转:http://blog.51cto.com/lindt/1864591
1.代码相关文件
/AOSP/frameworks/native/libs/ui
主要是bufferqueuecore与surfaceflinger中分配
GraphicBufferAllocator 通过hw_get_module()&gralloc_open与硬件提供的设备交互
ex: /hardware/qcom/display/libgralloc/alloc_controller.cpp etc.
/AOSP/frameworks/native/libs/gui
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
Android.mk IGraphicBufferAlloc.cpp
BitTube.cpp IGraphicBufferConsumer.cpp
BufferItemConsumer.cpp IGraphicBufferProducer.cpp
BufferItem.cpp IProducerListener.cpp
BufferQueueConsumer.cpp ISensorEventConnection.cpp
BufferQueueCore.cpp ISensorServer.cpp
BufferQueue.cpp ISurfaceComposerClient.cpp
BufferQueueProducer.cpp ISurfaceComposer.cpp
BufferSlot.cpp LayerState.cpp
CleanSpec.mk Sensor.cpp
ConsumerBase.cpp SensorEventQueue.cpp
CpuConsumer.cpp SensorManager.cpp
DisplayEventReceiver.cpp StreamSplitter.cpp
GLConsumer.cpp SurfaceComposerClient.cpp
GraphicBufferAlloc.cpp SurfaceControl.cpp
GuiConfig.cpp Surface.cpp
IConsumerListener.cpp SyncFeatures.cpp
IDisplayEventConnection.cpp tests
|
SurfaceComposerClient 中成员变量 sp<ISurfaceComposerClient> mClient;与surface.cpp binder通信
/AOSP/frameworks/native/services/surfaceflinger
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
Android.mk EventControlThread.cpp MODULE_LICENSE_APACHE2
Barrier.h EventControlThread.h MonitoredProducer.cpp
Client.cpp EventLog MonitoredProducer.h
Client.h EventThread.cpp RenderEngine
clz.h EventThread.h SurfaceFlingerConsumer.cpp
Colorizer.h FrameTracker.cpp SurfaceFlingerConsumer.h
DdmConnection.cpp FrameTracker.h SurfaceFlinger.cpp
DdmConnection.h Layer.cpp SurfaceFlinger.h
DisplayDevice.cpp LayerDim.cpp surfaceflinger.rc
DisplayDevice.h LayerDim.h tests
DisplayHardware Layer.h Transform.cpp
DispSync.cpp main_surfaceflinger.cpp Transform.h
DispSync.h MessageQueue.cpp
Effects MessageQueue.h
|
surfaceflinger管理surface及layer
AOSP/frameworks/base/core/java/android/view
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
|
AbsSavedState.java MagnificationSpec.aidl
accessibility MagnificationSpec.java
AccessibilityInteractionController.java MenuInflater.java
AccessibilityIterators.java MenuItem.java
ActionMode.java Menu.java
ActionProvider.java MotionEvent.aidl
animation MotionEvent.java
AnimationRenderStats.aidl OrientationEventListener.java
Choreographer.java OrientationListener.java
CollapsibleActionView.java package.html
ContextMenu.java PointerIcon.aidl
ContextThemeWrapper.java PointerIcon.java
DisplayAdjustments.java RemotableViewMethod.java
Display.aidl RenderNodeAnimator.java
DisplayEventReceiver.java RenderNode.java
DisplayInfo.aidl ScaleGestureDetector.java
DisplayInfo.java SearchEvent.java
Display.java SoundEffectConstants.java
DisplayListCanvas.java SubMenu.java
DragEvent.aidl Surface.aidl
DragEvent.java SurfaceControl.java
FallbackEventHandler.java SurfaceHolder.java
FocusFinderHelper.java Surface.java
FocusFinder.java SurfaceSession.java
FrameInfo.java SurfaceView.java
FrameStats.java textservice
GestureDetector.java TextureView.java
GhostView.java ThreadedRenderer.java
GraphicBuffer.aidl TouchDelegate.java
GraphicBuffer.java VelocityTracker.java
Gravity.java ViewAnimationUtils.java
HapticFeedbackConstants.java ViewConfiguration.java
HardwareLayer.java ViewDebug.java
HardwareRenderer.java ViewGroup.java
IApplicationToken.aidl ViewGroupOverlay.java
IAssetAtlas.aidl ViewHierarchyEncoder.java
IGraphicsStats.aidl View.java
IInputFilter.aidl ViewManager.java
IInputFilterHost.aidl ViewOutlineProvider.java
InflateException.java ViewOverlay.java
InputChannel.aidl ViewParent.java
InputChannel.java ViewPropertyAnimator.java
InputDevice.aidl ViewPropertyAnimatorRT.java
InputDevice.java ViewRootImpl.java
InputEvent.aidl ViewStructure.java
InputEventConsistencyVerifier.java ViewStub.java
InputEvent.java ViewTreeObserver.java
InputEventReceiver.java WindowAnimationFrameStats.aidl
InputEventSender.java WindowAnimationFrameStats.java
InputFilter.java WindowCallbackWrapper.java
inputmethod WindowContentFrameStats.aidl
InputQueue.java WindowContentFrameStats.java
IOnKeyguardExitResult.aidl WindowId.java
IRotationWatcher.aidl WindowInfo.aidl
IWindow.aidl WindowInfo.java
IWindowFocusObserver.aidl WindowInsets.java
IWindowId.aidl Window.java
IWindowManager.aidl WindowManager.aidl
IWindowSession.aidl WindowManagerGlobal.java
IWindowSessionCallback.aidl WindowManagerImpl.java
KeyCharacterMap.java WindowManagerInternal.java
KeyEvent.aidl WindowManager.java
KeyEvent.java WindowManagerPolicy.java
LayoutInflater.java
|
2. Activity显示
2.1 Activity创建
/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
handleLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent) {
...............
