linux内核关闭中断
In the last part we discussed evolution of the interrupt delivery process from the devices in the x86 system (PIC → APIC → MSI), general theory, and all the necessary terminology.
在上一部分中,我们讨论了来自x86系统中的设备(PIC→APIC→MSI),通用理论和所有必要术语的中断传递过程的演变。
In this practical part we will look at how to roll back to the use of obsolete methods of interrupt delivery in Linux, and in particular we will look at Linux kernel boot options:
在这个实际的部分中,我们将研究如何回滚到Linux中使用过时的中断传递方法,尤其是我们将研究Linux内核引导选项:
- pci=nomsi pci = nomsi
- noapic Noapic
- nolapic 空腹的
Also we will look at the order in which the OS looks for interrupt routing tables (ACPI/MPtable/$PIR) and what the impact is from the following boot options:
此外,我们还将研究操作系统寻找中断路由表(ACPI / MPtable / $ PIR)的顺序,以及以下引导选项的影响:
- pci=noacpi pci = noacpi
- acpi=noirq acpi = noirq
- acpi=off acpi = off
You've probably used some combination of these options when one of the devices in your system hasn't worked correctly because of an interrupt problem. We'll go through these options and find out what they do and how they change the kernel '/proc/interrupts' interface output.
当系统中的某个设备由于中断问题而无法正常工作时,您可能已经使用了这些选项的某种组合。 我们将研究这些选项,并找出它们的作用以及它们如何更改内核“ / proc / interrupts”接口的输出。
无需任何额外选项即可启动 (Boot without any extra options)
In this article for our interrupt investigation we will be using custom board with the Intel Haswell i7 CPU with the LynxPoint-LP chipset which runs coreboot.
在本文中进行中断调查时,我们将结合使用带有Hascore i7 CPU和LynxPoint-LP芯片组(运行coreboot)的定制板。
We will be getting information about interrupts in the Linux system through the command:
我们将通过以下命令获取有关Linux系统中中断的信息:
cat /proc/interruptsHere is the output when the kernel was booted without any external options:
这是在没有任何外部选项的情况下启动内核时的输出:
CPU0 CPU1 CPU2 CPU3
0: 15 0 0 0 IO-APIC-edge timer
1: 0 1 0 1 IO-APIC-edge i8042
8: 0 0 0 1 IO-APIC-edge rtc0
9: 0 0 0 0 IO-APIC-fasteoi acpi
12: 0 0 0 1 IO-APIC-edge
23: 16 247 7 10 IO-APIC-fasteoi ehci_hcd:usb1
56: 0 0 0 0 PCI-MSI-edge aerdrv,PCIe PME
57: 0 0 0 0 PCI-MSI-edge aerdrv,PCIe PME
58: 0 0 0 0 PCI-MSI-edge aerdrv,PCIe PME
59: 0 0 0 0 PCI-MSI-edge aerdrv,PCIe PME
60: 0 0 0 0 PCI-MSI-edge aerdrv,PCIe PME
61: 0 0 0 0 PCI-MSI-edge aerdrv,PCIe PME
62: 3118 1984 972 3454 PCI-MSI-edge ahci
63: 1 0 0 0 PCI-MSI-edge eth59
64: 2095 57 4 832 PCI-MSI-edge eth59-rx-0
65: 6 18 1 1309 PCI-MSI-edge eth59-rx-1
66: 13 512 2 1 PCI-MSI-edge eth59-rx-2
67: 10 61 232 2 PCI-MSI-edge eth59-rx-3
68: 169 0 0 0 PCI-MSI-edge eth59-tx-0
69: 14 14 4 205 PCI-MSI-edge eth59-tx-1
70: 11 491 3 0 PCI-MSI-edge eth59-tx-2
71: 20 19 134 50 PCI-MSI-edge eth59-tx-3
72: 0 0 0 0 PCI-MSI-edge eth58
73: 2 1 0 152 PCI-MSI-edge eth58-rx-0
74: 3 150 2 0 PCI-MSI-edge eth58-rx-1
75: 2 34 117 2 PCI-MSI-edge eth58-rx-2
76: 153 0 2 0 PCI-MSI-edge eth58-rx-3
77: 4 0 2 149 PCI-MSI-edge eth58-tx-0
78: 4 149 2 0 PCI-MSI-edge eth58-tx-1
79: 4 0 117 34 PCI-MSI-edge eth58-tx-2
80: 153 0 2 0 PCI-MSI-edge eth58-tx-3
81: 66 106 2 101 PCI-MSI-edge snd_hda_intel
82: 928 5657 262 224 PCI-MSI-edge i915
83: 545 56 32 15 PCI-MSI-edge snd_hda_intel
NMI: 0 0 0 0 Non-maskable interrupts
LOC: 4193 3644 3326 3499 Local timer interrupts
SPU: 0 0 0 0 Spurious interrupts
PMI: 0 0 0 0 Performance monitoring interrupts
IWI: 290 233 590 111 IRQ work interrupts
RTR: 3 0 0 0 APIC ICR read retries
RES: 1339 2163 2404 1946 Rescheduling interrupts
CAL: 607 537 475 559 Function call interrupts
TLB: 163 202 164 251 TLB shootdowns
TRM: 48 48 48 48 Thermal event interrupts
THR: 0 0 0 0 Threshold APIC interrupts
MCE: 0 0 0 0 Machine check exceptions
MCP: 3 3 3 3 Machine check polls
ERR: 0
MIS: 0File '/proc/interrupts' is the procfs Linux interface to the interrupt subsystem, and it presents a table about the number of interrupts on every CPU core in the system in the following form:
文件“ / proc / interrupts”是中断子系统的procfs Linux接口,它以以下形式显示有关系统中每个CPU内核上的中断数的表:
- First column: interrupt number 第一列:中断号
- CPUx columns: interrupt counters for every CPU core in the system CPUx列:系统中每个CPU内核的中断计数器
Next column: interrupt type:
下一栏:中断类型:
- IO-APIC-edge — edge-triggered interrupt for the I/O APIC controller IO-APIC-edge — I / O APIC控制器的边沿触发中断
- IO-APIC-fasteoi — level-triggered interrupt for the I/O APIC controller IO-APIC-fasteoi — I / O APIC控制器的级别触发的中断
- PCI-MSI-edge — MSI interrupt PCI-MSI-edge — MSI中断
- XT-PIC-XT-PIC — interrupt for the PIC controller (we will see it later) XT-PIC-XT-PIC — PIC控制器的中断(我们将在以后看到)
- Last column: device (driver) associated with this interrupt 最后一列:与此中断关联的设备(驱动程序)
Everything here is like it is supposed to be in the modern system. For the devices and drivers which support MSI/MSI-X, this is the type of interrupt that they use. The rest of the interrupt routing is done through the APIC controller.
