目录
3)关键字:is null或者、is not null和<>null和!=null
十二、查询时加锁(select xxx for update)
一、查询的完全限定写法
select 表名.列名 from 数据库.表名; //完全引用表名或列名
二、条件查询
select * from 表名 where 条件 [group by] [having] [order by] [limit];
三、模糊查询
关键字:like
说明:
通配符%代表任意多个字符,_代表任意单个字符;
转义符\,防止后面的_被当成通配符
例子:
select * from 表名 where name like %teve%'';
select * from 表名 where name like _\_%'';
四、范围查询
1)关键字:between and
不使用between and
select * from 表名 where id>=4 and id;
使用between and
select * from 表名 where id between 4 and 6;
2)关键字:in
不使用in
select * from 表名 where age =20 or age=21 or age=23;
使用in
select * from 表名 where age in(20,21,23);
3)关键字:is null或者、is not null和<>null和!=null
select * from 表名 where age is not ‘null’;
select * from 表名 where age <>‘null’; //注意要加引号
五、case when
1)方式1
select sid,
case sage
when 18 then '18岁'
when then '19岁'
else '其他'
end as '年龄查询'
2)方式2
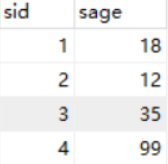
select sid,
case
when sage< 18 then '小'
when sage>18 then '大'
else null
end as '年龄查询'
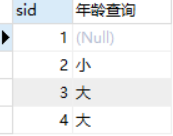
六、排序查询
语法
select 查询列表 from 表 where 条件 order by 排序列表 asc/desc; //asc升序,由小到大;desc降序,由大到小
例子
select * from 表名 order by salary asc, employee_id desc; //先按工资升序,再按员工编号降序
七、分组查询
1)用到分组函数
sum、avg、min、max、count
2)分组查询语法
select 分组函数(要统计的列),列1,列2 where 分组前筛选条件 group by 分组列表 order by 子句 having 分组后筛选条件;
3)分组查询特点
分组查询中的筛选条件分为两类
| 数据源 | 位置 | 关键字 | |
| 分组前筛选 | 原始表 | group by 子句的前面 | where |
| 分组后筛选 | 分组后的结果集 | group by 子句的后面 | having |
4)例子
例子1:查询课程总量(不重复)
select count(distinct courseName) from 表名;
例子2:查询平均工资