//根据类名以Java反射的方法创建一个Activity
Activity a = performLaunchActivity(r, customIntent);
handleResumeActivity(r.token,
false
, r.isForward,
!r.activity.mFinished && !r.startsNotResumed);
................}
|
2.2 handleResumeActivity
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
final
void
handleResumeActivity(IBinder token,
boolean
clearHide,
boolean
isForward,
boolean
reallyResume) {
.....................
if
(r.window ==
null
&& !a.mFinished && willBeVisible) {
r.window = r.activity.getWindow();
//得到一个view对象
View decor = r.window.getDecorView();
decor.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE);
//获得viewManager
ViewManager wm = a.getWindowManager();
WindowManager.LayoutParams l = r.window.getAttributes();
a.mDecor = decor;
l.type = WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_BASE_APPLICATION;
l.softInputMode |= forwardBit;
if
(a.mVisibleFromClient) {
a.mWindowAdded =
true
;
//将view加入viewmanager
wm.addView(decor, l);
}
}
..................................}
|
2.3 Activity 通过setContentView设置UI
Activity.java
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
public
void
setContentView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) {
getWindow().setContentView(view, params);
initWindowDecorActionBar();
}
public
Window getWindow() {
return
mWindow;
}
|
上面出现了两个和UI有关系的类:View和Window
2.4 Activity Window 与WindowManager
Activity.java
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
final
void
attach(Context context, ActivityThread aThread,
Instrumentation instr, IBinder token,
int
ident,
Application application, Intent intent, ActivityInfo info,
CharSequence title, Activity parent, String id,
NonConfigurationInstances lastNonConfigurationInstances,
Configuration config, String referrer, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor) {
//创建window对象
mWindow =
new
PhoneWindow(
this
);
mWindow.setCallback(
this
);
mWindow.setOnWindowDismissedCallback(
this
);
mWindow.getLayoutInflater().setPrivateFactory(
this
);
//创建windowManager
mWindow.setWindowManager(
(WindowManager)context.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE),
mToken, mComponent.flattenToString(),
(info.flags & ActivityInfo.FLAG_HARDWARE_ACCELERATED) !=
0
);
//保存WindowManager对象
mWindowManager = mWindow.getWindowManager();
|
setWindowManager由PhoneWindow父类window.java实现
Window.java
|
1
2
3
|
public
void
setWindowManager(WindowManager wm, IBinder appToken, String appName,){
mWindowManager = ((WindowManagerImpl)wm).createLocalWindowManager(
this
);
}
|
WindowManagerImpl.java
|
1
2
3
4
|
public
WindowManagerImpl createLocalWindowManager(Window parentWindow) {
return
new
WindowManagerImpl(mDisplay, parentWindow);
}
public
final
class
WindowManagerImpl
implements
WindowManager {}
|
(2.4)中流程总结
2.5 继续分析setContentView()
Activity.java
|
1
2
3
4
|
public
void
setContentView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) {
getWindow().setContentView(view, params);
initWindowDecorActionBar();
}
|
PhoneWindow.java
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
private
ViewGroup mContentParent;
public
void
setContentView(View view) {
setContentView(view,
new
ViewGroup.LayoutParams(MATCH_PARENT, MATCH_PARENT));
}
public
void
setContentView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) {
//mContentParent是一个viewGroup对象
if
(mContentParent ==
null
) {
installDecor();
}
if
(hasFeature(FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS)) {
view.setLayoutParams(params);
final
Scene newScene =
new
Scene(mContentParent, view);
transitionTo(newScene);
}
else
{
//把view加入到ViewGroup中
mContentParent.addView(view, params);
}
........}
|
mContentParent是一个ViewGroup类型,它从View中派生,所以也是一个UI单元。从它名字中“Group”所表达的意思分析,它还可以包含其他的View元素。这又是什么意思呢?也就是说,在绘制一个ViewGroup时,它不仅需要把自己的样子画出来,还需要把它包含的View元素的样子也画出来。读者可将它想象成一个容器,容器中的元素就是View。
installDecor()函数
主要用来给view绘制icon ,window title,logo, menu等等
2.6 重回handleResumeActivity
我们之所以分析2.5内容,是为了弄清楚View, ViewManager(就是WindowManager)这些对象
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
final
void
handleResumeActivity(IBinder token,
boolean
clearHide,
boolean
isForward,
boolean
reallyResume) {
.....................
