Lurcache源码深入分析
前言:本篇博客基于Lurcache源码分析安卓缓存实现原理,同时分析基于其内部实现的LinkedHashMap、Hash原理、Hash碰撞、如何解决Hash碰撞等问题。
目录
2.使用方法:
3.源码分析:
5.代码验证:
一、Lrucache概述:
- LRU (Least Recently Used) 即最近最少使用算法。在Android开发中,LruCache是基于LRU算法实现的。当缓存空间使用完的情况下,最久没被使用的对象会被清除出缓存。
- LruCache常用的场景是做图片内存缓存,电商类APP经常会用到图片,当我们对图片资源做了内存缓存,不仅可以增强用户体验,而且可以减少图片网络请求,减少用户流量耗费。
- LruCache是一个内存层面的缓存,如果想要进行本地磁盘缓存,推荐使用DiskLruCache(文末进行介绍),虽然没包含在官方API中,但是官方推荐我们使用。
二、使用方法:
package com.example.codeapplication;
import android.graphics.Bitmap;
import android.util.LruCache;
public class BitmapLurCache extends LruCache<String, Bitmap> {
/**
* @param maxSize for caches that do not override {@link #sizeOf}, this is
* the maximum number of entries in the cache. For all other caches,
* this is the maximum sum of the sizes of the entries in this cache.
* 设置缓存大小,建议当前应用可用最大内存的八分之一 即(int) (Runtime.getRuntime().maxMemory() / 1024 / 8)
*/
public BitmapLurCache(int maxSize) {
super(maxSize);
}
//计算当前节点的内存大小 这个方法需要重写 不然返回1
@Override
protected int sizeOf(String key, Bitmap value) {
return value.getByteCount()/1024;
}
//当节点移除时该方法会回调,可根据需求来决定是否重写该方法
@Override
protected void entryRemoved(boolean evicted, String key, Bitmap oldValue, Bitmap newValue) {
super.entryRemoved(evicted, key, oldValue, newValue);
}
}三、源码分析:
Lrucache构造方法:Look Look
/**
* @param maxSize for caches that do not override {@link #sizeOf}, this is
* the maximum number of entries in the cache. For all other caches,
* this is the maximum sum of the sizes of the entries in this cache.
*/
public LruCache(int maxSize) {
if (maxSize <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("maxSize <= 0");
}
this.maxSize = maxSize;
//我们发现实现用的是LinkedHashMap 注意最后的true 表示LinkedHashMap 中accessOrder设置为true
this.map = new LinkedHashMap<K, V>(0, 0.75f, true);
} /**
* Constructs an empty <tt>LinkedHashMap</tt> instance with the
* specified initial capacity, load factor and ordering mode.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity
* @param loadFactor the load factor
* @param accessOrder the ordering mode - <tt>true</tt> for
* access-order, <tt>false</tt> for insertion-order
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative
* or the load factor is nonpositive
*/
public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity,
float loadFactor,
boolean accessOrder) {
super(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
this.accessOrder = accessOrder;
}put方法源码:
/**
* Caches {@code value} for {@code key}. The value is moved to the head of
* the queue.
*
* @return the previous value mapped by {@code key}.
