What are the differences of Java methods start and run, or what is the need to run the thread through start method? Why not we call directly run method?
1. Thread (object) as a scheduling unit.
public void start() - The name may seem to be a misnomer here as this method only causes and not actually starts the execution. start() methods only schedules the thread for execution and not actually begins the execution of the thread.
This method will obviously result into two concurrent threads - one, from which this method is called and two, the new thread which executes the run() method of the new Thread instance.
If you don’t use run() method provided in JAVA then it will be as same as calling a general function, it is no longer a thread then.
2. Each thread starts in a separate call stack.
Invoking function run() method directly (same as running thread without run() method), the method goes onto the current call stack rather than at the beginning of a new call stack.
The start method is a natively implemented method that creates a seperate thread and then calls the thread's run() method, executing the code in the new thread.
3. You need to know that thread can have different states.
new - thread was created and can be started
runnable(可以运行的,就绪的) - thread is executing
running - The thread is in running state if the thread scheduler has selected it.
waiting - thread is waiting for other thread to finish; other thread will have to inform this thread that it finished by calling for example notify method on shared lock
timed waiting - similar to waiting but thread will stop waiting after some time automatically without waiting for signal from other thread
terminated - or dead. thread finished its task
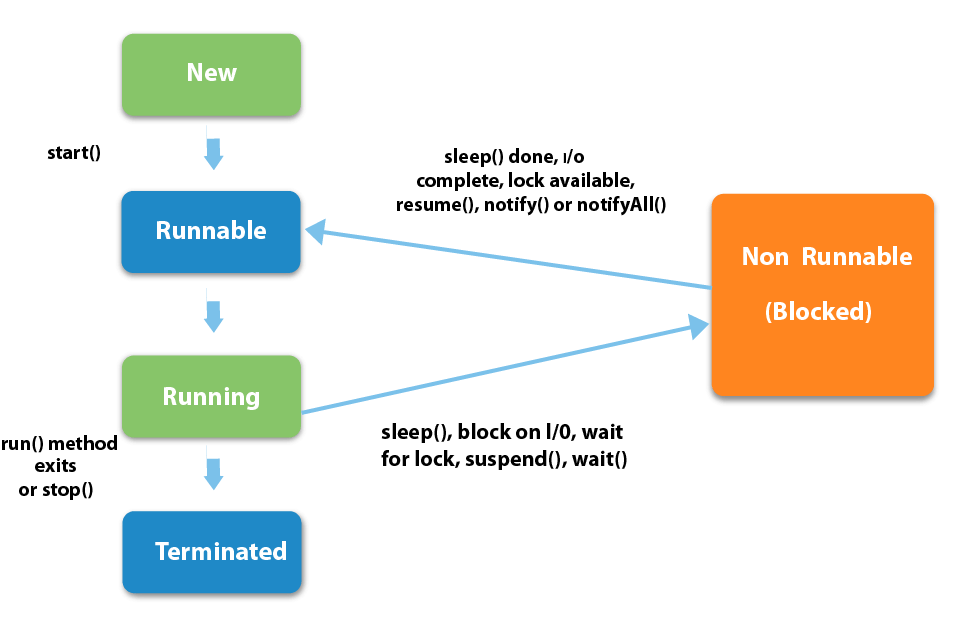
Life cycle of a thread (thread states) (a)
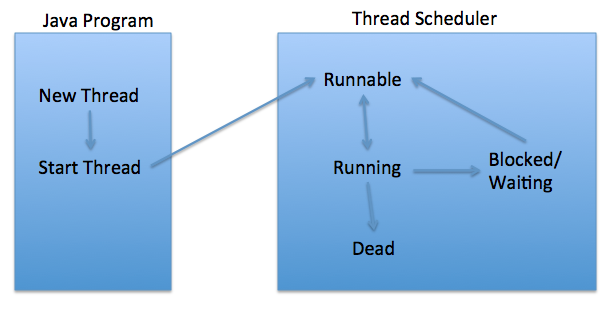
Life cycle of a thread (thread states) (b)
run method contains only code which needs to be executed when thread will work (when it will be in runnable state).
start method is needed to take care of changing state of threat from new to runnable so it could start working and use its (the invoked thread's) own resources (processor-time for instance) to execute code from run method.
When you call yourThread.run() code from run method will be executed by thread which invoked this method, but if you use yourThread.start() then code from run method will be executed using resources of yourThread.




 本文详细阐述了Java中线程的start和run方法的区别。start方法会创建并调度线程执行,而直接调用run方法只会将其当作普通方法执行。理解线程的不同状态(新建、可运行、运行、等待、超时等待、终止)对于正确管理线程至关重要。使用start方法能确保线程在适当的环境中运行,避免阻塞当前调用栈。
本文详细阐述了Java中线程的start和run方法的区别。start方法会创建并调度线程执行,而直接调用run方法只会将其当作普通方法执行。理解线程的不同状态(新建、可运行、运行、等待、超时等待、终止)对于正确管理线程至关重要。使用start方法能确保线程在适当的环境中运行,避免阻塞当前调用栈。
















 6892
6892

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