if
(r.window ==
null
&& !a.mFinished && willBeVisible) {
r.window = r.activity.getWindow();
//得到一个view对象
View decor = r.window.getDecorView();
decor.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE);
//获得viewManager
ViewManager wm = a.getWindowManager();
WindowManager.LayoutParams l = r.window.getAttributes();
a.mDecor = decor;
l.type = WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_BASE_APPLICATION;
l.softInputMode |= forwardBit;
if
(a.mVisibleFromClient) {
a.mWindowAdded =
true
;
//将view加入viewmanager
wm.addView(decor, l);
}
}
..................................}
|
分析wm.addView(decor,l)
WindowManagerImpl.java
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
public
final
class
WindowManagerImpl
implements
WindowManager {
private
final
WindowManagerGlobal mGlobal = WindowManagerGlobal.getInstance();
public
void
addView(
@NonNull
View view,
@NonNull
ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) {
applyDefaultToken(params);
mGlobal.addView(view, params, mDisplay, mParentWindow);
}
|
|
1
|
WindowManagerGlobal里面可以通过AIDL与IWindowManager.Stub.asInterface 及IWindowSessionCallback.Stub() IPC通信
|
WindowManagerGlobal.java
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
public
void
addView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params,
Display display, Window parentWindow) {
root =
new
ViewRootImpl(view.getContext(), display);
view.setLayoutParams(wparams);
mViews.add(view);
mRoots.add(root);
mParams.add(wparams);
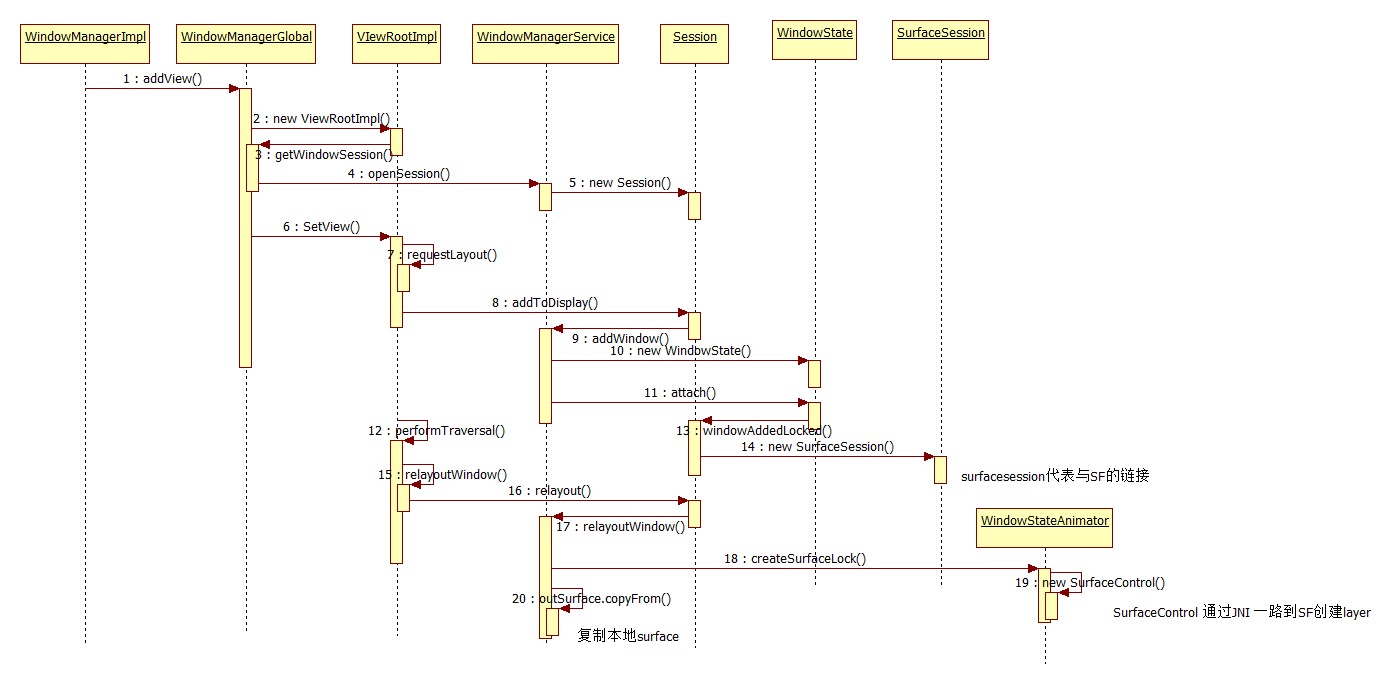
root.setView(view, wparams, panelParentView);
// TAG 1
|
2.6.1 ViewRootImpl又是什么东东?
ViewRootImpl.java
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
public
final
class
ViewRootImpl
implements
ViewParent,
View.AttachInfo.Callbacks, HardwareRenderer.HardwareDrawCallbacks{
final
IWindowSession mWindowSession;
final
Display mDisplay;
final
DisplayManager mDisplayManager;
final
W mWindow;
final
Surface mSurface =
new
Surface();
static
class
W
extends
IWindow.Stub {
private
final
WeakReference<ViewRootImpl> mViewAncestor;
private
final
IWindowSession mWindowSession;}
|
ViewRootImpl继承了Handler类,看来它能处理消息。ViewRootImpl果真重写了handleMessage函数
一个成员变量叫mSurface,它是Surface类型
|
1
2
|
surface.java
public
class
Surface
implements
Parcelable {
|
一个W类型的mWindow和一个View类型的mView变量
ViewRootImpl有一个成员变量mSurface,它是Surface类型,它和一块Raw Buffer有关联。
ViewRootImpl是一个ViewParent,它的子View的绘画操作,是在画布Surface上展开的
ViewRootImpl的构造
|
1
2
3
4
|
public
ViewRootImpl(Context context, Display display) {
mDisplay = display;
//Display.java Provides information about the size and density of a logical display.