这里的一切就像应该在现代系统中一样。 对于支持MSI / MSI-X的设备和驱动程序,这是它们使用的中断类型。 其余的中断路由是通过APIC控制器完成的。
Simplistically, the interrupt routing schematics can be drawn like this: (red lines are active routing paths and black lines are unused routing paths)
简单地说,中断路由原理图可以这样绘制:(红线是活动的路由路径,黑线是未使用的路由路径)
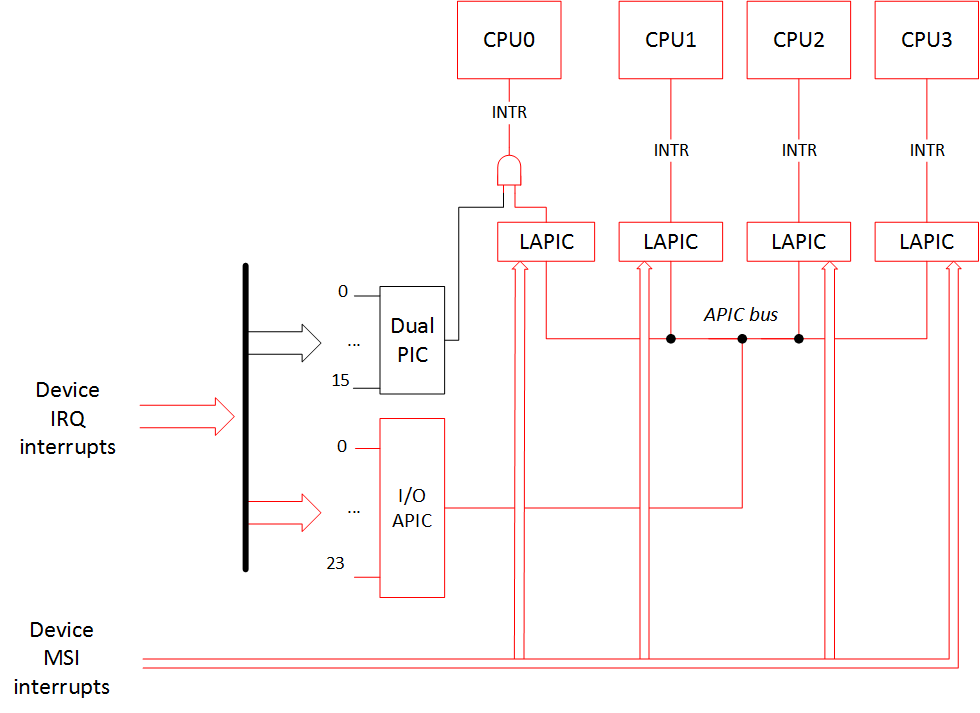
A device that supports MSI/MSI-X interrupts should have that particular capability listed in its PCI configuration space.
支持MSI / MSI-X中断的设备应具有其PCI配置空间中列出的特定功能。
As an example of that let's look at a little fragment of the lspci output for the devices that declare they use MSI/MSI-X. In our case it is a SATA controller (interrupt 'ahci'), two ethernet controllers (interrupts 'eth58*' and 'eth59*'), graphical controller ('i915'), and two HD Audio controllers ('snd_hda_intel').
例如,让我们看一下声明它们使用MSI / MSI-X的设备的lspci输出的一小部分。 在我们的例子中,它是一个SATA控制器(中断“ ahci”),两个以太网控制器(中断“ eth58 *”和“ eth59 *”),图形控制器(“ i915”)和两个HD音频控制器(“ snd_hda_intel”)。
lspci -v00:02.0 VGA compatible controller: Intel Corporation Haswell-ULT Integrated Graphics Controller (rev 09) (prog-if 00 [VGA controller])
...
Capabilities: [90] MSI: Enable+ Count=1/1 Maskable- 64bit-
Capabilities: [d0] Power Management version 2
Capabilities: [a4] PCI Advanced Features
Kernel driver in use: i915
00:03.0 Audio device: Intel Corporation Haswell-ULT HD Audio Controller (rev 09
...
Capabilities: [60] MSI: Enable+ Count=1/1 Maskable- 64bit-
Capabilities: [70] Express Root Complex Integrated Endpoint, MSI 00
Kernel driver in use: snd_hda_intel
00:1b.0 Audio device: Intel Corporation 8 Series HD Audio Controller (rev 04)
...
Capabilities: [60] MSI: Enable+ Count=1/1 Maskable- 64bit+
Capabilities: [70] Express Root Complex Integrated Endpoint, MSI 00
Capabilities: [100] Virtual Channel
Kernel driver in use: snd_hda_intel
00:1f.2 SATA controller: Intel Corporation 8 Series SATA Controller 1 [AHCI mode] (rev 04) (prog-if 01 [AHCI 1.0])
...
Capabilities: [80] MSI: Enable+ Count=1/1 Maskable- 64bit-
Capabilities: [70] Power Management version 3
Capabilities: [a8] SATA HBA v1.0
Kernel driver in use: ahci
05:00.0 Ethernet controller: Intel Corporation I350 Gigabit Network Connection (rev 01)
...
Capabilities: [50] MSI: Enable- Count=1/1 Maskable+ 64bit+
Capabilities: [70] MSI-X: Enable+ Count=10 Masked-
Capabilities: [a0] Express Endpoint, MSI 00
Kernel driver in use: igb
05:00.1 Ethernet controller: Intel Corporation I350 Gigabit Network Connection (rev 01)
...
Capabilities: [50] MSI: Enable- Count=1/1 Maskable+ 64bit+
Capabilities: [70] MSI-X: Enable+ Count=10 Masked-
Capabilities: [a0] Express Endpoint, MSI 00
Kernel driver in use: igbAs we see, all of these devices either have a string «MSI: Enable+» or «MSI-X: Enable+».
如我们所见,所有这些设备都具有字符串«MSI:Enable +»或«MSI-X:Enable +»。
Let's downgrade our system! For a start let's boot with the kernel option 'pci=nomsi'.
让我们降级我们的系统! 首先,让我们使用内核选项“ pci = nomsi”启动。
pci = nomsi (pci=nomsi)
Because of this option MSI interrupts become IO-APIC/XT-PIC depending on the interrupt controller in use.
