原文:http://blog.youkuaiyun.com/guyongqiangx/article/details/72604355,感谢作者的辛勤付出
Android从7.0开始引入新的OTA升级方式,A/B System Updates,这里将其叫做A/B系统,涉及的内容较多,分多篇对A/B系统的各个方面进行分析。本文为第四篇,系统的启动和升级。
本文基于AOSP 7.1.1_r23 (NMF27D)代码进行分析。
1. 系统的启动
1.1 bootloader检查slot metadata
系统复位后,bootloader会去读取boot_control私有的存储数slot metadata并进行解析,以此确定从哪一个slot启动。
以下是android官方的一个bootloader加载流程图:
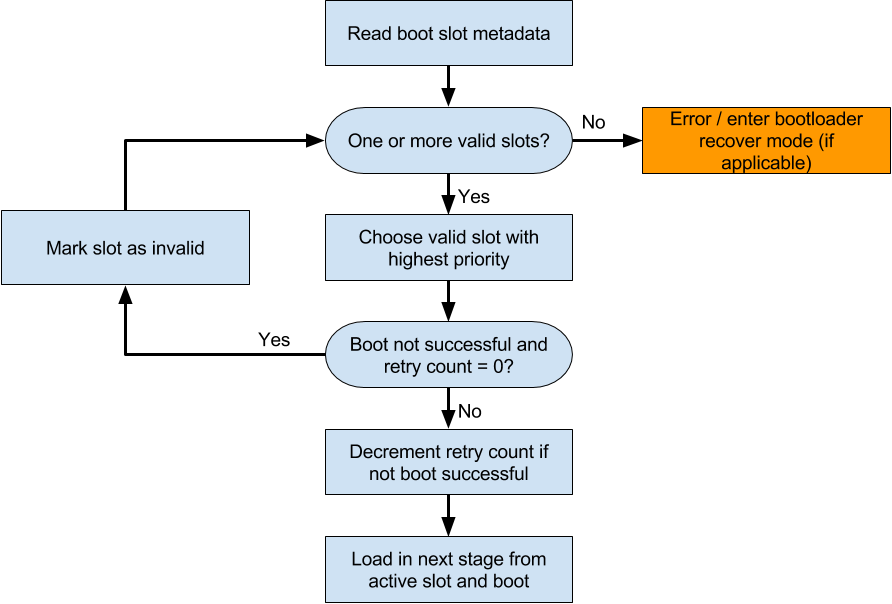
大致启动流程如下:
- 系统启动后,
bootloader读取分区元数据slot metadata; - 检查分区元数据中是否有可启动的分区,如果没有可启动分区,直接进入
bootloader的recovery mode(即bootloader下的刷机模式),一般是进入fastboot命令行; - 如果分区元数据中有可启动的分区,则选择所有可启动分区中优先级最高的
slot(例如,直接选择当前设置为active的分区); - 检查所选择分区的
retry count(retry count表示当前分区可以尝试启动的次数); - 如果当前选择分区的
retry count为0,且没有启动成功(启动成功的分区会标记为successful),则将所选择分区标记为无效分区(通常设置为unbootable),然后重复第2步,查找下一个可以启动的分区; - 如果当前选择的分区尝试启动次数
retry count不为0,则表示还可以继续尝试从当前分区启动,需要将其retry count进行递减,然后加载相应的slot进行启动;
1.2 linux系统的启动
上一步中,bootloader会根据slot metadata确定读取哪一个slot的boot分区进行启动。
每一个slot上有两个rootfs:
boot分区自带recovery mode的ramdisk;system分区包含了Android系统的rootfs;
启动中,如何选择加载boot分区的ramdisk还是system分区的rootfs呢?
答案是由kernel的命令行参数skip_initramfs来决定。
下面来看skip_initramfs参数是如何起作用的。
系统同时包含init\noinitramfs.c和init\initramfs.c的代码,并在initramfs.c模块中定义并解析skip_initramfs参数:
# init\initramfs.c
static int __initdata do_skip_initramfs;
static int __init skip_initramfs_param(char *str)
{
if (*str)
return 0;
# 设置do_skip_initramfs标志
do_skip_initramfs = 1;
return 1;
}
# 用于解析命令行的`skip_initramfs`参数
__setup("skip_initramfs", skip_initramfs_param);
如果命令行设置了skip_initramfs,则do_skip_initramfs会被设置为1。
Linux调用populate_rootfs默认会并加载boot分区自带的ramdisk,但如果do_skip_initramfs被
设置为1,则调用default_rootfs生成一个极小的rootfs:
# init\initramfs.c
static int __init populate_rootfs(void)
{
char *err;
# 如果do_skip_initramfs置1,则调用default_rootfs生成一个极小的rootfs
if (do_skip_initramfs)
return default_rootfs();
# 没有设置do_skip_initramfs的情况下,才会解析并加载`boot`分区所包含的`ramdisk`
err = unpack_to_rootfs(__initramfs_start, __initramfs_size);
if (err)
panic("%s", err); /* Failed to decompress INTERNAL initramfs */
...