mWindowSession = WindowManagerGlobal.getWindowSession();
// IWindowSession AIDLmWindo w = new W(this); //内部W对象,实际是与window通信的AIDL static class W extends IWindow.Stub
mDisplayManager = (DisplayManager)context.getSystemService(Context.DISPLAY_SERVICE);
|
WindowManagerGlobal.getWindowSession()将建立Activity的ViewRoot和WindowManagerService的关系
WindowManagerGlobal.java
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
public
static
IWindowSession getWindowSession() {
IWindowManager windowManager = getWindowManagerService();
//得到Iwindowmanager对象,
//IWindowManager 的AIDL Bn端是WindowManagerService class WindowManagerService extends IWindowManager.Stub
sWindowSession = windowManager.openSession(
//然后通过AIDL得到windowsession aidl 对象 不清楚为啥已经有了windowmanager的aidl 干嘛还需要windowsession aidl
new
IWindowSessionCallback.Stub() { })
}
public
static
IWindowManager getWindowManagerService() {
sWindowManagerService = IWindowManager.Stub.asInterface(
ServiceManager.getService(
"window"
));
//得到WindowManager AIDL BP对象
try
{
sWindowManagerService = getWindowManagerService();
ValueAnimator.setDurationScale(sWindowManagerService.getCurrentAnimatorScale());
}
catch
(RemoteException e) {}
|
ViewRootImpl和WMS的关系
/frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/WindowManagerService.java
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
public
class
WindowManagerService
extends
IWindowManager.Stub
implements
Watchdog.Monitor, WindowManagerPolicy.WindowManagerFuncs {}
public
IWindowSession openSession(IWindowSessionCallback callback, IInputMethodClient client,
IInputContext inputContext) {
Session session =
new
Session(
this
, callback, client, inputContext);
return
session;
}
|
/frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/Session.java
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
final
class
Session
extends
IWindowSession.Stub
implements
IBinder.DeathRecipient {
final
WindowManagerService mService;
final
IWindowSessionCallback mCallback;
final
IInputMethodClient mClient;
|
分析完ViewRootImpl创建过程后,现在返回TAG 1处继续分析ViewRootImpl.setView()
2.6.2 ViewRootImpl.setView()
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
public
void
setView(View view, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs, View panelParentView) {
// Compute surface insets required to draw at specified Z value.
// TODO: Use real shadow insets for a constant max Z.
if
(!attrs.hasManualSurfaceInsets) {
final
int
surfaceInset = (
int
) Math.ceil(view.getZ() *
2
);
attrs.surfaceInsets.set(surfaceInset, surfaceInset, surfaceInset, surfaceInset);}
//计算Z轴坐标
requestLayout();
res = mWindowSession.addToDisplay(mWindow, mSeq, mWindowAttributes,
getHostVisibility(), mDisplay.getDisplayId(),
mAttachInfo.mContentInsets, mAttachInfo.mStableInsets,
mAttachInfo.mOutsets, mInputChannel);
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
|
//requestLayout()流程 TAG2
public
void
requestLayout() { scheduleTraversals();}
void
scheduleTraversals() {
mTraversalBarrier = mHandler.getLooper().getQueue().postSyncBarrier();
mChoreographer.postCallback(
Choreographer.CALLBACK_TRAVERSAL, mTraversalRunnable,
null
);
notifyRendererOfFramePending();
pokeDrawLockIfNeeded();}
final
TraversalRunnable mTraversalRunnable =
new
TraversalRunnable();
//Runnable实现多线程,避免点继承的局限,一个类可以继承多个接口.适合于资源的共享
final
class
TraversalRunnable
implements
Runnable {
@Override
public
void
run() {
doTraversal();
}
}
void
doTraversal() {
performTraversals();}
private
void
performTraversals() {
//mSurface是 surface.java 对象, final Surface mSurface = new Surface();
// surface.java 通过jni 可以操作Surface.cpp 中surface对象 Surface::Surface(
// const sp<IGraphicBufferProducer>& bufferProducer,
// bool controlledByApp)
if
(mSurface.isValid()) {
if
(mAttachInfo.mHardwareRenderer !=
null
) {
try
{
hwInitialized = mAttachInfo.mHardwareRenderer.initialize(mSurface);
if
(hwInitialized && (host.mPrivateFlags
& View.PFLAG_REQUEST_TRANSPARENT_REGIONS) ==
0
) {
// Don't pre-allocate if transparent regions
// are requested as they may not be needed
mSurface.allocateBuffers();
}
}
//Interface for rendering a view hierarchy using hardware acceleration.
final
HardwareRenderer hardwareRenderer = mAttachInfo.mHardwareRenderer;
hardwareRenderer.setup(mWidth, mHeight, mAttachInfo,
mWindowAttributes.surfaceInsets);
}
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
mWindowSession.addToDisplay流程
//mWindowSession(IWindowSession) 通过AIDL 与Session.java交互 final class Session extends IWindowSession.Stub
public