由于此选项,MSI中断将变为IO-APIC / XT-PIC,具体取决于所使用的中断控制器。
In this case the priority choice is still modern APIC controller, so the interrupt picture will be:
在这种情况下,优先级选择仍然是现代的APIC控制器,因此中断画面为:
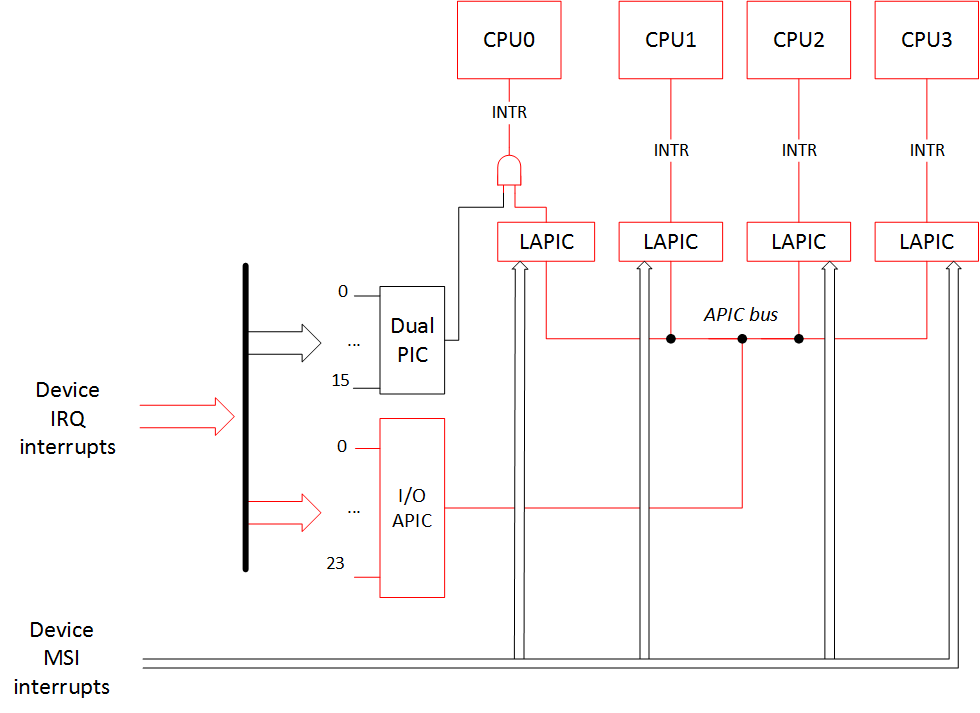
Output of /proc/interrupts:
/ proc / interrupts的输出:
CPU0 CPU1 CPU2 CPU3
0: 15 0 0 0 IO-APIC-edge timer
1: 0 1 0 1 IO-APIC-edge i8042
8: 0 0 1 0 IO-APIC-edge rtc0
9: 0 0 0 0 IO-APIC-fasteoi acpi
12: 0 0 0 1 IO-APIC-edge
16: 1314 5625 342 555 IO-APIC-fasteoi i915, snd_hda_intel, eth59
17: 5 0 1 34 IO-APIC-fasteoi eth58
21: 2882 2558 963 2088 IO-APIC-fasteoi ahci
22: 26 81 2 170 IO-APIC-fasteoi snd_hda_intel
23: 23 369 8 8 IO-APIC-fasteoi ehci_hcd:usb1
NMI: 0 0 0 0 Non-maskable interrupts
LOC: 3011 3331 2435 2617 Local timer interrupts
SPU: 0 0 0 0 Spurious interrupts
PMI: 0 0 0 0 Performance monitoring interrupts
IWI: 197 228 544 85 IRQ work interrupts
RTR: 3 0 0 0 APIC ICR read retries
RES: 1708 2349 1821 1569 Rescheduling interrupts
CAL: 520 554 509 555 Function call interrupts
TLB: 187 181 205 179 TLB shootdowns
TRM: 102 102 102 102 Thermal event interrupts
THR: 0 0 0 0 Threshold APIC interrupts
MCE: 0 0 0 0 Machine check exceptions
MCP: 2 2 2 2 Machine check polls
ERR: 0
MIS: 0As expected, all MSI/MSI-X interrupts have disappeared. Instead of them devices now use interrupts of 'IO-APIC-fasteoi' type.
正如预期的那样,所有MSI / MSI-X中断都消失了。 现在,设备代替它们使用“ IO-APIC-fasteoi”类型的中断。
Let us draw our attention to the fact that earlier, before enabling this kernel boot option, each of the 'eth58' and 'eth59' had nine interrupts! But now each of them has only one interrupt. Recall that without the MSI, one function in the PCI device can have only one interrupt!
让我们引起注意的事实是,在启用此内核引导选项之前,'eth58'和'eth59'每个都有9个中断! 但是现在它们每个只有一个中断。 回想一下,没有MSI,PCI设备中的一个功能只能有一个中断!
Here is a little info from the 'dmesg' command about the ethernet controllers' initialization:
以下是来自dmesg命令的有关以太网控制器初始化的一些信息:
— boot without the 'pci=nomsi' option:
—不使用“ pci = nomsi”选项启动:
igb: Intel(R) Gigabit Ethernet Network Driver - version 5.0.5-k
igb: Copyright (c) 2007-2013 Intel Corporation.
acpi:acpi_pci_irq_enable: igb 0000:05:00.0: PCI INT A -> GSI 16 (level, low) -> IRQ 16
igb 0000:05:00.0: irq 63 for MSI/MSI-X
igb 0000:05:00.0: irq 64 for MSI/MSI-X
igb 0000:05:00.0: irq 65 for MSI/MSI-X
igb 0000:05:00.0: irq 66 for MSI/MSI-X
igb 0000:05:00.0: irq 67 for MSI/MSI-X
igb 0000:05:00.0: irq 68 for MSI/MSI-X
igb 0000:05:00.0: irq 69 for MSI/MSI-X
igb 0000:05:00.0: irq 70 for MSI/MSI-X
igb 0000:05:00.0: irq 71 for MSI/MSI-X
igb 0000:05:00.0: irq 63 for MSI/MSI-X
igb 0000:05:00.0: irq 64 for MSI/MSI-X
igb 0000:05:00.0: irq 65 for MSI/MSI-X
igb 0000:05:00.0: irq 66 for MSI/MSI-X
igb 0000:05:00.0: irq 67 for MSI/MSI-X
igb 0000:05:00.0: irq 68 for MSI/MSI-X
igb 0000:05:00.0: irq 69 for MSI/MSI-X
igb 0000:05:00.0: irq 70 for MSI/MSI-X
igb 0000:05:00.0: irq 71 for MSI/MSI-X
igb 0000:05:00.0: added PHC on eth0
igb 0000:05:00.0: Intel(R) Gigabit Ethernet Network Connection
igb 0000:05:00.0: eth0: (PCIe:5.0Gb/s:Width x1) 00:15:d5:03:00:2a
igb 0000:05:00.0: eth0: PBA No: 106300-000
igb 0000:05:00.0: Using MSI-X interrupts. 4 rx queue(s), 4 tx queue(s)
acpi:acpi_pci_irq_enable: igb 0000:05:00.1: PCI INT B -> GSI 17 (level, low) -> IRQ 17
igb 0000:05:00.1: irq 72 for MSI/MSI-X
igb 0000:05:00.1: irq 73 for MSI/MSI-X
igb 0000:05:00.1: irq 74 for MSI/MSI-X
igb 0000:05:00.1: irq 75 for MSI/MSI-X
igb 0000:05:00.1: irq 76 for MSI/MSI-X
igb 0000:05:00.1: irq 77 for MSI/MSI-X
igb 0000:05:00.1: irq 78 for MSI/MSI-X
igb 0000:05:00.1: irq 79 for MSI/MSI-X
igb 0000:05:00.1: irq 80 for MSI/MSI-X
igb 0000:05:00.1: irq 72 for MSI/MSI-X
igb 0000:05:00.1: irq 73 for MSI/MSI-X
igb 0000:05:00.1: irq 74 for MSI/MSI-X
igb 0000:05:00.1: irq 75 for MSI/MSI-X
igb 0000:05:00.1: irq 76 for MSI/MSI-X
igb 0000:05:00.1: irq 77 for MSI/MSI-X
igb 0000:05:00.1: irq 78 for MSI/MSI-X
igb 0000:05:00.1: irq 79 for MSI/MSI-X
igb 0000:05:00.1: irq 80 for MSI/MSI-X
igb 0000:05:00.1: added PHC on eth1
igb 0000:05:00.1: Intel(R) Gigabit Ethernet Network Connection
igb 0000:05:00.1: eth1: (PCIe:5.0Gb/s:Width x1) 00:15:d5:03:00:2b
igb 0000:05:00.1: eth1: PBA No: 106300-000
igb 0000:05:00.1: Using MSI-X interrupts. 4 rx queue(s), 4 tx queue(s)— boot with the 'pci=nomsi' option:
—使用“ pci = nomsi”选项启动:
igb: Intel(R) Gigabit Ethernet Network Driver - version 5.0.5-k
igb: Copyright (c) 2007-2013 Intel Corporation.