return 0;
}
default_rootfs的内容很简单,用于在内存中生成一个极小的rootfs,仅包含/dev和root两个文件夹以及一个设备节点/dev/console:
# init\noinitramfs.c
/*
* Create a simple rootfs that is similar to the default initramfs
*/
static int __init default_rootfs(void)
{
int err;
# 创建/dev文件夹用于存放/dev/console设备节点
err = sys_mkdir((const char __user __force *) "/dev", 0755);
if (err < 0)
goto out;
# 创建/dev/console设备节点
err = sys_mknod((const char __user __force *) "/dev/console",
S_IFCHR | S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR,
new_encode_dev(MKDEV(5, 1)));
if (err < 0)
goto out;
# 创建/root目录,作为根用户root的home
err = sys_mkdir((const char __user __force *) "/root", 0700);
if (err < 0)
goto out;
return 0;
out:
printk(KERN_WARNING "Failed to create a rootfs\n");
return err;
}
因此skip_initramfs参数决定了加载哪一个rootfs,进入哪一个系统。
-
加载
android系统的命令行参数
skip_initramfs rootwait ro init=/init root="/dev/dm-0 dm=system none ro,0 1 android-verity <public-key-id> <path-to-system-partition>"
例如Broadcom的7252SSFFDR3参考平台的启动Android系统的参数为:mem=1016m@0m mem=1024m@2048m bmem=339m@669m bmem=237m@2048m \ brcm_cma=784m@2288m \ ramoops.mem_address=0x3F800000 ramoops.mem_size=0x800000 ramoops.console_size=0x400000 \ buildvariant=userdebug \ veritykeyid=id:7e4333f9bba00adfe0ede979e28ed1920492b40f buildvariant=eng \ rootwait init=/init ro \ root=/dev/dm-0 dm="system none ro,0 1 android-verity PARTUUID=c49e0acb-1b38-95e5-548a-2b7260e704a4" skip_initramfs除去
rootfs不相关的参数,看起来是这样的:
rootwait init=/init ro root=/dev/dm-0 dm="system none ro,0 1 android-verity PARTUUID=c49e0acb-1b38-95e5-548a-2b7260e704a4" skip_initramfs
命令行中,文件系统的
root设备由参数root="/dev/dm-0 dm=system none ro,0 1 android-verity <public-key-id> <path-to-system-partition>"指定,显然,这里的root参数设置将设备名设置为/dev/dm-0,至于设备/dev/dm-0是一个什么设备,作用为何,属于另一个话题dm-verity,此处不再展开讨论。
-
加载
recovery系统的命令行参数
rootwait init=/init ro
例如Broadcom的7252SSFFDR3参考平台的启动Recovery的参数为:mem=1016m@0m mem=1024m@2048m bmem=339m@669m bmem=237m@2048m \ brcm_cma=784m@2288m \ ramoops.mem_address=0x3F800000 ramoops.mem_size=0x800000 ramoops.console_size=0x400000 \ rootwait init=/init ro \ buildvariant=userdebug veritykeyid=id:7e4333f9bba00adfe0ede979e28ed1920492b40f buildvariant=eng除去
rootfs不相关的参数,看起来是这样的:
rootwait init=/init ro
默认
linux是不支持参数skip_initramfs参数的,Android系统中为了跳过boot分区的ramdisk,引入了这个命令行参数,参考以下提交:
1.3 Android系统的启动
linux启动后,通过dm-verify机制校验system分区,完成后加载system分区内包含的rootfs,通过/init程序解析/init.rc脚本,完成Android系统的启动。
这部分的启动过程跟传统的系统启动是一样的。
1.4 Recovery系统的启动
linux启动后,根据参数,加载boot分区的ramdisk,通过/init程序解析/init.rc脚本,启动Recovery系统。
这部分的启动过程跟传统的Recovery系统启动是一样的。
2. 系统的升级
A/B系统升级包的制作方式跟传统系统升级包制作方式基本一致,主要分为两步:
- 编译系统文件
- 制作升级包
升级方式根据升级包的内容分为两种:
- 完整升级,升级包包含完整的系统,对内容进行全新升级;
- 增量升级/差分升级,升级包仅包含跟当前系统不一样的内容,对系统进行打补丁式升级;
2.1 完整升级
-
升级包的制作
-
第一步,编译系统
$ source build/envsetup.sh $ lunch bcm7252ssffdr4-userdebug $ mkdir dist_output $ make -j32 dist DIST_DIR=dist_output [...] $ ls -lh dist-output/*target_files* -rw-r--r-- 1 ygu users 566M May 21 14:49 bcm7252ssffdr4-target_files-eng.ygu.zip -
第二步,制作安装包
$ ./build/tools/releasetools/ota_from_target_files dist-output/bcm7252ssffdr4-target_files-eng.ygu.zip full-ota.zip $ ls -lh dist-output -rw-r--r-- 1 ygu users 270M May 21 14:51 full-ota.zip
-
-
升级包的内容
解压缩