int
addToDisplay(IWindow window,
int
seq, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs,
int
viewVisibility,
int
displayId, Rect outContentInsets, Rect outStableInset s,Rect outOutsets, InputChannel outInputChannel) {
return
mService.addWindow(
this
, window, seq, attrs, viewVisibility, displayId,
outContentInsets, outStableInsets, outOutsets, outInputChannel);
}
final
WindowManagerService mService;
WindowManagerService.java
public
int
addWindow(Session session, IWindow client,
int
seq,
WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs,
int
viewVisibility,
int
displayId,
Rect outContentInsets, Rect outStableInsets, Rect outOutsets,
InputChannel outInputChannel) {
//windowstate A window in the window manager.class WindowState implements WindowManagerPolicy.WindowState
WindowState win =
new
WindowState(
this
, session, client, token,
attachedWindow, appOp[
0
], seq, attrs, viewVisibility, displayContent);
win.attach();
}
WindowState.java
void
attach() {
mSession.windowAddedLocked();}
Session.java
void
windowAddedLocked() {
mSurfaceSession =
new
SurfaceSession();
mService.mSessions.add(
this
);
mNumWindow++;
}
|
ViewRootImpl 与WMS关系总结
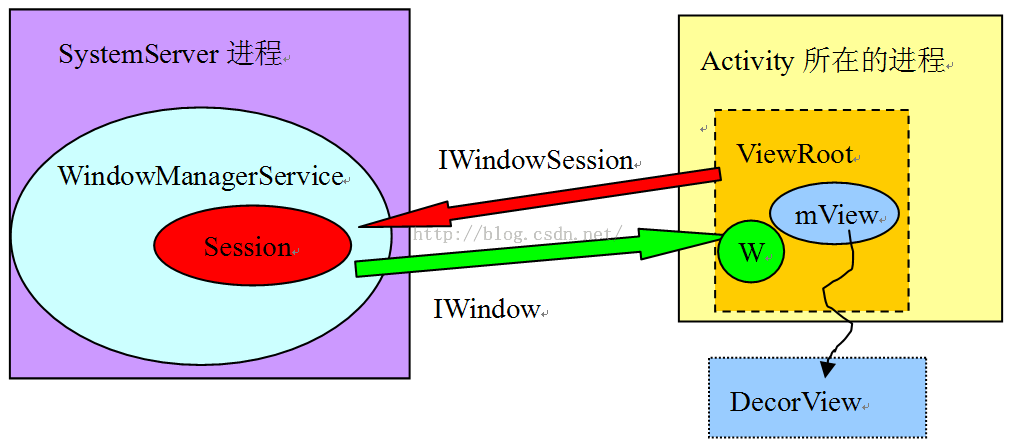 ViewRootImpl通过IWindowSession和WMS进程进行跨进程通信。
ViewRootImpl通过IWindowSession和WMS进程进行跨进程通信。
ViewRootImpl内部有一个W类型的对象,它也是一个基于Binder通信的类,W是IWindow的Bn端,用于响应请求。IWindow定义在另一个aidl文件IWindow.aidl中
IWindowSession
System private per-application interface to the window manager.
IWindow
API back to a client window that the Window Manager uses to inform it of interesting things happening.
IWindow.aidl
void dispatchAppVisibility(boolean visible);
void dispatchWallpaperCommand(
void dispatchDragEvent(in DragEvent event);
void dispatchWindowShown();
这里的事件指的就是按键、触屏等事件。那么,一个按键事件是如何被分发的呢?下面是它大致的流程:WMS所在的SystemServer进程接收到按键事件。WMS找到UI位于屏幕顶端的进程所对应的IWindow对象,调用这个IWindow对象的dispatchKey。IWindow对象的Bn端位于ViewRoot中,ViewRoot再根据内部View的位置信息找到真正处理这个事件的View,最后调用dispatchKey函数完成按键的处理。(这段过程没有去跟代码)
2.7 Activity的UI绘制
在TAG2处分析过requestLayout。根据前面的分析可知,最终调用到performTraversals()
ViewRootImpl.java
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
private
void
performTraversals() {
relayoutResult = relayoutWindow(params, viewVisibility, insetsPending);
//TAG3
performDraw();
//开始绘制
}
private
int
relayoutWindow(WindowManager.LayoutParams params,
int
viewVisibility,
boolean
insetsPending)
throws
RemoteException {
int
relayoutResult = mWindowSession.relayout(
mWindow, mSeq, params,
(
int
) (mView.getMeasuredWidth() * appScale +
0
.5f),
(
int
) (mView.getMeasuredHeight() * appScale +
0
.5f),
viewVisibility, insetsPending ? WindowManagerGlobal.RELAYOUT_INSETS_PENDING :
0
,
mWinFrame, mPendingOverscanInsets, mPendingContentInsets, mPendingVisibleInsets,
mPendingStableInsets, mPendingOutsets, mPendingConfiguration, mSurface);
}
//这个函数通过AIDL调用到WMS relayoutWindow().暂时不继续分析
private
void
performDraw() {
draw(fullRedrawNeeded);}
private
void
draw(
boolean
fullRedrawNeeded){
mAttachInfo.mHardwareRenderer.draw(mView, mAttachInfo,
this
);
//hw render完成draw
//HardwareRenderer.java abstract void draw() }
|
2.8 Activity 总结
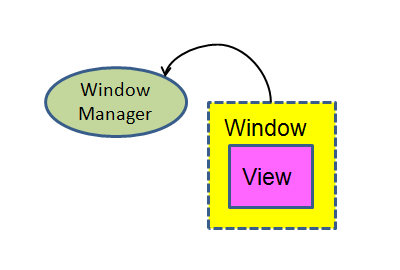
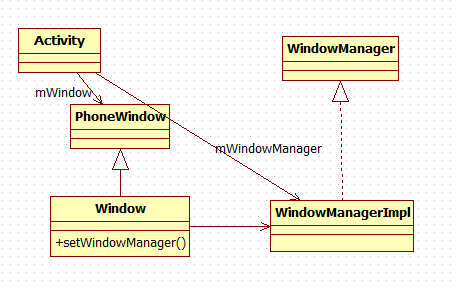
Activity的顶层View是DecorView,而我们在onCreate函数中通过setContentView设置的View只不过是这个DecorView中的一部分罢了。DecorView是一个FrameLayout类型的ViewGroup。
Activity和UI有关,它包含一个Window(真实类型是PhoneWindow)和一个WindowManager(真实类型是LocalWindowManager)对象。这两个对象将控制整个Activity的显示。
LocalWindowManager使用了WindowManagerImpl做为最终的处理对象(Proxy模式),这个WindowManagerImpl中有一个ViewRootImpl对象。ViewRootImpl实现了ViewParent接口,它有两个重要的成员变量,一个是mView,它指向Activity顶层UI单元的DecorView,另外有一个mSurface,这个Surface包含了一个Canvas(画布)(这个surface java对象可以通过JNI 与 surface.cpp中对象交互)。除此之外,ViewRooImplt还通过Binder系统和WindowManagerService进行了跨进程交互。
ViewRoot能处理Handler的消息,Activity的显示就是由ViewRoot在它的performTraversals函数中完成的。
3. Surface对象
终于可以分析java与C++处surface对象了,先回忆下surface是如何创建的
|
1
2
|
ViewRootImpl.java
final
Surface mSurface =
new
Surface();
|
ViewRootImpl通过IWindowSession和WMS交互,而WMS中会调用的一个attach函数,会构造一个SurfaceSession,前面遇到过但没有继续分析
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
WindowState.java
void
attach() {
mSession.windowAddedLocked();}
Session.java
void
windowAddedLocked() {
mSurfaceSession =
new
SurfaceSession();
mService.mSessions.add(
this
);
mNumWindow++;
}
SurfaceSession.java
//* An instance of this class represents a connection to the surface
//* flinger, from which you can create one or more Surface instances that will
//* be composited to the screen.