acpi:acpi_pci_irq_enable: igb 0000:05:00.0: PCI INT A -> GSI 16 (level, low) -> IRQ 16
igb 0000:05:00.0: added PHC on eth0
igb 0000:05:00.0: Intel(R) Gigabit Ethernet Network Connection
igb 0000:05:00.0: eth0: (PCIe:5.0Gb/s:Width x1) 00:15:d5:03:00:2a
igb 0000:05:00.0: eth0: PBA No: 106300-000
igb 0000:05:00.0: Using legacy interrupts. 1 rx queue(s), 1 tx queue(s)
acpi:acpi_pci_irq_enable: igb 0000:05:00.1: PCI INT B -> GSI 17 (level, low) -> IRQ 17
igb 0000:05:00.1: added PHC on eth1
igb 0000:05:00.1: Intel(R) Gigabit Ethernet Network Connection
igb 0000:05:00.1: eth1: (PCIe:5.0Gb/s:Width x1) 00:15:d5:03:00:2b
igb 0000:05:00.1: eth1: PBA No: 106300-000
igb 0000:05:00.1: Using legacy interrupts. 1 rx queue(s), 1 tx queue(s)Because of the decreased number of interrupts per device, enabling this option can lead to a significant performance limitation of the device driver, and that is not even counting that according to the Intel research 'Reducing Interrupt Latency Through the Use of Message Signaled Interrupts', MSI interrupts 3 times faster than the IO-APIC interrupts and 5 times faster than the PIC interrupts.
由于每个设备的中断数量减少,因此启用此选项可能会严重限制设备驱动程序的性能,根据英特尔的研究“通过使用消息信号中断来减少中断延迟” ,这甚至还没有算在内 。 MSI中断比IO-APIC中断快3倍,比PIC中断快5倍。
Noapic (noapic)
This option disables I/O APIC. MSI interrupts can still find their way to all of the CPUs, but the rest of interrupts from the devices can go only to CPU0, because PIC is only connected to CPU0. However, LAPIC is working and all other CPUs can still work and handle interrupts.
此选项禁用I / O APIC。 MSI中断仍然可以通向所有CPU,但是来自设备的其余中断只能到达CPU0,因为PIC仅连接到CPU0。 但是,LAPIC正在工作,所有其他CPU仍可以工作并处理中断。
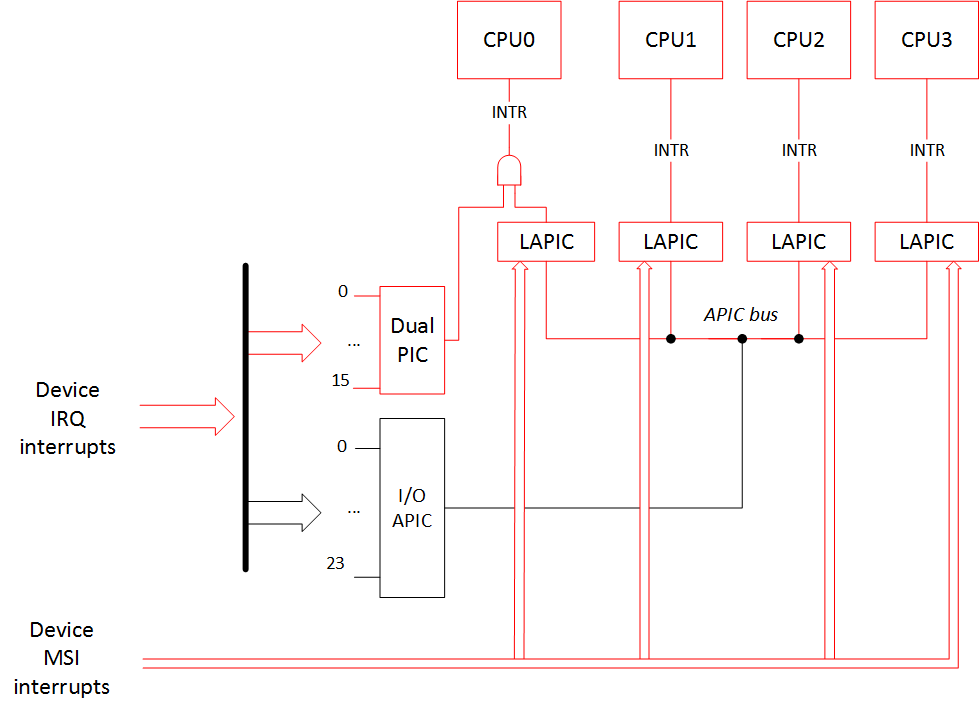
CPU0 CPU1 CPU2 CPU3
0: 5 0 0 0 XT-PIC-XT-PIC timer
1: 2 0 0 0 XT-PIC-XT-PIC i8042
2: 0 0 0 0 XT-PIC-XT-PIC cascade
8: 1 0 0 0 XT-PIC-XT-PIC rtc0
9: 0 0 0 0 XT-PIC-XT-PIC acpi
12: 172 0 0 0 XT-PIC-XT-PIC ehci_hcd:usb1
56: 0 0 0 0 PCI-MSI-edge aerdrv, PCIe PME
57: 0 0 0 0 PCI-MSI-edge aerdrv, PCIe PME
58: 0 0 0 0 PCI-MSI-edge aerdrv, PCIe PME
59: 0 0 0 0 PCI-MSI-edge aerdrv, PCIe PME
60: 0 0 0 0 PCI-MSI-edge aerdrv, PCIe PME
61: 0 0 0 0 PCI-MSI-edge aerdrv, PCIe PME
62: 2833 2989 1021 811 PCI-MSI-edge ahci
63: 0 1 0 0 PCI-MSI-edge eth59
64: 301 52 9 3 PCI-MSI-edge eth59-rx-0
65: 12 24 3 178 PCI-MSI-edge eth59-rx-1
66: 14 85 6 2 PCI-MSI-edge eth59-rx-2
67: 17 24 307 1 PCI-MSI-edge eth59-rx-3
68: 70 18 8 10 PCI-MSI-edge eth59-tx-0
69: 7 0 0 23 PCI-MSI-edge eth59-tx-1
70: 15 227 2 2 PCI-MSI-edge eth59-tx-2
71: 18 6 27 2 PCI-MSI-edge eth59-tx-3
72: 0 0 0 0 PCI-MSI-edge eth58
73: 1 0 0 27 PCI-MSI-edge eth58-rx-0
74: 1 22 0 5 PCI-MSI-edge eth58-rx-1
75: 1 0 22 5 PCI-MSI-edge eth58-rx-2
76: 23 0 0 5 PCI-MSI-edge eth58-rx-3
77: 1 0 0 27 PCI-MSI-edge eth58-tx-0
78: 1 22 0 5 PCI-MSI-edge eth58-tx-1
79: 1 0 22 5 PCI-MSI-edge eth58-tx-2
80: 23 0 0 5 PCI-MSI-edge eth58-tx-3
81: 187 17 70 7 PCI-MSI-edge snd_hda_intel
82: 698 1647 247 129 PCI-MSI-edge i915
83: 438 135 16 59 PCI-MSI-edge snd_hda_intel
NMI: 0 0 0 0 Non-maskable interrupts
LOC: 1975 2499 2245 1474 Local timer interrupts
SPU: 0 0 0 0 Spurious interrupts
PMI: 0 0 0 0 Performance monitoring interrupts
IWI: 132 67 429 91 IRQ work interrupts
RTR: 3 0 0 0 APIC ICR read retries
RES: 1697 2178 1903 1541 Rescheduling interrupts
CAL: 561 496 534 567 Function call interrupts
TLB: 229 254 170 137 TLB shootdowns
TRM: 78 78 78 78 Thermal event interrupts
THR: 0 0 0 0 Threshold APIC interrupts
MCE: 0 0 0 0 Machine check exceptions
MCP: 2 2 2 2 Machine check polls
ERR: 0
MIS: 0As we see, all IO-APIC-* interrupts have turned into XT-PIC-XT-PIC, and all of these interrupts have been routed to CPU0 only. MSI interrupts on the other hand have remained unchanged and go to all of the CPUs.