*/
public final V put(K key, V value) {
if (key == null || value == null) {//不允许key 和 value 为 null
throw new NullPointerException("key == null || value == null");
}
V previous;
synchronized (this) {//多线程安全
putCount++;
//size 表示当期使用的缓存大小 safeSizeOf 会掉用sizeOf方法 用于计算当前节点的大小
size += safeSizeOf(key, value);
// 将新节点放入LinkedHashMap 如果有返回值,表示map集合中存在旧值
previous = map.put(key, value);
if (previous != null) {//存在旧值 在移除旧值后 更新缓存大小
size -= safeSizeOf(key, previous);
}
}
//有旧值移除 回调entryRemoved
if (previous != null) {
entryRemoved(false, key, previous, value);
}
trimToSize(maxSize);//整理每个节点 主要判断当前size是否超过maxSize
return previous;
}
public void trimToSize(int maxSize) {
while (true) {
K key;
V value;
synchronized (this) {
if (size < 0 || (map.isEmpty() && size != 0)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(getClass().getName()
+ ".sizeOf() is reporting inconsistent results!");
}
//size <= maxSize 停止遍历列表,不然继续遍历列表修剪节点。
if (size <= maxSize || map.isEmpty()) {
break;
}
Map.Entry<K, V> toEvict = map.entrySet().iterator().next();
key = toEvict.getKey();
value = toEvict.getValue();
map.remove(key);
size -= safeSizeOf(key, value);
evictionCount++;
}
entryRemoved(true, key, value, null);
}
}
private int safeSizeOf(K key, V value) {
int result = sizeOf(key, value);//调用了sizeOf方法
if (result < 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Negative size: " + key + "=" + value);
}
return result;
}
//sizeOf的默认实现
protected int sizeOf(K key, V value) {
return 1;
}
//entryRemoved的默认实现
protected void entryRemoved(boolean evicted, K key, V oldValue, V newValue) {}get方法源码:
/**
* Returns the value for {@code key} if it exists in the cache or can be
* created by {@code #create}. If a value was returned, it is moved to the
* head of the queue. This returns null if a value is not cached and cannot
* be created.
*/
public final V get(K key) {
if (key == null) {//key不能为 null
throw new NullPointerException("key == null");
}
V mapValue;
synchronized (this) {//线程同步
mapValue = map.get(key);//调用LinkedHashMap 的get方法
if (mapValue != null) {
hitCount++;
return mapValue;//找到返回
}
missCount++;
}
/*
* Attempt to create a value. This may take a long time, and the map
* may be different when create() returns. If a conflicting value was
* added to the map while create() was working, we leave that value in
* the map and release the created value.
*/
V createdValue = create(key);//缓存没有情况下走创建流程
if (createdValue == null) {
return null;
}
synchronized (this) {
createCount++;
mapValue = map.put(key, createdValue);
if (mapValue != null) {
// There was a conflict so undo that last put
map.put(key, mapValue);
} else {
size += safeSizeOf(key, createdValue);
}
}
if (mapValue != null) {
entryRemoved(false, key, createdValue, mapValue);
return mapValue;
} else {
trimToSize(maxSize);
return createdValue;
}
}
//创建方法默认空实现 可根据需求决定是否重写该方法
protected V create(K key) {
return null;
}remove方法源码:
/**
* Removes the entry for {@code key} if it exists.
*
* @return the previous value mapped by {@code key}.
*/
public final V remove(K key) {
if (key == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("key == null");
}
V previous;
synchronized (this) {//线程同步
previous = map.remove(key);//获得移除的节点
if (previous != null) {//当节点不为空 更新缓存大小
size -= safeSizeOf(key, previous);
}
}
if (previous != null) {
//当节点移除时回调entryRemoved方法
entryRemoved(false, key, previous, null);
}
return previous;
}通过对上述几个方法源代码分析,我们知道LruCache如何控制及更新缓存的大小的,主要是在线程同步块里对size字段进行更新,然后根据size字段和maxSize字段的大小关系来修剪节点。但如何做到最近最少使用呢?LinkedHashMap 帮我们做到最近最少使用的排序。
四、LinkedHashMap的实现:
//继承了HashMap 说明LinkedHashMap 的查找效率依然是O(1)
public class LinkedHashMap<K,V>
extends HashMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>
{
//重新定义了节点 用于实现链表
private transient LinkedHashMapEntry<K,V> header;
private static class LinkedHashMapEntry<K,V> extends HashMapEntry<K,V> {
LinkedHashMapEntry<K,V> before, after;
}
}LinkedHashMap并没有重写HashMap的put方法,下面看HashMap的实现:
public V put(K key, V value) {
if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) {
inflateTable(threshold);
}
if (key == null)
//HashMap的特点 可以放key为null的值
return putForNullKey(value);
//得到hash值
int hash = sun.misc.Hashing.singleWordWangJenkinsHash(key);
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
for (HashMapEntry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;//存在旧值 就把旧值移除掉 并返回旧值 由此可知 当我们更换缓存中已存在的值时,并不会影响它在链表中位置
}
}
modCount++;
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);//LinkedHashMap 重写了该方法
return null;
}
//LinkedHashMap中实现
/**
* This override alters behavior of superclass put method. It causes newly
* allocated entry to get inserted at the end of the linked list and
* removes the eldest entry if appropriate.