select avg(salary) from 表名;
例子4:查询每个工种的最高工资
select max(salary),job_id,job_name from 表名 group by job_id;
例子5:查询每个位置上的部门个数
select count(*),location_id from department group by location_id;
例子6:查询哪个部门的员工个数>=2
(1)查询每个部门的员工个数
select count(*),department_id from 表名 group by department_id;
(2)根据一的结果进行筛选,查询哪个部门员工个数>=2
select count(*),department_id from 表名 group by department_id having count(*)>=2;
例子7:查询每个工种有奖金的员工的最高工资>12000的工种编号和最高工资
(1)查询每个工种有奖金的员工的最高工资
select max(salary),job_id from 表名 where commission_pct is not 'null' group by job_id;
(2)根据一的结果进行筛选,筛选出最高工资>12000
select max(salary),job_id from 表名 where commission_pct is not 'null' group by job_id having max(salary)>12000;
例子8:按多个字段进行分组
题目:查询每个部门每个工种的员工的平均工资
select avg(salary),department_id,job_id from group by department_id,job_id;
八、连接查询
1)分类
内连接(inner join)、外连接(左和右)、交叉连接(cross join)、全连接(full join)
2)内连接(inner join)
特点:取两张表查询结果的交集
分类:内连接又分为等值连接、非等值连接和自连接
补充:内连接的inner join中的inner可以省略。
1.等值连接
语法:
select tab1.col1,tab2.col2 from tab1,tab2 where tab1.id =tab2.id;
select tab1.col1,tab2.col2 from tab1 inner join tab2 ON tab1.id =tab2.id;
例子1:查询哪个部门的员工数大于等于3的部门名和员工个数,并按个数降序。
select count(*) as 个数,department_name from employee e
inner join department d ON e.department_id =d.department_id
group by department_id having count(*)>=3 order by count(*) desc;
例子2(三表连接):查询员工名、部门名、工种名,并按部门名降序
select name,department_name,job_tietle from employee as e
inner join department as d on e.department_id =d.department_id
inner join jobs as j ON e.job_id =j.job_id