如我们所见,所有IO-APIC- *中断都变成了XT-PIC-XT-PIC,并且所有这些中断仅被路由到CPU0。 另一方面,MSI中断保持不变,并传递给所有CPU。
空腹的 (nolapic)
This kernel boot option disables LAPIC. MSI interrupts can't work without LAPIC, and I/O APIC can't work without LAPIC either. All of the device interrupts can only go to the PIC, and it works with the CPU0 only. And without LAPIC the rest of the CPUs besides CPU0 won't work.
此内核引导选项禁用LAPIC。 没有LAPIC,MSI中断将无法工作;没有LAPIC,I / O APIC也将无法工作。 所有的设备中断只能发送到PIC,并且仅适用于CPU0。 如果没有LAPIC,除了CPU0之外的其他CPU将无法工作。
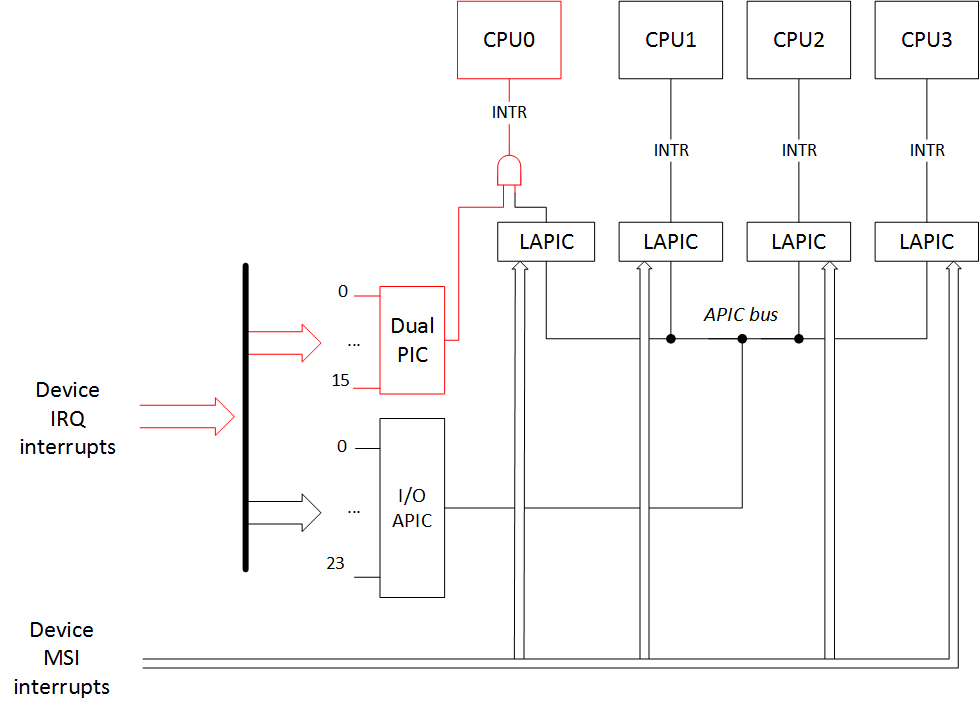
Output of /proc/interrupts:
/ proc / interrupts的输出:
CPU0
0: 6416 XT-PIC-XT-PIC timer
1: 2 XT-PIC-XT-PIC i8042
2: 0 XT-PIC-XT-PIC cascade
3: 5067 XT-PIC-XT-PIC aerdrv, aerdrv, PCIe PME, PCIe PME, i915, snd_hda_intel, eth59
4: 32 XT-PIC-XT-PIC aerdrv, aerdrv, PCIe PME, PCIe PME, eth58
5: 0 XT-PIC-XT-PIC aerdrv, PCIe PME
6: 0 XT-PIC-XT-PIC aerdrv, PCIe PME
8: 1 XT-PIC-XT-PIC rtc0
9: 0 XT-PIC-XT-PIC acpi
11: 274 XT-PIC-XT-PIC snd_hda_intel
12: 202 XT-PIC-XT-PIC ehci_hcd:usb1
15: 7903 XT-PIC-XT-PIC ahci
NMI: 0 Non-maskable interrupts
LOC: 0 Local timer interrupts
SPU: 0 Spurious interrupts
PMI: 0 Performance monitoring interrupts
IWI: 0 IRQ work interrupts
RTR: 0 APIC ICR read retries
RES: 0 Rescheduling interrupts
CAL: 0 Function call interrupts
TLB: 0 TLB shootdowns
TRM: 0 Thermal event interrupts
THR: 0 Threshold APIC interrupts
MCE: 0 Machine check exceptions
MCP: 1 Machine check polls
ERR: 0
MIS: 0选项组合: (Combinations of options:)
Actually there is only one combination for the new variant of routing: «noapic pci=nomsi». In this case all interrupts from the devices only go to the CPU0 through the PIC controller. But the LAPIC system is still working, so all the other CPUs can work and handle interrupts.
实际上,路由的新变体只有一种组合:«noapic pci = nomsi»。 在这种情况下,来自设备的所有中断仅通过PIC控制器进入CPU0。 但是LAPIC系统仍在工作,因此所有其他CPU都可以工作并处理中断。
You cannot combine any other options with «nolapic» since it makes I/O APIC and MSI unaccessible. Therefore, if you've ever added Linux kernel boot options like «noapic nolapic» (or the most common case «acpi=off noapic nolapic») it seems like you've written some extra letters.