full-ota.zip可以看到其内容:$ mkdir full-ota $ unzip full-ota.zip -d full-ota Archive: full-ota.zip signed by SignApk extracting: full-ota/payload.bin inflating: full-ota/META-INF/com/android/metadata inflating: full-ota/care_map.txt inflating: full-ota/payload_properties.txt inflating: full-ota/META-INF/com/android/otacert inflating: full-ota/META-INF/MANIFEST.MF inflating: full-ota/META-INF/CERT.SF inflating: full-ota/META-INF/CERT.RSA $ ls -lh full-ota total 270M drwxr-sr-x 3 ygu users 4.0K May 21 18:14 META-INF -rw-r--r-- 1 ygu users 36 Jan 1 2009 care_map.txt -rw-r--r-- 1 ygu users 270M Jan 1 2009 payload.bin -rw-r--r-- 1 ygu users 154 Jan 1 2009 payload_properties.txt $ tree -l full-ota full-ota |-- META-INF | |-- CERT.RSA | |-- CERT.SF | |-- MANIFEST.MF | `-- com | `-- android | |-- metadata | `-- otacert |-- care_map.txt |-- payload.bin `-- payload_properties.txt 3 directories, 8 files其中,
payload.bin是系统要更新的数据文件,payload_properties.txt包含了升级内容的一些属性信息,如下:$ cat full-ota/payload_properties.txt FILE_HASH=ozGgyQEcnkI5ZaX+Wbjo5I/PCR7PEZka9fGd0nWa+oY= FILE_SIZE=282164983 METADATA_HASH=GLIKfE6KRwylWMHsNadG/Q8iy5f7ENWTatvMdBlpoPg= METADATA_SIZE=21023升级时会使用到
payload_properties.txt里面的信息。 -
系统包的使用
A/B系统在debug模式下会包含升级应用update_engine_client,其参数如下:bcm7252ssffdr4:/ # which update_engine_client /system/bin/update_engine_client bcm7252ssffdr4:/ # update_engine_client --help Android Update Engine Client --cancel (Cancel the ongoing update and exit.) type: bool default: false --follow (Follow status update changes until a final state is reached. Exit status is 0 if the update succeeded, and 1 otherwise.) type: bool default: false --headers (A list of key-value pairs, one element of the list per line. Used when --update is passed.) type: string default: "" --help (Show this help message) type: bool default: false --offset (The offset in the payload where the CrAU update starts. Used when --update is passed.) type: int64 default: 0 --payload (The URI to the update payload to use.) type: string default: "http://127.0.0.1:8080/payload" --reset_status (Reset an already applied update and exit.) type: bool default: false --resume (Resume a suspended update.) type: bool default: false --size (The size of the CrAU part of the payload. If 0 is passed, it will be autodetected. Used when --update is passed.) type: int64 default: 0 --suspend (Suspend an ongoing update and exit.) type: bool default: false --update (Start a new update, if no update in progress.) type: bool default: false将
payload.bin文件放到可以通过http访问的地方,然后在命令行调用update_engine_client进行升级:bcm7252ssffdr4:/ # update_engine_client \ --payload=http://stbszx-bld-5/public/android/full-ota/payload.bin \ --update \ --headers="\ FILE_HASH=ozGgyQEcnkI5ZaX+Wbjo5I/PCR7PEZka9fGd0nWa+oY= \ FILE_SIZE=282164983 METADATA_HASH=GLIKfE6KRwylWMHsNadG/Q8iy5f7ENWTatvMdBlpoPg= \ METADATA_SIZE=21023 \ "其中
headers选项需要填写payload_properties.txt文件的内容。
2.2 增量升级/差分升级
差分包升级与完整包升级除了升级包的制作不一样之外,生成的升级包文件内容一样,使用update_engine_client进行升级的操作也完全一样,因此这里仅说明差分包的制作。
差分升级包的制作
-
第一步,对
android进行改动并编译系统差分升级时,需要保留原有系统的生成文件,然后修改后生成新的系统文件,这里假定原有系统生成文件位于:dist_output,修改后生成的系统文件位于dist_output-new,编译方式跟完整包的生成方式一样。
$ source build/envsetup.sh $ lunch bcm7252ssffdr4-userdebug $ mkdir dist_output $ make -j32 dist DIST_DIR=dist_output [...] $ ls -lh dist-output-new/*target_files* -rw-r--r-- 1 ygu users 566M May 21 15:27 bcm7252ssffdr4-target_files-eng.ygu.zip -
第二步,制作安装包
对比原有系统文件和修改后的系统文件生成差分包,这里通过
-i指定差分包生成的基线(baseline)。$./build/tools/releasetools/ota_from_target_files \ -i dist-output/bcm7252ssffdr4-target_files-eng.ygu.zip \ dist-output-new/bcm7252ssffdr4-target_files-eng.ygu.zip \ incremental-ota.zip
2.3 升级日志样本
调用update_engine_client进行升级后可以通过logcat查看其升级日志,如:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
以上logcat信息已经去掉了时间戳,原始的log信息请参考:update_engine_client log
update_engine更新操作成功后会提示Update successfully applied, waiting to reboot.,要求系统进行重启,重启后会设置相应分区slot的属性为successful,表明系统能够成功启动。
重启系统,检查Android系统的编译版本和时间戳,验证升级是否成功。






















 1547
1547

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








