package cn.cc.day22;
import java.util.Random;
/**
* @author CC
* 有一个框,里边可以放入10个馒头,顾客来买。
* 师傅在做,框满了通知顾客买,框空了通知师傅做。
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Foods foods = new Foods();
Producter p = new Producter(foods);
//创建线程
Thread t1 = new Thread(p,"生产者1");
Thread t2 = new Thread(p,"生产者2");
Consumer c = new Consumer(foods);
Thread t3 = new Thread(c,"消费者1");
Thread t4 = new Thread(c,"消费者2");
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
t4.start();
}
}
class Foods{
int num = 0;
boolean flag = true;//标记做/买馒头
//生产功能
public synchronized void product() {
//如果在买馒头,则暂停
while(flag == false) {
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//做馒头的过程
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
num++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"生产了第"+num+"个馒头");
if (num == 10) {
System.out.println("来买哇!做好了!------------------");
flag = !flag;
notifyAll();
}
}
//消费功能
public synchronized void consumer() {
//如果在做馒头,则暂停
while(flag == true) {
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//买馒头的过程
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//产生随机买的馒头数
Random rd = new Random();
int n = rd.nextInt(num)+1;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"消费了"+n+"个馒头");
num = num-n;
if (num == 0) {
System.out.println("快做吧!没吃的了-----------");
flag = !flag;
notifyAll();
}
}
}
//生产线程
class Producter implements Runnable{
Foods foods = null;
public Producter(Foods foods) {
this.foods = foods;
}
@Override
public void run() {
int i = 0;//此循环是为了让时间片有机会轮转,i大于5即可
while(i < 100) {//i为5的话,两个线程正好各执行5次
foods.product();
i++;
}
}
}
//消费线程
class Consumer implements Runnable{
Foods foods = null;
public Consumer(Foods foods) {
this.foods = foods;
}
@Override
public void run() {
int i = 0;//此循环是为了让时间片有机会轮转,i大于5即可
while(i < 100) {
foods.consumer();
i++;
}
}
}
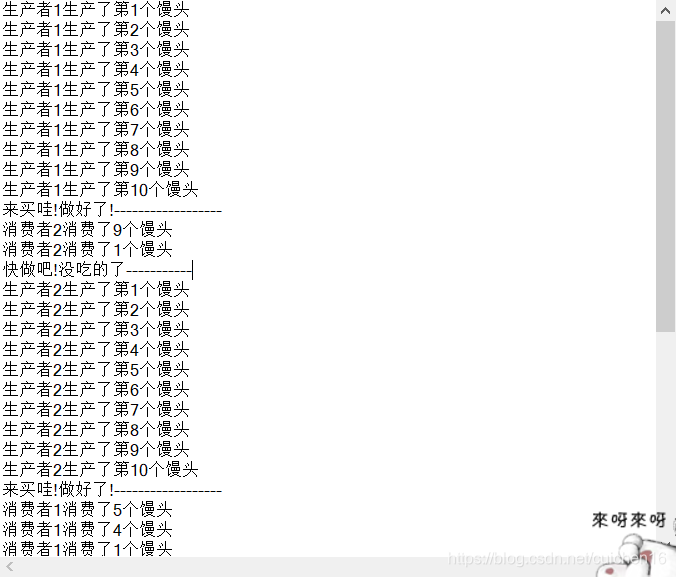
加循环并且休眠目的: 延长线程执行时间,让其他线程有机会轮转进来(让CPU有轮转的时间)
交替打印A,B各10次
// 打印机类
public class Printer {
private boolean hasBufferToPrint = false ; // 打印缓冲区是否有内容可以打印
// 打印A:相当于生产者,放一张纸
public synchronized void printA() {
while (hasBufferToPrint) { // 缓冲区还有内容
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.print( "A" );
hasBufferToPrint = true ;
notify(); // 唤醒打印B的线程
}
// 打印B:相当于消费者,消耗缓冲区中的纸,打印纸张
public synchronized void printB() {
while (!hasBufferToPrint) {
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.print( "B" );
hasBufferToPrint = false ;
notify(); // 唤醒打印A的线程
}
static class ThreadA extends Thread {
private Printer printer;
public ThreadA(Printer printer) {
this .printer = printer;
}
public void run() {
for ( int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) {
printer.printA();
}
}
}
static class ThreadB extends Thread {
private Printer printer;
public ThreadB(Printer printer) {
this .printer = printer;
}
public void run() {
for ( int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) {
printer.printB();
}
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Printer printer = new Printer(); // A、B线程共享同一个打印机
Thread a = new ThreadA(printer);
Thread b = new ThreadB(printer);
a.start();
b.start();
}
}





 本文详细介绍了如何使用Java实现生产者-消费者模型,通过线程间的同步与等待,实现资源的有效分配。代码示例中,一个框可以存放10个馒头,生产者制作馒头,消费者购买馒头,通过synchronized关键字和wait/notify方法确保线程间正确协调。
本文详细介绍了如何使用Java实现生产者-消费者模型,通过线程间的同步与等待,实现资源的有效分配。代码示例中,一个框可以存放10个馒头,生产者制作馒头,消费者购买馒头,通过synchronized关键字和wait/notify方法确保线程间正确协调。
















 400
400

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








