Type 来历
我们知道,Type 是 JDK5 开始引入的,其引入主要是为了泛型,没有泛型的之前,只有所谓的原始类型。此时,所有的原始类型都通过字节码文件类 Class 类进行抽象。Class 类的一个具体对象就代表一个指定的原始类型。
泛型出现之后,也就扩充了数据类型。从只有原始类型扩充了参数化类型、类型变量类型、泛型数组类型,也就是 Type 的子接口。
那为什么没有统一到 Class 下,而是增加一个 Type 呢?(Class 也是种类的意思,Type 是类型的意思)
是为了程序的扩展性,最终引入了 Type 接口作为 Class,ParameterizedType,GenericArrayType,TypeVariable 和 WildcardType 这几种类型的总的父接口。这样实现了 Type 类型参数接受以上五种子类的实参或者返回值类型就是 Type 类型的参数。
Java 类型分类
Java 的所有类型包括:
- raw type:原始类型,对应 Class
- parameterized types:参数化类型,对应 ParameterizedType
- array types:数组类型,对应 GenericArrayType
- type variables:类型变量,对应 TypeVariable
- primitive types:基本类型,仍然对应 Class
1 中的 Class,不仅仅指平常所指的类,还包括数组、接口、注解、枚举等结构。
3 中的数组类型 GenericArrayType,应该指的是 2、4 类型数组,而不是一般我们说的数组,我们一般所说的数组是指 1、5 类型数组,他们还是 1,也就是 Class 类型。
TypeVariable
类型参数,描述类型,表示泛指任意或相关一类类型,泛型声明所声明的类型参数,仅仅用作参数占位符的标识符。
public interface TypeVariable<D extends GenericDeclaration> extends Type, AnnotatedElement {
//
AnnotatedType[] getAnnotatedBounds();
//返回表示此类型变量的上限的 Type对象的数组
Type[] getBounds();
//获取声明该类型变量实体(即获得类、方法或构造器名)
D getGenericDeclaration();
//返回此类型变量的名称,表示占位符
String getName();
}
public class CustomTypeVariable<T> {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Type[] types = CustomTypeVariable.class.getTypeParameters();
TypeVariable typeVariable = (TypeVariable) types[0];
//Output: T
typeVariable.getName();
//Output: Object
typeVariable.getBounds()[0];
//Output: com.aspire.search.test.CustomTypeVariable
typeVariable.getGenericDeclaration();
}
}
ParameterizedType
参数化类型,形如:Object<T, K>,即常说的泛型,是 Type 的子接口。
public interface ParameterizedType extends Type {
//返回类型参数数组
Type[] getActualTypeArguments();
//返回此类型Type对象
Type getRawType();
//返回一个 Type对象,表示此类型为其成员的类型
Type getOwnerType();
}
public class CustomParameterizedType {
static List<String> contains = new ArrayList<>();
public Map.Entry<String,String> mapEntry;
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException, NoSuchMethodException {
//字段
Field field = CustomParameterizedType.class.getDeclaredField("mapEntry");
ParameterizedType paramterTypes = (ParameterizedType) field.getGenericType();
Type[] types = paramterTypes.getActualTypeArguments();
//Output: java.util.Map$Entry
String rawType = paramterTypes.getRawType().getTypeName();
//Output: java.util.Map
Type ownerType = paramterTypes.getOwnerType();
//Output: [java.lang.String, java.lang.String]
Type[] typeArgs = paramterTypes.getActualTypeArguments();
}
}
GenericArrayType
泛型数组,描述的是形如:A<T>[] 或 T[] 类型
public interface GenericArrayType extends Type {
// 返回泛型数组类型
Type getGenericComponentType();
}
public class CustomGenericArrayType<T> {
private T[] var;
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException {
//GenericArrayType实例对象
Type fruitType = CustomGenericArrayType.class.getDeclaredField("var").getGenericType();
//泛型类型T
Type var1 = ((GenericArrayType)fruitType).getGenericComponentType();
}
}
WildcardType
通配符表达式,泛型表达式,也可以说是,限定性的泛型,形如:? extends classA、?super classB。
public interface WildcardType extends Type {
//返回类型变量下限
Type[] getLowerBounds();
//返回类型变量上限
Type[] getUpperBounds();
}
public class CustomWildcardType {
private List<? extends Fruit> ft1;
private List<? super Apple> ft2;
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException {
//读取参数化类型(ParameterizedType): List<? extends Fruit>
Type var1 = CustomWildcardType.class.getDeclaredField("ft1").getGenericType();
Type var2 = CustomWildcardType.class.getDeclaredField("ft2").getGenericType();
WildcardType w1 = (WildcardType) ((ParameterizedType) var1).getActualTypeArguments()[0];
WildcardType w2 = (WildcardType) ((ParameterizedType) var2).getActualTypeArguments()[0];
//Output: com.aspire.search.test.Fruit
Type type1 = w1.getUpperBounds()[0];
//Output: com.aspire.search.test.Apple
Type type2 = w2.getLowerBounds()[0];
}
}
SerializableTypeWrapper 类
Type 类型的包装类,从上面可知,Type 包括:原始类型,而泛型又可以衍生出:类型参数以及通配符表达式。获取类型信息不仅仅是局限于原始类型信息,如果是泛型,还需要知道它的类型参数或通配符参数等信息,那如何提供获取这些信息的工具?这里用到了 SerializableTypeWrapper 包装类,其内部通过不同的 Type 类型实现不同接口的代理类实现。client - >TypeWriter -> Proxy:
先看类型包装器接口,TypeProvider 是字段类型、方法入参类型、方法返回类型的包装类,高层模块通过该实例获取类型的相关信息,包括泛型的原始类型、类型参数等等:
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
interface TypeProvider extends Serializable {
/**
* 返回类型
*/
@Nullable
Type getType();
/**
* 返回类型源
*/
@Nullable
default Object getSource() {
return null;
}
}
字段 Field 对象包装器,仅仅对字段的封装,可以理解为字段的代理类:
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
static class FieldTypeProvider implements TypeProvider {
private final String fieldName;
// 得到目标属性所在类对应的Class对象
private final Class<?> declaringClass;
private transient Field field;
public FieldTypeProvider(Field field) {
this.fieldName = field.getName();
this.declaringClass = field.getDeclaringClass();
this.field = field;
}
@Override
public Type getType() {
// 返回字段的声明类型
return this.field.getGenericType();
}
@Override
public Object getSource() {
return this.field;
}
private void readObject(ObjectInputStream inputStream) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
inputStream.defaultReadObject();
try {
this.field = this.declaringClass.getDeclaredField(this.fieldName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Could not find original class structure", ex);
}
}
}
方法参数包装器,其实就是对方法参数类型的代理类:
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
static class MethodParameterTypeProvider implements TypeProvider {
// 方法名
@Nullable
private final String methodName;
// 参数类型
private final Class<?>[] parameterTypes;
// 得到目标属性所在类对应的Class对象
private final Class<?> declaringClass;
// 参数索引
private final int parameterIndex;
private transient MethodParameter methodParameter;
public MethodParameterTypeProvider(MethodParameter methodParameter) {
this.methodName = (methodParameter.getMethod() != null ? methodParameter.getMethod().getName() : null);
this.parameterTypes = methodParameter.getExecutable().getParameterTypes();
this.declaringClass = methodParameter.getDeclaringClass();
this.parameterIndex = methodParameter.getParameterIndex();
this.methodParameter = methodParameter;
}
@Override
public Type getType() {
return this.methodParameter.getGenericParameterType();
}
@Override
public Object getSource() {
return this.methodParameter;
}
private void readObject(ObjectInputStream inputStream) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
inputStream.defaultReadObject();
try {
if (this.methodName != null) {
this.methodParameter = new MethodParameter(
this.declaringClass.getDeclaredMethod(this.methodName, this.parameterTypes), this.parameterIndex);
}
else {
this.methodParameter = new MethodParameter(
this.declaringClass.getDeclaredConstructor(this.parameterTypes), this.parameterIndex);
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Could not find original class structure", ex);
}
}
}
返回参数包装器,方法返回类型代理类,注意这里的 provider 属性,它指向泛型实例对象。例如,获取 List<String> 字段的原始类型,即调用代理类的 getRawType() 方法,即最终调用 MethodInvokeTypeProvider.getType(),此时 provider 执行 List 的包装类。
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
static class MethodInvokeTypeProvider implements TypeProvider {
private final TypeProvider provider;
private final String methodName; //方法名
private final Class<?> declaringClass; // 所在类对应的Class对象
private final int index;
private transient Method method;
@Nullable
private transient volatile Object result;
public MethodInvokeTypeProvider(TypeProvider provider, Method method, int index) {
this.provider = provider;
this.methodName = method.getName();
this.declaringClass = method.getDeclaringClass();
this.index = index;
this.method = method;
}
@Override
@Nullable
public Type getType() {
Object result = this.result;
if (result == null) {
// 延迟调用目标方法
result = ReflectionUtils.invokeMethod(this.method, this.provider.getType());
// 缓存结果
this.result = result;
}
return (result instanceof Type[] ? ((Type[]) result)[this.index] : (Type) result);
}
@Override
@Nullable
public Object getSource() {
return null;
}
private void readObject(ObjectInputStream inputStream) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
inputStream.defaultReadObject();
Method method = ReflectionUtils.findMethod(this.declaringClass, this.methodName);