public
final
class
SurfaceSession {
private
static
native
long
nativeCreate();
private
static
native
void
nativeDestroy(
long
ptr);
private
static
native
void
nativeKill(
long
ptr);}
|
由注释可见,surfacesession负责与SF的连接
在2.7处Activity UI 绘制时,遇到过relayoutWindow(),现在继续看该函数
ViewRootImpl.java
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
|
private
void
performTraversals() {
relayoutResult = relayoutWindow(params, viewVisibility, insetsPending);
//TAG3
performDraw();
//开始绘制
}
private
int
relayoutWindow(WindowManager.LayoutParams params,
int
viewVisibility,
boolean
insetsPending)
throws
RemoteException {
int
relayoutResult = mWindowSession.relayout(
mWindow, mSeq, params,
(
int
) (mView.getMeasuredWidth() * appScale +
0
.5f),
(
int
) (mView.getMeasuredHeight() * appScale +
0
.5f),
viewVisibility, insetsPending ? WindowManagerGlobal.RELAYOUT_INSETS_PENDING :
0
,
mWinFrame, mPendingOverscanInsets, mPendingContentInsets, mPendingVisibleInsets,
mPendingStableInsets, mPendingOutsets, mPendingConfiguration, mSurface);
}
//这个函数通过AIDL调用到WMS relayoutWindow()
Session.java
public
int
relayout(IWindow window,
int
seq, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs,..){
int
res = mService.relayoutWindow(
this
,....);}
WindowManagerService.java
public
int
relayoutWindow(Session session, IWindow client,
int
seq,
WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs,
int
requestedWidth,....){
SurfaceControl surfaceControl = winAnimator.createSurfaceLocked();
//TAG4 创建本地surfacecontrol 通过JNI会调用C++最终创建layer, java层保存的surfacecontrol对象是一个surfaceControl.cpp 中对象
//JNI处返回的surfacecontrol
//surface->incStrong((void *)nativeCreate);
//return reinterpret_cast<jlong>(surface.get());
outSurface.copyFrom(surfaceControl);
//将本地surface拷贝到outSurface }
WindowStateAnimator.java
SurfaceControl createSurfaceLocked() {
final
WindowState w = mWin;
mSurfaceControl =
new
SurfaceControl(
mSession.mSurfaceSession,
attrs.getTitle().toString(),
width, height, format, flags);
// Start a new transaction and apply position & offset.
SurfaceControl.openTransaction();
mSurfaceControl.setLayer(mAnimLayer);
mSurfaceControl.setAlpha(
0
);
SurfaceControl.closeTransaction();
return
mSurfaceControl;
}
|
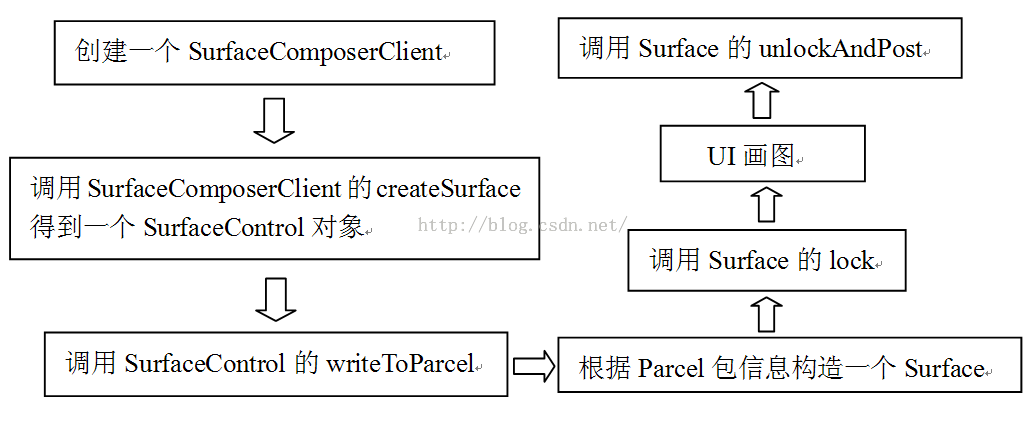
SurfaceControl是个什么对象?与Surface有何关系
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/SurfaceControl.java
看SurfaceControl构造函数说明,surfacecontrol根据name创建surface
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
|
/**
* Create a surface with a name.
* <p>
* The surface creation flags specify what kind of surface to create and
* certain options such as whether the surface can be assumed to be opaque
* and whether it should be initially hidden. Surfaces should always be
* created with the {@link #HIDDEN} flag set to ensure that they are not
* made visible prematurely before all of the surface's properties have been
* configured.