*/
//将节点放在链表的末尾
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
// Remove eldest entry if instructed
LinkedHashMapEntry<K,V> eldest = header.after;
if (eldest != header) {
boolean removeEldest;
size++;
try {
removeEldest = removeEldestEntry(eldest);//hook 默认为false 让用户重写removeEldestEntry 来决定是否移除eldest节点
} finally {
size--;
}
if (removeEldest) {
removeEntryForKey(eldest.key);
}
}
super.addEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);
}
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<K,V> eldest) {
return false;
}
//HashMap中addEntry:
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) {
resize(2 * table.length);
hash = (null != key) ? sun.misc.Hashing.singleWordWangJenkinsHash(key) : 0;
bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length);
}
//LinkedHashMap重写了该方法
createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);
}
//LinkedHashMap中
void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
HashMapEntry<K,V> old = table[bucketIndex];
LinkedHashMapEntry<K,V> e = new LinkedHashMapEntry<>(hash, key, value, old);
table[bucketIndex] = e;
//把该节点插入到链表头部 最近使用访问到的在最前边原则
e.addBefore(header);
size++;
}
LinkedHashMap重写了get方法:
public V get(Object key) {
//使用HashMap的getEntry方法,验证了我们所说的查询效率为O(1)
LinkedHashMapEntry<K,V> e = (LinkedHashMapEntry<K,V>)getEntry(key);
if (e == null)
return null;
e.recordAccess(this);//在找到节点后调用节点recordAccess方法
return e.value;
}
//LinkedHashMapEntry
void recordAccess(HashMap<K,V> m) {
LinkedHashMap<K,V> lm = (LinkedHashMap<K,V>)m;
if (lm.accessOrder) {//accessOrder该值默认为false 但是 在LruCache中设置为true
lm.modCount++;
remove();//该方法将本身节点移除链表
addBefore(lm.header);//将自己添加到节点尾部 保证最近使用的节点位于链表末尾
}
}LinkedHashMap的并没有重写HashMap的remove方法,依然是调用HashMap的remove方法,代码如下:
public V remove(Object key) {
Entry<K,V> e = removeEntryForKey(key);
return (e == null ? null : e.getValue());
}
final Entry<K,V> removeEntryForKey(Object key) {
if (size == 0) {
return null;
}
int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : sun.misc.Hashing.singleWordWangJenkinsHash(key);
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
HashMapEntry<K,V> prev = table[i];
HashMapEntry<K,V> e = prev;
while (e != null) {
HashMapEntry<K,V> next = e.next;
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) {
modCount++;
size--;
if (prev == e)
table[i] = next;
else
prev.next = next;
//注意这一行 开头我们说过 LinkedHashMap用的节点是自己定义的LinkedHashMapEntry ,继承自HashMapEntry
e.recordRemoval(this);
return e;
}
prev = e;
e = next;
}
return e;