order by department_name desc;
2.非等值连接
例子:
select e.name,j.grade_level from employee as e inner jonin job_grade as j ON e.salary between j.lowest_sal and highest_sal;
3.自连接
一张表自己连接自己
例子:查询员工名和其上级的名称。
select e.name,m.name from employee as e inner join employee as m on e.mannager_id =m.id;
3)外连接(left、right)
左外连接:left outer join(特点:查询结果以左边表(主表)为准。左边表查出来有几条数据,一共就有几条数据)
右外连接:right outer join(特点:查询结果以右边表(主表)为准。右边表查出来有几条数据,一共就有几条数据)
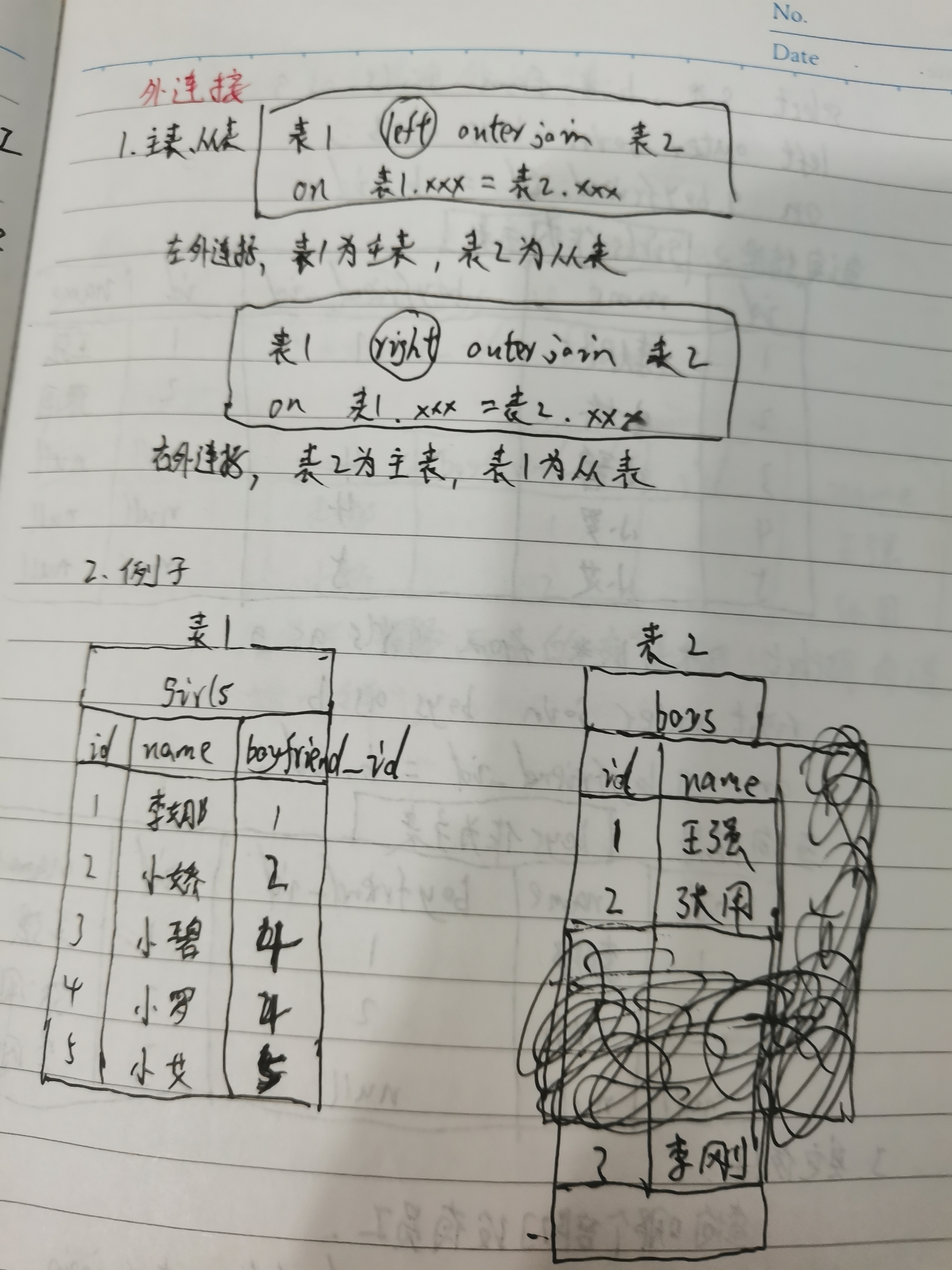
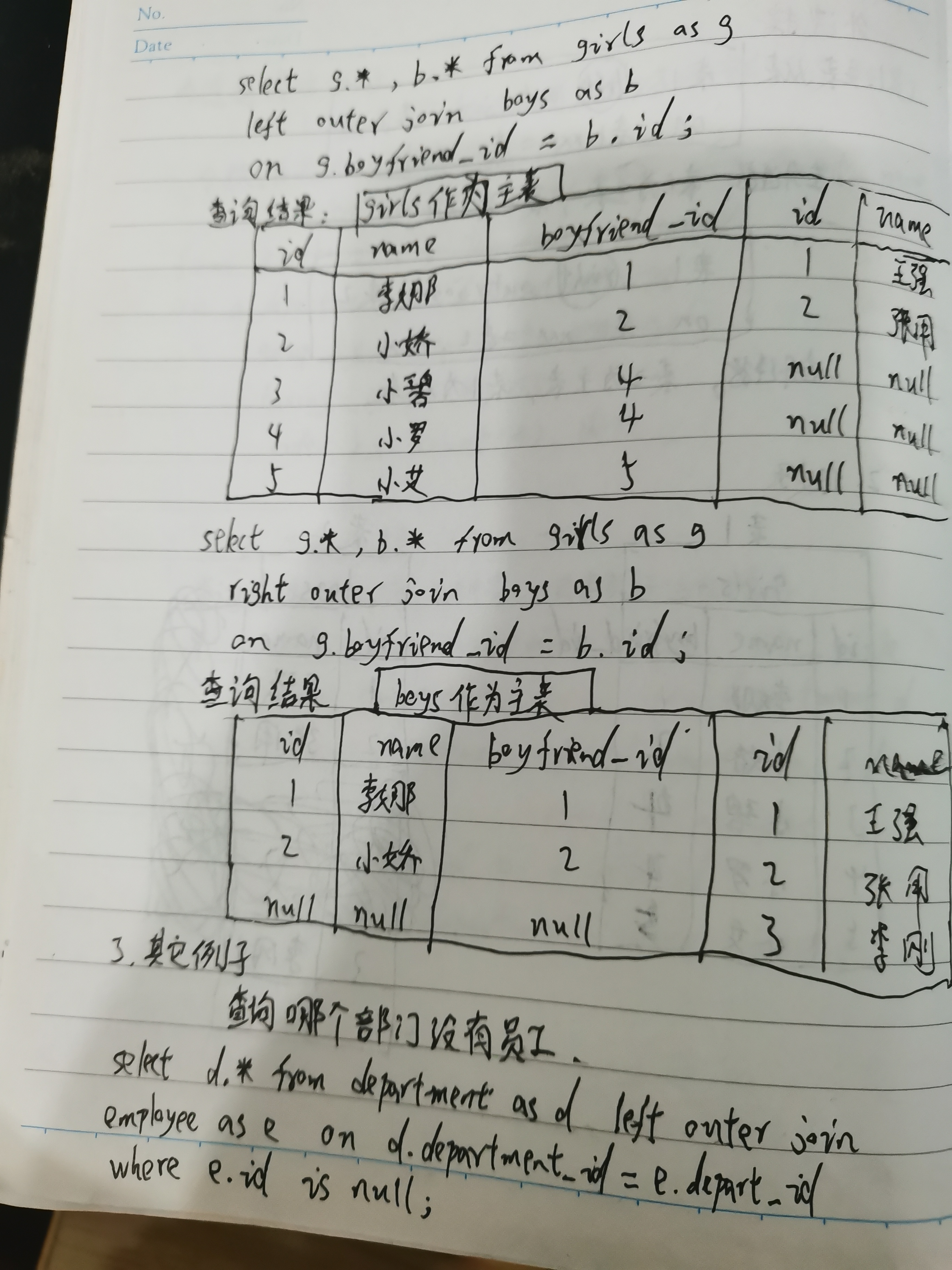
4)交叉连接,又称“笛卡尔连接”或"笛卡尔积"
假如A表中的数据为m行,B表中的数据有n行,那么A和B做笛卡尔积,结果为m*n行
例子:
| id1 | name1 |
| 1 | 张一 |
| 2 | 李二 |
| id2 | name2 |
| 1 | zs |
| 2 | ls |
| 3 | ww |
查询SQL:select * FROM 表1 CROSS JOIN 表2;
| id1 | name1 | id2 | name2 |
| 1 | 张一 | 1 | zs |
| 1 | 张一 | 2 | ls |
| 1 | 张一 | 3 | ww |
| 2 | 李二 | 1 | zs |
| 2 | 李二 | 2 | ls |
| 2 | 李二 | 3 | ww |
5)全连接full join
特点:取两张表查询结果的并集
注意:mysql不支持full join,执行会报错
例子:
| id1 | name1 |
| 1 | 张一 |
| 2 | 李二 |
| 5 | 王五 |
| id2 | name2 |
| 1 | zs |
| 2 | ls |
| 3 | ww |
查询SQL:select * FROM 表1 FULL JOIN 表2;
| id1 | name1 | id2 | name2 |
| 1 | 张一 | 1 | zs |
| 2 | 李二 | 2 | ls |
| 5 | 王五 | null | null |
| null | null | 3 | 22 |
九、子查询
1)外查询和内查询、关联子查询
查询语句分为:外(父)查询(主查询)、内查询(子查询)
外查询仅使用内查询的最终结果,外查询和内查询没关联。
关联子查询:内查询会引用外查询的对象。比如select name,age from student where sid<=3 as sResult and age>(select age from sResult limit 1);
2)子查询分类
1.按返回结果分类
- 标量子查询(单行子查询):1行1列
- 列子查询(多行子查询):1列多行
- 行子查询:1行多列
- 表子查询:多行多列
2.按位置分类
- select后from前:标量子查询
- from后where前:表子查询