* <p>
* Good practice is to first create the surface with the {@link #HIDDEN} flag
* specified, open a transaction, set the surface layer, layer stack, alpha,
* and position, call {@link #show} if appropriate, and close the transaction.
*
* @param session The surface session, must not be null.
* @param name The surface name, must not be null.
* @param w The surface initial width.
* @param h The surface initial height.
* @param flags The surface creation flags. Should always include {@link #HIDDEN}
* in the creation flags.
*
* @throws throws OutOfResourcesException If the SurfaceControl cannot be created.
*/
public
SurfaceControl(SurfaceSession session,
String name,
int
w,
int
h,
int
format,
int
flags){
mNativeObject = nativeCreate(session, name, w, h, format, flags);
}
通过JNI android_view_SurfaceControl.cpp
static
jlong nativeCreate(JNIEnv* env, jclass clazz, jobject sessionObj,
jstring nameStr, jint w, jint h, jint format, jint flags) {
ScopedUtfChars name(env, nameStr);
sp<SurfaceComposerClient> client(android_view_SurfaceSession_getClient(env, sessionObj));
sp<SurfaceControl> surface = client->createSurface(
String8(name.c_str()), w, h, format, flags); }
调用SurfaceComposiClient.cpp
sp<SurfaceControl> SurfaceComposerClient::createSurface(
const
String8& name,
uint32_t w,
uint32_t h,
PixelFormat format,
uint32_t flags){
sp<SurfaceControl> sur;
sp<IGraphicBufferProducer> gbp;
status_t err = mClient->createSurface(name, w, h, format, flags,
&handle, &gbp);
//mClient 是一个sp<ISurfaceComposerClient>对象,由class Client : public BnSurfaceComposerClient来接收IPC交互,
sur =
new
SurfaceControl(
this
, handle, gbp);
// 最终通过JNI返回到TAG4处
return
sur;
}
Client.cpp
// ISurfaceComposerClient interface
/* Client是用来与surfaceflinger交互的桥梁,在sf中被创建
sp<ISurfaceComposerClient> SurfaceFlinger::createConnection()
{
sp<ISurfaceComposerClient> bclient;
sp<Client> client(new Client(this));
*/
status_t Client::createSurface(
const
String8& name,
uint32_t w, uint32_t h, PixelFormat format, uint32_t flags,
sp<IBinder>* handle,
sp<IGraphicBufferProducer>* gbp){
result = flinger->createLayer(name, client, w, h, format, flags,
handle, gbp);}
//这里面的flinger是由Client::Client(const sp<SurfaceFlinger>& flinger)在创建时保存起来的
: mFlinger(flinger)
}
Surfaceflinger.cpp
status_t SurfaceFlinger::createLayer(
const
String8& name,
const
sp<Client>& client,
uint32_t w, uint32_t h, PixelFormat format, uint32_t flags,
sp<IBinder>* handle, sp<IGraphicBufferProducer>* gbp){
sp<Layer> layer;
switch
(flags & ISurfaceComposerClient::eFXSurfaceMask) {
case
ISurfaceComposerClient::eFXSurfaceNormal:
result = createNormalLayer(client,
//创建普通layer gbp是在layer中进行赋值
name, w, h, flags, format,
handle, gbp, &layer);
break
;
case
ISurfaceComposerClient::eFXSurfaceDim:
result = createDimLayer(client,
//创建磨砂layer gbp是在layer中进行赋值
name, w, h, flags,
handle, gbp, &layer);
break
;
default
:
result = BAD_VALUE;
break
;
result = addClientLayer(client, *handle, *gbp, layer);
//attach this layer to the client
}
//Client中createSurface函数,调用的是SF中createLayer
//与前面ViewrootImpl.java中 final Surface mSurface = new Surface();有何区分?Layer与surface是如何区分? 前面遇到java surface用于drawSoftware或hwRender时 ex drawsoftware() canvas = mSurface.lockCanvas(dirty);mView.draw(canvas);
|
lockCanvas
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
Surface.java
* Gets a {
@link
Canvas}
for
drawing into
this
surface.
public
Canvas lockCanvas(Rect inOutDirty){
mLockedObject = nativeLockCanvas(mNativeObject, mCanvas, inOutDirty);
return
mCanvas;
}
|
调用JNI
android_view_Surface.cpp
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
|
static
jlong nativeLockCanvas(JNIEnv* env, jclass clazz,
jlong nativeObject, jobject canvasObj, jobject dirtyRectObj) {
sp<Surface> surface(
reinterpret_cast
<Surface *>(nativeObject));
Rect dirtyRect;
Rect* dirtyRectPtr = NULL;
if
(dirtyRectObj) {
dirtyRect.left = env->GetIntField(dirtyRectObj, gRectClassInfo.left);
dirtyRect.top = env->GetIntField(dirtyRectObj, gRectClassInfo.top);
dirtyRect.right = env->GetIntField(dirtyRectObj, gRectClassInfo.right);
dirtyRect.bottom = env->GetIntField(dirtyRectObj, gRectClassInfo.bottom);
dirtyRectPtr = &dirtyRect;
}
ANativeWindow_Buffer outBuffer;
status_t err = surface->lock(&outBuffer, dirtyRectPtr);
//一块表示脏区域的dirtyRectPtr
//从surface.cpp 中dequeueBuffer()获得一个GraphicBuffer, 然后将buffer的长宽,format 等赋制给outBuffer,
//
SkImageInfo info = SkImageInfo::Make(outBuffer.width, outBuffer.height,
convertPixelFormat(outBuffer.format),
kPremul_SkAlphaType);
SkBitmap bitmap;
ssize_t bpr = outBuffer.stride * bytesPerPixel(outBuffer.format);
bitmap.setInfo(info, bpr);
if
(outBuffer.width > 0 && outBuffer.height > 0) {
bitmap.setPixels(outBuffer.bits);
// bitmap 指向一片存储区域
}
else
{
// be safe with an empty bitmap.