}
//LinkedHashMapEntry 中recordRemoval
void recordRemoval(HashMap<K,V> m) {
remove();
}
private void remove() {//更改指针来移除自身
before.after = after;
after.before = before;
}总结:
- LruCache是继承自HashMap,它的查找效率依然是O(1);
- LruCache内部又维护了一个双向链表结构,当我们有访问操作时候,被访问节点会移到链表结尾;
- 在Lrucache的put、get和remove方法中,对集合操作时使用了synchronized关键字,来保证线程安全;
- LinkedHashMap重写的方法有:addEntry方法、createEntry方法、get方法
五、代码验证:
1.首先创建LRUCache,我们设置其大小为4:
private void test() {
LruCache<String,String> lruCache = new LruCache<>(4);
lruCache.put("a","这是第1个放进去的值");
lruCache.put("b","这是第2个放进去的值");
lruCache.put("c","这是第3个放进去的值");
lruCache.put("d","这是第4个放进去的值");
print(lruCache);
}
private void print(LruCache<String,String> lruCache){
Map map =lruCache.snapshot();
Iterator<String> iterator = map.keySet().iterator();
String key;
while (iterator.hasNext()){
key = iterator.next();
Log.i("LruCacheItem","key ="+key+" value ="+map.get(key));
}
}输出结果:
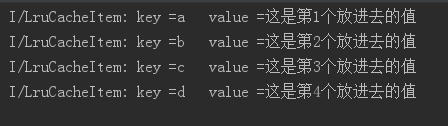
2.当我们访问链表中一个元素时候,该元素会移到队列末尾,测试如下:
private void test() {
LruCache<String,String> lruCache = new LruCache<>(4);
lruCache.put("a","这是第1个放进去的值");
lruCache.put("b","这是第2个放进去的值");
lruCache.put("c","这是第3个放进去的值");
lruCache.put("d","这是第4个放进去的值");
lruCache.get("c");
print(lruCache);
}输出结果:
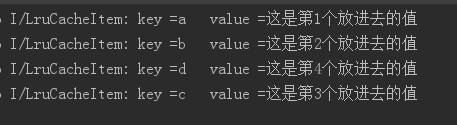
3.当我们放入元素超过总的大小时,队列首部元素会被移除:
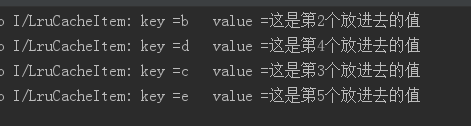
private void test() {
LruCache<String,String> lruCache = new LruCache<>(4);
lruCache.put("a","这是第1个放进去的值");
lruCache.put("b","这是第2个放进去的值");
lruCache.put("c","这是第3个放进去的值");
lruCache.put("d","这是第4个放进去的值");
lruCache.get("c");
lruCache.put("e","这是第5个放进去的值");
print(lruCache);
}输出结果:
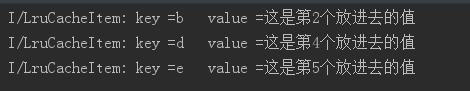
4.移除相对简单,不会改变队列里元素的相对顺序,只是该元素出队列而已,测试如下:
private void test() {
LruCache<String,String> lruCache = new LruCache<>(4);
lruCache.put("a","这是第1个放进去的值");
lruCache.put("b","这是第2个放进去的值");
lruCache.put("c","这是第3个放进去的值");
lruCache.put("d","这是第4个放进去的值");
lruCache.get("c");
lruCache.put("e","这是第5个放进去的值");
lruCache.remove("c");
print(lruCache);
}输出结果:
二、如何解决Hash冲突
在hash碰撞的情况下,主要的处理方法有:
1. 开放地址法
开放地执法有一个公式:Hi=(H(key)+di) MOD m i=1,2,…,k(k<=m-1)
基本思想:当发生地址冲突时,按照某种方法继续探测哈希表中的其他存储单元,直到找到空位置为止。
- 线性探测再散列 di=1,2,3,…,m-1 这种方法的特点是:冲突发生时,顺序查看表中下一单元,直到找出一个空单元或查遍全表。
- 二次探测再散列
,
,
,
... 这种方法的特点是:冲突发生时,在表的左右进行跳跃式探测,比较灵活。
- 伪随机探测再散列 di=伪随机数序列
2. rehash(再hash法)
使用第二个或第三个...计算地址,直到无冲突。比如:按首字母进行hash冲突了,则按照首字母第二位,进行hash寻址。
3. 链地址法(拉链法)
创建一个链表数组,数组中每一格就是一个链表。若遇到哈希冲突,则将冲突的值加到链表中即可。java hashmap使用的就是拉链法解决hash碰撞。
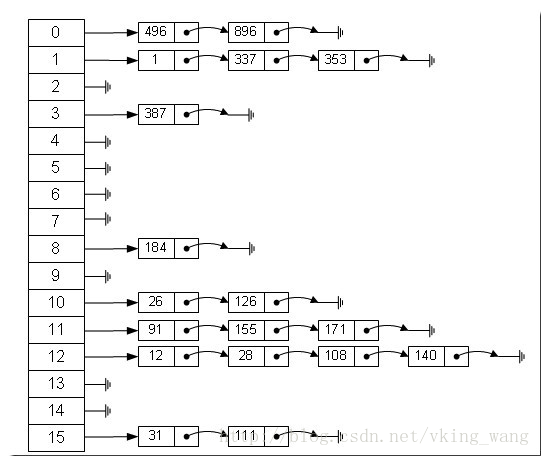