您不能将其他任何选项与«nolapic»组合使用,因为它会使I / O APIC和MSI无法访问。 因此,如果您曾经添加过诸如«noapic nolapic»之类的Linux内核引导选项(或者最常见的情况是«acpi = off noapic nolapic»),则似乎您已经写了一些额外的字母。
Finally, here is the result of the options «noapic pci=nomsi» to our interrupt routing picture:
最后,这是我们的中断路由图片的选项«noapic pci = nomsi»的结果:
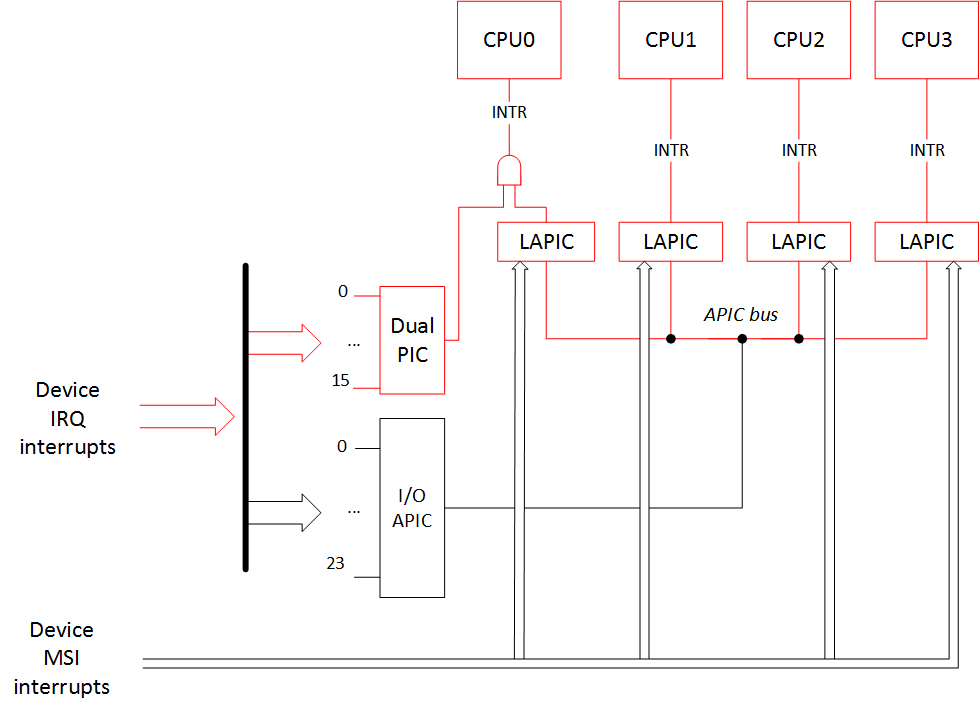
And the output of /proc/interrupts is:
/ proc / interrupts的输出是:
CPU0 CPU1 CPU2 CPU3
0: 5 0 0 0 XT-PIC-XT-PIC timer
1: 2 0 0 0 XT-PIC-XT-PIC i8042
2: 0 0 0 0 XT-PIC-XT-PIC cascade
3: 5072 0 0 0 XT-PIC-XT-PIC i915, snd_hda_intel, eth59
4: 32 0 0 0 XT-PIC-XT-PIC eth58
8: 1 0 0 0 XT-PIC-XT-PIC rtc0
9: 0 0 0 0 XT-PIC-XT-PIC acpi
11: 281 0 0 0 XT-PIC-XT-PIC snd_hda_intel
12: 200 0 0 0 XT-PIC-XT-PIC ehci_hcd:usb1
15: 7930 0 0 0 XT-PIC-XT-PIC ahci
NMI: 0 0 0 0 Non-maskable interrupts
LOC: 2595 2387 2129 1697 Local timer interrupts
SPU: 0 0 0 0 Spurious interrupts
PMI: 0 0 0 0 Performance monitoring interrupts
IWI: 159 90 482 135 IRQ work interrupts
RTR: 3 0 0 0 APIC ICR read retries
RES: 1568 1666 1810 1833 Rescheduling interrupts
CAL: 431 556 549 558 Function call interrupts
TLB: 124 184 156 274 TLB shootdowns
TRM: 116 116 116 116 Thermal event interrupts
THR: 0 0 0 0 Threshold APIC interrupts
MCE: 0 0 0 0 Machine check exceptions
MCP: 2 2 2 2 Machine check polls
ERR: 0
MIS: 0中断路由表和选项«acpi = noirq»,«pci = noacpi»,«acpi = off» (Interrupt routing tables and the options «acpi=noirq», «pci=noacpi», «acpi=off»)
How does the operating system get information about the device interrupt routing? The BIOS prepares such info for the OS in the form of:
操作系统如何获取有关设备中断路由的信息? BIOS通过以下形式为操作系统准备此类信息:
- ACPI tables (_PIC/_PRT functions) ACPI表(_PIC / _PRT函数)
- _MP_ table (MPtable) _MP_表(MPtable)
- $PIR table $ PIR表
- Registers 0x3C/0x3D of the device's PCI configuration space 注册设备PCI配置空间的0x3C / 0x3D
It is worth to note for the MSI interrupts declaration that the BIOS doesn't need to do anything extra (beside declaring the use of the LAPIC): all the aforementioned routing information is needed only for the APIC/PIC interrupt lines.
对于MSI中断声明,值得注意的是BIOS不需要做任何额外的事情(除了声明使用LAPIC之外):所有上述路由信息仅对于APIC / PIC中断线才需要。
Tables in the list above are presented in the order of priority. Let's examine it in detail.
