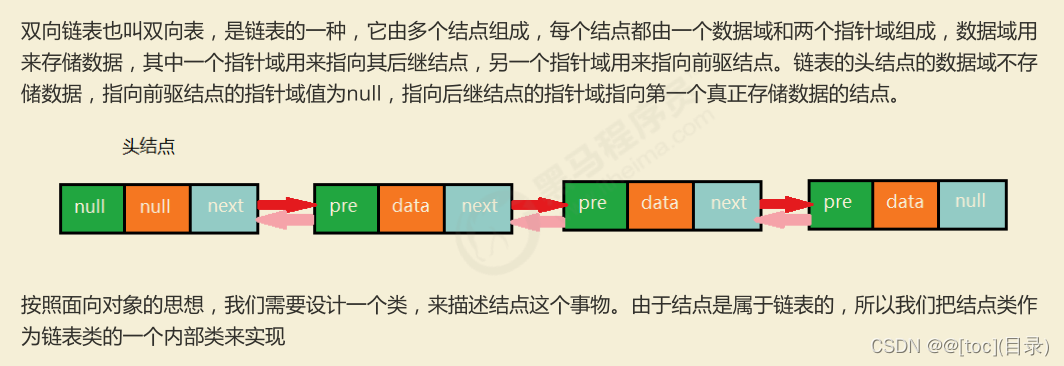
实现代码
package demo0110.algorithm.linear;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class TowWayLinkList<T> implements Iterable<T>{
private Node head;
private Node last;
private int N;
public TowWayLinkList(){
last = null;
head = new Node(null,null,null);
N = 0;
}
public void clear(){
last = null;
head.next = last;
head.pre = null;
head.item = null;
N = 0;
}
public int length(){
return N;
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return N==0;
}
public void insert(T t){
if (last == null){
last = new Node(t,head,null);
head.next = last;
}else{
Node oldLast = last;
Node node = new Node(t,oldLast,null);
oldLast.next=node;
last = node;
}
N++;
}
public void insert(int i,T t){
if (i>=N||i<0){
throw new RuntimeException("位置不合法");
}
Node pre = head;
for (int index = 0;index<i;index++){
pre = pre.next;
}
Node cur = pre.next;
Node newNode = new Node(t,pre,cur);
cur.pre = newNode;
pre.next = newNode;
N++;
}
public T get(int i){
if (i<0||i>=N){
throw new RuntimeException("位置不合法");
}
Node curr = head.next;
for (int index = 0;index<i;index++){
curr = curr.next;
}
return curr.item;
}
public int indexOf(T t){
Node n = head;
for (int i =0;n.next!=null;i++){
n=n.next;
if (n.item.equals(t)){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
public T remove(int i){
if (i<0||i>=N){
throw new RuntimeException("位置不合法");
}
Node pre = head;
for (int index = 0;index<i;index++){
pre = pre.next;
}
Node curr = pre.next;
Node curr_next = curr.next;
pre.next = curr_next;
curr_next.pre=pre;
N--;
return curr.item;
}
public T getFirst(){
if (isEmpty()){
return null;
}
return head.next.item;
}
public T getLast(){
if (isEmpty()){
return null;
}
return last.item;
}
@Override
public Iterator<T> iterator() {
return new TIterator();
}
private class TIterator implements Iterator{
private Node n = head;
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return n.next!=null;
}
@Override
public Object next() {
n = n.next;
return n.item;
}
}
private class Node{
public Node pre;
public Node next;
public T item;
public Node(T item,Node pre,Node next){
this.item = item;
this.pre = pre;
this.next = next;
}
}
}
测试代码
package demo0110.algorithm.test;
import demo0110.algorithm.linear.TowWayLinkList;
public class TowWayLinkListTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TowWayLinkList<String> list = new TowWayLinkList<>();
list.insert("c");
list.insert("d");
list.insert("e");
list.insert("f");
list.insert(0,"a");
list.insert(1,"b");
for (String str:list){
System.out.println(str);
}
System.out.println("----------------");
System.out.println(list.get(2));
System.out.println(list.remove(3));
System.out.println(list.length());
System.out.println(list.getFirst());
System.out.println(list.getLast());
}
}


























 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