bitmap.setPixels(NULL);
}
Canvas* nativeCanvas = GraphicsJNI::getNativeCanvas(env, canvasObj);
nativeCanvas->setBitmap(bitmap);
//将Bitmap设置到这个Canvas中,这样进UI绘画时就有画布了
// Create another reference to the surface and return it. This reference
// should be passed to nativeUnlockCanvasAndPost in place of mNativeObject,
// because the latter could be replaced while the surface is locked.
sp<Surface> lockedSurface(surface);
lockedSurface->incStrong(&sRefBaseOwner);
return
(jlong) lockedSurface.get();
}
|
lockCanvas获得一块存储区域,然后将它和Canvas绑定到一起,这样,UI绘画的结果就记录在这块存储区域里了
再看unlockCanvas
Surface.java
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
private
void
unlockSwCanvasAndPost(Canvas canvas) {
// 只有sw 渲染的才走这边?
try
{
nativeUnlockCanvasAndPost(mLockedObject, canvas);
}
finally
{
nativeRelease(mLockedObject);
mLockedObject =
0
;
}
}
|
android_view_Surface.cpp
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
static
void
nativeUnlockCanvasAndPost(JNIEnv* env, jclass clazz,
jlong nativeObject, jobject canvasObj) {
sp<Surface> surface(
reinterpret_cast
<Surface *>(nativeObject));
// detach the canvas from the surface
Canvas* nativeCanvas = GraphicsJNI::getNativeCanvas(env, canvasObj);
nativeCanvas->setBitmap(SkBitmap());
// unlock surface
status_t err = surface->unlockAndPost();
}
|
Surface.cpp
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
status_t Surface::unlockAndPost()
{
status_t err = mLockedBuffer->unlockAsync(&fd);
//通过mGraphicBufferProducer->queueBuffer
err = queueBuffer(mLockedBuffer.get(), fd);
}
|
直接使用别人的图片surface画图过程
回忆下上文surface 是如何创建的
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
sp<SurfaceControl> SurfaceComposerClient::createSurface(
const
String8& name,
uint32_t w,
uint32_t h,
PixelFormat format,
uint32_t flags){
sp<IGraphicBufferProducer> gbp;
status_t err = mClient->createSurface(name, w, h, format, flags,
&handle, &gbp);
ALOGE_IF(err,
"SurfaceComposerClient::createSurface error %s"
,
strerror
(-err));
if
(err == NO_ERROR) {
sur =
new
SurfaceControl(
this
, handle, gbp);
}
}
|
|
1
|
mClient sp<ISurfaceComposerClient> mClient;
|
class Client : public BnSurfaceComposerClient
Client 中mFlinger sp<SurfaceFlinger> mFlinger; 这样SurfaceComposerClient 就通过IPC 与surfaceflinger 交互起来了
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
status_t Client::createSurface(
const
String8& name,
uint32_t w, uint32_t h, PixelFormat format, uint32_t flags,
sp<IBinder>* handle,
sp<IGraphicBufferProducer>* gbp)
{
sp<MessageBase> msg =
new
MessageCreateLayer(mFlinger.get(),
name,
this
, w, h, format, flags, handle, gbp);
mFlinger->postMessageSync(msg);
return
static_cast
<MessageCreateLayer*>( msg.get() )->getResult();
}
|
Client::createSurface() 与 android_view_Surface.cpp 中nativeReadFromParcel
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
surfacecontrol.cpp
status_t SurfaceControl::writeSurfaceToParcel(
const
sp<SurfaceControl>& control, Parcel* parcel)
{
sp<IGraphicBufferProducer> bp;
if
(control != NULL) {
bp = control->mGraphicBufferProducer;
}
return
parcel->writeStrongBinder(IInterface::asBinder(bp));
//Surface 核心是不是就是IGraphicBufferProducer 指针
}
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
android_view_Surface.cpp
static
jlong nativeReadFromParcel(JNIEnv* env, jclass clazz,
jlong nativeObject, jobject parcelObj) {
Parcel* parcel = parcelForJavaObject(env, parcelObj);
sp<Surface> self(
reinterpret_cast
<Surface *>(nativeObject));
sp<IBinder> binder(parcel->readStrongBinder());
// update the Surface only if the underlying IGraphicBufferProducer
// has changed.
if
(self != NULL
&& (IInterface::asBinder(self->getIGraphicBufferProducer()) == binder)) {
// same IGraphicBufferProducer, return ourselves
return
jlong(self.get());
// 直接返回surface sp
}
//当GraphicBufferProducer改变时,新建一个surface,并将原先surface decStrong 释放,返回新surface指针
sp<Surface> sur;
sp<IGraphicBufferProducer> gbp(interface_cast<IGraphicBufferProducer>(binder));
if
(gbp != NULL) {
// we have a new IGraphicBufferProducer, create a new Surface for it
sur =
new
Surface(gbp,
true
);
// and keep a reference before passing to java
sur->incStrong(&sRefBaseOwner);
}
if
(self != NULL) {
// and loose the java reference to ourselves
self->decStrong(&sRefBaseOwner);
}
return
jlong(sur.get());
|
























 1494
1494

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