上面列表中的表按优先级顺序显示。 让我们详细研究一下。
Let's assume the BIOS has presented all this data and we boot our OS without any extra boot options:
假设BIOS提供了所有这些数据,并且我们在没有任何额外启动选项的情况下启动了操作系统:
- OS finds ACPI tables. 操作系统找到ACPI表。
- ОS executes ACPI function "_PIC", passing it the argument stating that the boot should happen in APIC mode. Here there is function code that usually saves the chosen mode in a variable (for example, PICM=1). ОS执行ACPI函数“ _PIC”,并向其传递表明应在APIC模式下进行引导的参数。 这里有一些功能代码,通常会将所选模式保存在一个变量中(例如,PICM = 1)。
- To access interrupt routing info the OS calls ACPI function "_PRT". This checks the PICM variable and returns routing for the APIC mode case. 为了访问中断路由信息,操作系统调用ACPI函数“ _PRT”。 这将检查PICM变量并返回APIC模式情况的路由。
In the case when we boot with the option
如果我们使用选项启动
Noapic (noapic)
:
:
- OS finds ACPI tables 操作系统找到ACPI表
- ОS executes ACPI function "_PIC", passing it the argument stating that the boot should happen in PIC mode. Here there is function code that usually saves the chosen mode in a variable (for example, PICM=0) ОS执行ACPI函数“ _PIC”,并向其传递表明应在PIC模式下进行引导的参数。 这里有一些功能代码,通常会将所选模式保存在变量中(例如,PICM = 0)
- To access interrupt routing info the OS calls ACPI function "_PRT". This checks the PICM variable and returns routing for the PIC mode case. 为了访问中断路由信息,操作系统调用ACPI函数“ _PRT”。 这将检查PICM变量,并在PIC模式下返回路由。
If ACPI tables aren't present or interrupt routing with ACPI is disabled through the option
如果不存在ACPI表或通过选项禁用了使用ACPI的中断路由
acpi = noirq (acpi=noirq)
or
要么
pci = noacpi (pci=noacpi)
(or ACPI subsystem is completely disabled with the
(或ACPI子系统被完全禁用
acpi = off (acpi=off)
option), then the OS looks for the MPtable (_MP_) to get all the interrupt routing information:
选项),然后操作系统会寻找MPtable(_MP_)来获取所有中断路由信息:
- OS can't find/doesn't look at the ACPI tables 操作系统找不到/不查看ACPI表
- OS finds MPtable (_MP_) 操作系统发现MPtable(_MP_)
If ACPI tables aren't present or interrupt routing with ACPI is disabled through the option
如果不存在ACPI表或通过选项禁用了使用ACPI的中断路由
acpi = noirq (acpi=noirq)
or
要么
pci = noacpi (pci=noacpi)
(or ACPI subsystem is completely disabled with the
(或ACPI子系统被完全禁用
acpi = off (acpi=off)
option), and if the MPtable (_MP_) is not present either (or there is a boot option
选项),如果MPtable(_MP_)也不存在(或有启动选项)
Noapic (noapic)
or
要么
空腹的 (nolapic)
):
):
- OS can't find/doesn't look at the ACPI tables 操作系统找不到/不查看ACPI表
- OS can't find/doesn't look at the MPtable (_MP_) 操作系统找不到/看不到MPtable(_MP_)
- OS finds $PIR table 操作系统找到$ PIR表
If there is no $PIR table or it is not full, then the OS will look at the registers 0x3C/0x3D of the device's PCI configuration space to guess interrupt routing.
如果没有$ PIR表或表不完整,则OS将查看设备PCI配置空间的寄存器0x3C / 0x3D,以猜测中断路由。
Here is a picture summarizing all of this:
这是概述所有这些的图片:
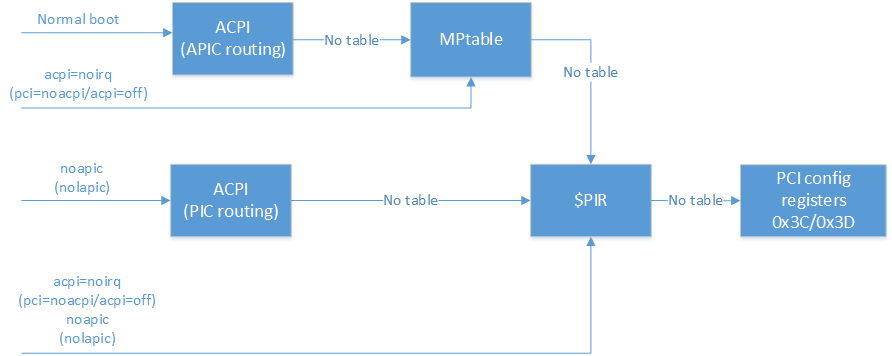
One should remember that not every BIOS provides all of these three tables (ACPI/MPtable/$PIR), so if you've passed an option to your bootloader (e.g. GRUB) that disables the use of ACPI or ACPI and MPtable for the interrupt routing, it is possible that your system won't boot.
应当记住,并非每个BIOS都提供所有这三个表(ACPI / MPtable / $ PIR),因此,如果您已将一个选项传递给引导加载程序(例如GRUB),则该选项禁止对中断使用ACPI或ACPI和MPtable路由,则系统可能无法启动。
注1 (Note 1)
: In the case when we try to boot in APIC mode with the option 'acpi=noirq' and without MPtable present, the picture of interrupts will be like in the case of normal booting with only the 'noapic' option. The operating system will go to PIC mode by itself. In the case when you try to boot without any ACPI tables at all ('acpi=off') and without MPtable present, then the picture will be like this:
注意:如果我们尝试使用选项'acpi = noirq'且没有MPtable的情况下以APIC模式启动,则中断的情况类似于仅使用'noapic'选项进行常规启动的情况。 操作系统将自行进入PIC模式。 如果您尝试完全不使用任何ACPI表('acpi = off')并且不使用MPtable进行引导,则情况如下所示:
CPU0
0: 6 XT-PIC-XT-PIC timer
1: 2 XT-PIC-XT-PIC i8042
2: 0 XT-PIC-XT-PIC cascade
8: 0 XT-PIC-XT-PIC rtc0
12: 373 XT-PIC-XT-PIC ehci_hcd:usb1
16: 0 PCI-MSI-edge PCIe PME
17: 0 PCI-MSI-edge PCIe PME
18: 0 PCI-MSI-edge PCIe PME
19: 0 PCI-MSI-edge PCIe PME
20: 0 PCI-MSI-edge PCIe PME
21: 0 PCI-MSI-edge PCIe PME
22: 8728 PCI-MSI-edge ahci
23: 1 PCI-MSI-edge eth59
24: 1301 PCI-MSI-edge eth59-rx-0
25: 113 PCI-MSI-edge eth59-tx-0
26: 0 PCI-MSI-edge eth58
27: 45 PCI-MSI-edge eth58-rx-0
28: 45 PCI-MSI-edge eth58-tx-0
29: 1280 PCI-MSI-edge snd_hda_intel
NMI: 2 Non-maskable interrupts
LOC: 24076 Local timer interrupts
SPU: 0 Spurious interrupts
PMI: 2 Performance monitoring interrupts
IWI: 2856 IRQ work interrupts