- where后:标量子查询、列子查询、行子查询
3.按执行顺序分类
可分为相关(关联)子查询、不相关(非关联)子查询。
(1)相关子查询:先执行主查询,再执行子查询
标量子查询中:where 20>(子查询语句);
多行子查询中:exists
(2)不相关子查询:先执行子查询,再执行主查询
标量子查询中:where 列名>(子查询语句)
多行子查询中:in、all、some(any)
3)子查询的操作符
1.标量子查询、行子查询
(1)操作符有哪些
>、=、和!=、between and
(2)例子
标量子查询:
例子1:查询工资最少的员工的基本信息
select * from employee where salary=(select min(salary) from employee);
例子2:查询最低工资高于4号部门的最高工资的部门id和其最低工资
select depart_id,min(salary) from employee
group by depart_id
having min(salary)>(select max(salary) from employee where depart_id=4);
行子查询:
例子1:查询公号最小且工资最高的员工的基本信息
SELECT *FROM employee WHERE (employee_id,salary)=(SELECT MIN(employee_id),MAX(salary) FROM employees);
2.列子查询
(1)操作符有哪些
in和not in、some(any)、all、exists和not exists
(2)in
等于子查询结果的任意一个值
(3)any(some)
和子查询结果中的任意一个比较
注意:=any相当于in,<>any相当于not in
(4)all
和子查询结果中的所有值比较
(5)exists
检查子查询结果是否为空。存在数据就返回值True,否则返回False
注意:和and一起用的情况特殊,例子如下:
查询 course 表中是否存在 id=1 的课程,如果存在,就查询出 student 表中 age 字段大于 24 的记录。
SELECT * FROM student
WHERE age>24 AND EXISTS(SELECT course_name FROM course WHERE id=1);
(6)补充说明
列子查询的all和any(some)可以被单行子查询替代
例子1:返回比job_id为“IT_ProG”任一工资低的员工
select name from employee where salary<any(select distinct salary from employee where job_id='IT_ProG');
可以替换为
select name from employee where salary<(select max(salary) from employee where job_id='IT_ProG');
例子2:返回比job_id为“IT_ProG”所有工资低的员工
select name from employee where salary<all(select distinct salary from employee where job_id='IT_ProG');
可以替换为
select name from employee where salary<(select min(salary) from employee where job_id='IT_ProG');