哈希表是由链表+数组组成
通过hash(key)%len存储到相对应的数组中,如140%16=12.意味着数组下标相同,并不表示hashCode相同。
三、DiskLruCache介绍
概述:
- 缓存的
key为String类型,且必须匹配正则表达式[a-z0-9_-]{1,64}; - 一个key可以对应多个value,
value类型为字节数组,大小在0 ~ Integer.MAX_VALUE之间; - 缓存的目录必须为专用目录,因为DiskLruCache可能会删除或覆盖该目录下的文件。
- 添加缓存操作具备原子性,但多个进程不应该同时使用同一个缓存目录。
1.添加依赖:
// add dependence
implementation 'com.jakewharton:disklrucache:2.0.2'2.创建DiskLruCache对象:
/*
* directory – 缓存目录
* appVersion - 缓存版本
* valueCount – 每个key对应value的个数
* maxSize – 缓存大小的上限
*/
DiskLruCache diskLruCache = DiskLruCache.open(directory, 1, 1, 1024 * 1024 * 10);3.添加/获取缓存:
/**
* 添加一条缓存,一个key对应一个value
*/
public void addDiskCache(String key, String value) throws IOException {
File cacheDir = context.getCacheDir();//得到系统缓存目录
DiskLruCache diskLruCache = DiskLruCache.open(cacheDir, 1, 1, 1024 * 1024 * 10);//通过系统缓存目录,得到专有缓存目录
DiskLruCache.Editor editor = diskLruCache.edit(key);//得到编辑者
// index与valueCount对应,分别为0,1,2...valueCount-1
editor.newOutputStream(0).write(value.getBytes());//value是字节数组类型
editor.commit();//提交
diskLruCache.close();//关闭
}4.获取缓存:
/**
* 获取一条缓存,一个key对应一个value
*/
public void getDiskCache(String key) throws IOException {
File directory = context.getCacheDir();
DiskLruCache diskLruCache = DiskLruCache.open(directory, 1, 1, 1024 * 1024 * 10);
String value = diskLruCache.get(key).getString(0);
diskLruCache.close();
}5.添加/获取缓存(一对多)
/**
* 添加缓存,1个key对应2个value
*/
public void addDiskCache(String key, String value1, String value2) throws IOException {
File directory = context.getCacheDir();
DiskLruCache diskLruCache = DiskLruCache.open(directory, 1, 2, 1024 * 1024 * 10);
DiskLruCache.Editor editor = diskLruCache.edit(key);
editor.newOutputStream(0).write(value1.getBytes());
editor.newOutputStream(1).write(value2.getBytes());
editor.commit();
diskLruCache.close();
}/**
* 获取缓存,1个key对应2个value
*/
public void getDiskCache(String key) throws IOException {
File directory = context.getCacheDir();
DiskLruCache diskLruCache = DiskLruCache.open(directory, 1, 2, 1024);
DiskLruCache.Snapshot snapshot = diskLruCache.get(key);
String value1 = snapshot.getString(0);
String value2 = snapshot.getString(1);
diskLruCache.close();
}





 本文深入解析LRU缓存算法在Android中的实现原理,包括LruCache的使用方法、内部结构、LinkedHashMap的定制以及如何解决哈希冲突。同时介绍了DiskLruCache的使用,适合于本地磁盘缓存。
本文深入解析LRU缓存算法在Android中的实现原理,包括LruCache的使用方法、内部结构、LinkedHashMap的定制以及如何解决哈希冲突。同时介绍了DiskLruCache的使用,适合于本地磁盘缓存。
















 6067
6067

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