RTR: 0 APIC ICR read retries
RES: 0 Rescheduling interrupts
CAL: 0 Function call interrupts
TLB: 0 TLB shootdowns
TRM: 34 Thermal event interrupts
THR: 0 Threshold APIC interrupts
MCE: 0 Machine check exceptions
MCP: 2 Machine check polls
ERR: 0
MIS: 0This happens because without the ACPI MADT table (Multiple APIC Description Table) and the necessary info from the MPtable, the operating system doesn't know APIC identifiers (APIC IDs) for the other CPUs and can't work with them. But the LAPIC of the main CPU0 works because we haven't disabled it, and MSI interrupts can still go to it. So the interrupt picture would be:
发生这种情况的原因是,如果没有ACPI MADT表( 多个APIC描述表 )和MPtable中的必要信息,则操作系统将不知道其他CPU的APIC标识符(APIC ID),因此无法使用它们。 但是主CPU0的LAPIC可以工作,因为我们尚未将其禁用,并且MSI中断仍然可以传递给它。 因此,中断画面将是:
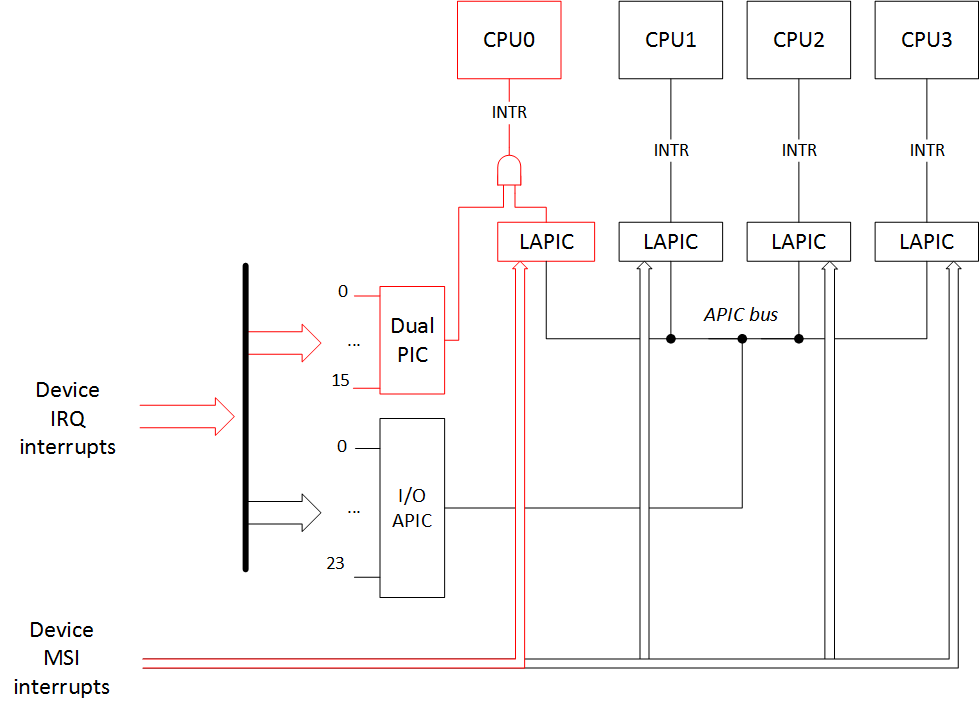
笔记2 (Note 2)
: In general, interrupt routing with the use of ACPI in an APIC case should match the interrupt routing with the MPtable. Also, the interrupt routing with the use of ACPI in a PIC case should match the interrupt routing with the $PIR table. Therefore the '/proc/interrupts' output should not differ. But in my investigation I've noticed one strange fact. For some reason in the case of interrupt routing through the MPtable there is a cascade interrupt «XT-PIC-XT-PIC cascade» in the output:
注意:通常,在APIC情况下使用ACPI进行中断路由时,应将中断路由与MPtable匹配。 同样,在PIC情况下使用ACPI的中断路由应与$ PIR表匹配。 因此,“ / proc / interrupts”输出不应有差异。 但是在调查中,我注意到了一个奇怪的事实。 由于某种原因,在通过MPtable进行中断路由时,输出中会出现一个级联中断《 XT-PIC-XT-PIC级联》:
CPU0 CPU1 CPU2 CPU3
0: 15 0 0 0 IO-APIC-edge timer
1: 2 0 0 0 IO-APIC-edge i8042
2: 0 0 0 0 XT-PIC-XT-PIC cascade
8: 0 1 0 0 IO-APIC-edge rtc0
9: 0 0 0 0 IO-APIC-edge acpi
...It is a little bit strange that it happens like that, but it seems like the kernel source documentation says that it is OK.
发生这样的事情有点奇怪,但是似乎内核源文档说还可以。
包容性 (Сonclusion)
In conclusion we review for one more time the discussed options.
总之,我们再讨论了所讨论的选项。
Interrupt controller choice options:
中断控制器选择选项:
pci = nomsi (pci=nomsi)
— MSI interrupts become IO-APIC/XT-PIC depending on the interrupt controller in use.
—根据使用的中断控制器,MSI中断将变为IO-APIC / XT-PIC。
Noapic (noapic)
— Disables I/O APIC. MSI interrupts can still go to all the other CPUs, the rest of the device interrupts can only go to the PIC, and it works with the CPU0 only. But LAPIC still works and other CPUs can work and handle interrupts.
—禁用I / O APIC。 MSI中断仍然可以传递给所有其他CPU,其余的设备中断只能传递给PIC,并且仅适用于CPU0。 但是LAPIC仍然可以工作,其他CPU可以工作并处理中断。
noapic pci = nomsi (noapic pci=nomsi)
— All of the device interrupts can only go to the PIC, and it works with the CPU0 only. But LAPIC works and other CPUs can work and handle interrupts.
—所有的设备中断只能发送到PIC,并且仅适用于CPU0。 但是LAPIC可以工作,其他CPU可以工作并处理中断。
空腹的 (nolapic)
— Disables LAPIC. MSI interrupts can't work without LAPIC, and I/O APIC can't work without LAPIC. All of the device interrupts can only go to the PIC, and it works with the CPU0 only. And without LAPIC the rest of the CPUs besides CPU0 won't work.
—禁用LAPIC。 没有LAPIC,MSI中断将无法工作;没有LAPIC,I / O APIC将无法工作。 所有的设备中断只能发送到PIC,并且仅适用于CPU0。 如果没有LAPIC,除了CPU0之外的其他CPU将无法工作。
Interrupt tables priority options:
中断表优先选项:
没有选择 (no options)
— routing through the APIC with the help of ACPI tables
—在ACPI表的帮助下通过APIC进行路由
Noapic (noapic)
— routing through the PIC with the help of ACPI tables
-在ACPI表的帮助下通过PIC进行路由
acpi = noirq (acpi=noirq)
(
(
pci = noacpi (pci=noacpi)
/
/
acpi = off (acpi=off)
) — routing through the APIC with the help of MPtable
)—在MPtable的帮助下通过APIC进行路由
acpi = noirq (acpi=noirq)
(
(
pci = noacpi (pci=noacpi)
/
/
acpi = off (acpi=off)
)
)
Noapic (noapic)
(
(
空腹的 (nolapic)
) — routing through the PIC with the help of $PIR
)-在$ PIR的帮助下通过PIC进行路由
In the next part we will look at how coreboot configures the chipset for the interrupt routing.
在下一部分中,我们将研究coreboot如何为中断路由配置芯片组。
致谢 (Acknowledgments)
Special thanks to Jacob Garber from the coreboot community for helping me with this article translation
特别感谢coreboot社区的Jacob Garber帮助我完成本文翻译
linux内核关闭中断




 本文深入探讨了如何在Linux内核中回滚到使用过时的中断传递方法,重点关注pci=nomsi、noapic、nolapic等引导选项。文章详细解释了这些选项如何改变中断处理和内核/proc/interrupts接口输出,并分析了中断路由表的查找顺序及其影响。内容包括选项组合、中断控制器选择以及中断表优先级选项的详细说明。
本文深入探讨了如何在Linux内核中回滚到使用过时的中断传递方法,重点关注pci=nomsi、noapic、nolapic等引导选项。文章详细解释了这些选项如何改变中断处理和内核/proc/interrupts接口输出,并分析了中断路由表的查找顺序及其影响。内容包括选项组合、中断控制器选择以及中断表优先级选项的详细说明。
















 1104
1104

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