十、分页查询
1)limit关键字的语法
语法1:select * from student limit 起始位置,size
语法2:select * from student limit 起始位置 offset size
起始位置:要显示条目的起始索引(默认从0开始)
size:要显示的条目个数
案例:查询第10条到第13条(共4条)
写法1:select * from student limit 9,4; //4表示返回4行,9表示从表的第10行开始
写法2:select * from student limit 4 offset 9;
2)如何分页
select * from studnet limit (当前页码-1)*每页记录条数 ,每页记录条数;
十一、联合查询
(1)union、union all
1.含义
将多次查询结果合并成一个结果
2.特点
适用于合并多个表的查询结果;
union默认去重,union all 包含所有的重复项;
union去除重复的方式等效于distinct关键字,它是指输出字段列表的组合无重复,不是指剔除单个字段下的重复值
3.要求
两个查询结果集的列数必须相等,否则会报错
4.例子
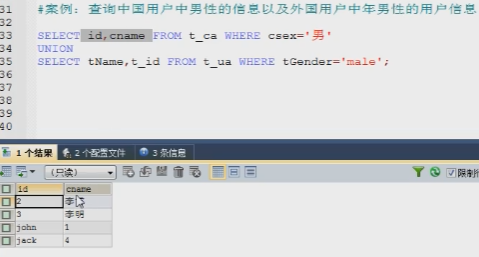
其中第一个select出的id只有2、3;第二个select出的t_id只有1、4
(2)minus、intersect
用于比较2个查询结果的差异
Oracle特有的,mysql和sqlserver都没有。不过mysql、sqlserver可以通过NOT EXISTS配合LEFT JOIN来实现
minus:取差集,左表减去右表剩余的数据
intersect:取交集
例子:
查询sql1 minus 查询sql1
十二、查询时加锁(select xxx for update)
作用
查询时锁定查询记录,防止查询时内容被修改出现并发问题(脏读、幻读、不可重复读),导致查询结果不是我们想要的
原理
查询时加悲观锁:
- 如果查询条件用了含索引,那么select xxx for update就会进行行锁;
- 如果查询条件都是普通字段(不含索引),那么select xxx for update就会进行锁表
应用案例
select a,b from 表名 where a=1 for update;
update 表名 set b=2 where a=1;
commit
与直接“update 表名 set b=2 where a=1”的区别在于:
可以防止第三方在commit之前修改数据





 本文全面介绍了SQL查询的各种操作,包括完全限定查询、条件查询、模糊查询、范围查询、CASE WHEN表达式、排序和分组查询、连接查询、子查询、分页查询、联合查询以及查询时的锁定机制。详细讲解了每个操作的关键字、用法及示例,是SQL学习者的宝贵资料。
本文全面介绍了SQL查询的各种操作,包括完全限定查询、条件查询、模糊查询、范围查询、CASE WHEN表达式、排序和分组查询、连接查询、子查询、分页查询、联合查询以及查询时的锁定机制。详细讲解了每个操作的关键字、用法及示例,是SQL学习者的宝贵资料。
















 46万+
46万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








