名称 3 路由key
chan.queueBind("direct02", "directEx", "jt1711");
chan.basicQos(1);
//定义消费者
QueueingConsumer consumer=new QueueingConsumer(chan);
//消费者与队列绑定
chan.basicConsume("direct02",false, consumer);
while(true){
Delivery delivery= consumer.nextDelivery();
System.out.println("二号消费者接收到"+
new String(delivery.getBody()));
chan.basicAck(delivery.getEnvelope().
getDeliveryTag(), false);
}
}
@Test
public void topicSend() throws Exception{
//获取连接
Connection conn = ConnectionUtil.getConn();
Channel chan = conn.createChannel();
//声明交换机
//参数意义,1 交换机名称,2 类型:fanout,direct,topic
chan.exchangeDeclare("topicEx", "topic");
//发送消息
String msg="主题模式的消息";
chan.basicPublish("topicEx", "jt1712.add.update",
null, msg.getBytes());
}
@Test
public void topicRec01() throws Exception{
System.out.println("一号消费者等待接收消息");
//获取连接
Connection conn = ConnectionUtil.getConn();
Channel chan = conn.createChannel();
//声明队列
chan.queueDeclare("topic01", false, false, false, null);
//声明交换机
chan.exchangeDeclare("topicEx", "topic");
//绑定队列到交换机
//参数 1 队列名称,2 交换机名称 3 路由key
chan.queueBind("topic01", "topicEx", "jt1712");
chan.basicQos(1);
//定义消费者
QueueingConsumer consumer=new QueueingConsumer(chan);
//消费者与队列绑定
chan.basicConsume("topic01",false, consumer);
while(true){
Delivery delivery= consumer.nextDelivery();
System.out.println("一号消费者接收到"+
new String(delivery.getBody()));
chan.basicAck(delivery.getEnvelope().
getDeliveryTag(), false);
}
}
@Test
public void topicRec02() throws Exception{
System.out.println("二号消费者等待接收消息");
//获取连接
Connection conn = ConnectionUtil.getConn();
Channel chan = conn.createChannel();
//声明队列
chan.queueDeclare("topic02", false, false, false, null);
//声明交换机
chan.exchangeDeclare("topicEx", "topic");
//绑定队列到交换机
//参数 1 队列名称,2 交换机名称 3 路由key
chan.queueBind("topic02", "topicEx", "jt1712.#");
chan.basicQos(1);
//定义消费者
QueueingConsumer consumer=new QueueingConsumer(chan);
//消费者与队列绑定
chan.basicConsume("topic02",false, consumer);
while(true){
Delivery delivery= consumer.nextDelivery();
System.out.println("二号消费者接收到"+
new String(delivery.getBody()));
chan.basicAck(delivery.getEnvelope().
getDeliveryTag(), false);
}
}
}





 本文介绍了RabbitMQ的五种工作模式:simple模式、work模式、publish/fanout发布订阅、routing路由模式和topic主题模式。每个模式都有其特定的应用场景和案例,例如simple模式适用于聊天室,work模式用于处理任务队列,publish/fanout适用于邮件群发,routing模式常用于错误处理,而topic模式则通过*和#进行灵活的消息匹配。
本文介绍了RabbitMQ的五种工作模式:simple模式、work模式、publish/fanout发布订阅、routing路由模式和topic主题模式。每个模式都有其特定的应用场景和案例,例如simple模式适用于聊天室,work模式用于处理任务队列,publish/fanout适用于邮件群发,routing模式常用于错误处理,而topic模式则通过*和#进行灵活的消息匹配。
















 452
452

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