if (method == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot find method on deserialization: " + this.methodName);
}
if (method.getReturnType() != Type.class && method.getReturnType() != Type[].class) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Invalid return type on deserialized method - needs to be Type or Type[]: " + method);
}
this.method = method;
}
}
看下 SerializableTypeWrapper 类的类属性常量:
private static final Class<?>[] SUPPORTED_SERIALIZABLE_TYPES = {
GenericArrayType.class, ParameterizedType.class, TypeVariable.class, WildcardType.class};
static final ConcurrentReferenceHashMap<Type, Type> cache = new ConcurrentReferenceHashMap<>(256);
从上面的代码可以看出:
- 定义了一个 Class 类型的数组,其子元素分别为 GenericArrayType、ParameterizedType、TypeVariable、WildcardType,也就是为不同的泛型代理实现的接口。
- 使用 cache 缓存已创建的代理
获取类型对外暴露的静态方法,该方法在类型的代理类中也会被调用,在代理类中调用是为了获取泛型的相关类型信息:
@Nullable
static Type forTypeProvider(TypeProvider provider) {
Type providedType = provider.getType();
if (providedType == null || providedType instanceof Serializable) {
/**
* 作为获取原始类型还是与泛型相关的信息(泛型原始类型、参数类型)入口
* 注意:
* 1、原始类型,对应 Class,Class实现Serializable接口,直接返回
* 2、泛型类型如List<String>,返回其代理类
*/
return providedType;
}
if (GraalDetector.inImageCode() || !Serializable.class.isAssignableFrom(Class.class)) {
// 如果类型在当前运行时环境中通常不可序列化,那么跳过任何包装尝试
return providedType;
}
// 获取给定提供者的可序列化类型代理
Type cached = cache.get(providedType);
if (cached != null) {
return cached;
}
for (Class<?> type : SUPPORTED_SERIALIZABLE_TYPES) {
if (type.isInstance(providedType)) {
ClassLoader classLoader = provider.getClass().getClassLoader();
Class<?>[] interfaces = new Class<?>[] {type, SerializableTypeProxy.class, Serializable.class};
InvocationHandler handler = new TypeProxyInvocationHandler(provider);
cached = (Type) Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, interfaces, handler);
cache.put(providedType, cached);
return cached;
}
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unsupported Type class: " + providedType.getClass().getName());
}
泛型代理类实现的接口,定义获取类型包装器 TypeProvider 对象协议:
interface SerializableTypeProxy {
/**
* 返回基础类型
*/
TypeProvider getTypeProvider();
}
关联的调用处理程序,当在代理实例上调用方法时,方法调用将被编码并分派到其调用处理程序的invoke方法。
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
private static class TypeProxyInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {
//类型包装类,例如List<String>的包装类
private final TypeProvider provider;
public TypeProxyInvocationHandler(TypeProvider provider) {
this.provider = provider;
}
@Override
@Nullable
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, @Nullable Object[] args) throws Throwable {
/**
* 重写equals方法
*/
if (method.getName().equals("equals") && args != null) {
Object other = args[0];
// Unwrap proxies for speed
if (other instanceof Type) {
other = unwrap((Type) other);
}
// 确定给定的对象是否相等
return ObjectUtils.nullSafeEquals(this.provider.getType(), other);
}
/**
* 重写hashCode方法
*/
else if (method.getName().equals("hashCode")) {
// 返回给定对象的哈希码
return ObjectUtils.nullSafeHashCode(this.provider.getType());
}
/**
* 实现SerializableTypeProxy.getTypeProvider()方法
*/
else if (method.getName().equals("getTypeProvider")) {
// 执行getTypeProvider方法
return this.provider;
}
/**
* 实现Type子接口返回Type类型的方法:
* GenericArrayType.getGenericComponentType()
* ParameterizedType.getRawType()/getOwnerType()
*/
if (Type.class == method.getReturnType() && args == null) {
return forTypeProvider(new MethodInvokeTypeProvider(this.provider, method, -1));
}
/**
* 实现Type子接口返回Type[]类型的方法:
* ParameterizedType.getActualTypeArguments()
* TypeVariable.getBounds()
* WildcardType.getUpperBounds()/getLowerBounds()
*/
else if (Type[].class == method.getReturnType() && args == null) {
/**
* 1: ParameterizedType.getActualTypeArguments()
* 返回一个表示此类型的实际类型参数的Type数组,eg: Hash<String, String>返回[class java.lang.String, class java.lang.String]
*/
Type[] result = new Type[((Type[]) method.invoke(this.provider.getType())).length];
for (int i = 0; i < result.length; i++) {
result[i] = forTypeProvider(new MethodInvokeTypeProvider(this.provider, method, i));
}
return result;
}
try {
return method.invoke(this.provider.getType(), args);
}
catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw ex.getTargetException();
}
}
}
接下来看下 SerializableTypeWrapper 对外暴露的其他方法:
// 返回泛型类型的可序列化变体
@Nullable
public static Type forField(Field field) {
return forTypeProvider(new FieldTypeProvider(field));
}
// 返回方法参数泛型类型的可序列化变体
@Nullable
public static Type forMethodParameter(MethodParameter methodParameter) {
return forTypeProvider(new MethodParameterTypeProvider(methodParameter));
}
// 返回原始类型
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static <T extends Type> T unwrap(T type) {
Type unwrapped = type;
while (unwrapped instanceof SerializableTypeProxy) {
unwrapped = ((SerializableTypeProxy) type).getTypeProvider().getType();
}
return (unwrapped != null ? (T) unwrapped : type);
}
获取 Type 实例的调用过程:
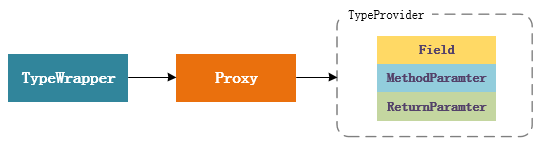
总结:
通过使用代理类的方式来获取具体的类型信息,特别是想要获取泛型相关的信息时,很直观。
接下来看下参数化类型 ParameterizedType 代理类:
public final class $Proxy0 extends Proxy implements ParameterizedType, SerializableTypeProxy, Serializable {
private static Method m1;
private static Method m6;
private static Method m5;
private static Method m2;
private static Method m7;
private static Method m3;
private static Method m4;
private static Method m0;
public $Proxy0(InvocationHandler var1) throws {
super(var1);
}
// public final boolean equals(Object var1) {...}
// public final String toString() {...}
// public final int hashCode() {...}
public final String getTypeName() throws {
try {
return (String)super.h.invoke(this, m6, (Object[])null);
} catch (RuntimeException | Error var2) {
throw var2;
} catch (Throwable var3) {
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var3);
}
}
public final Type getOwnerType() throws {
try {
return (Type)super.h.invoke(this, m5, (Object[])null);
} catch (RuntimeException | Error var2) {
throw var2;
} catch (Throwable var3) {
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var3);
}
}
public final TypeProvider getTypeProvider() throws {
try {
return (TypeProvider)super.h.invoke(this, m7, (Object[])null);
} catch (RuntimeException | Error var2) {
throw var2;
} catch (Throwable var3) {
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var3);
}
}
public final Type[] getActualTypeArguments() throws {
try {
return (Type[])super.h.invoke(this, m3, (Object[])null);
} catch (RuntimeException | Error var2) {
throw var2;
} catch (Throwable var3) {
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var3);
}
}
public final Type getRawType() throws {
try {
return (Type)super.h.invoke(this, m4, (Object[])null);
} catch (RuntimeException | Error var2) {
throw var2;
} catch (Throwable var3) {
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var3);
}
}
static {
try {
m1 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("equals", Class.forName("java.lang.Object"));
m6 = Class.forName("java.lang.reflect.ParameterizedType").getMethod("getTypeName");
m5 = Class.forName("java.lang.reflect.ParameterizedType").getMethod("getOwnerType");
m2 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("toString");
m7 = Class.forName("com.wiket.proxy.Client$SerializableTypeProxy").getMethod("getTypeProvider");
m3 = Class.forName("java.lang.reflect.ParameterizedType").getMethod("getActualTypeArguments");
m4 = Class.forName("java.lang.reflect.ParameterizedType").getMethod("getRawType");
m0 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("hashCode");
} catch (NoSuchMethodException var2) {
throw new NoSuchMethodError(var2.getMessage());
} catch (ClassNotFoundException var3) {
throw new NoClassDefFoundError(var3.getMessage());
}
}
}





 本文详细探讨了Java泛型的引入背景,Type接口及其子接口的功能与应用,包括ParameterizedType、GenericArrayType、TypeVariable和WildcardType。通过具体示例,讲解了泛型在实际编程中的作用与优势。
本文详细探讨了Java泛型的引入背景,Type接口及其子接口的功能与应用,包括ParameterizedType、GenericArrayType、TypeVariable和WildcardType。通过具体示例,讲解了泛型在实际编程中的作用与优势。
















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








