二叉排序树(BST)
section1 : 二叉排序树的简介
1.1 什么是二叉排序树
二叉排序树(Binary Sort Tree),又称二叉查找树(Binary Search Tree),亦称二叉搜索树。是数据结构中的一类。在一般情况下,查询效率比链表结构要高
1.2 二叉排序树的定义
一棵空树,或者是具有下列性质的二叉树:
- 若左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值
- 若右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于它的根结点的值
- 左、右子树也分别为二叉排序树
- 没有键值相等的结点
2. 二叉排序树优势分析
- 当使用数组进行数据的操作时: 删除,插入的效率较低,因为涉及到插入,删除点之后数据的移动操作;
- 当使用链表进行数据的操作时, 删除,插入数据的效率较高,但是查询的效率很低
- 使用BST进行数据的操作, 会按照数据的id值去查找对应的元素,每次递归查询的数据量减半,因此查询效率高于链表; 且能实现像链表类似的增删方式,因此删除和添加效率也可以保证;
3. 二叉排序树实例
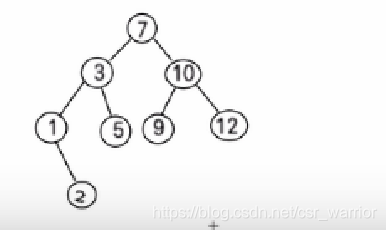
3.1 创建二叉排序树
3.1.1 创建BST的思路:
- 首先定义一个BiarySortTreeNode的类, 作为BST的一个节点对象; 属性包含属性值(int value),指向左子树的指针(BinarySortTreeNode left)和指向右子树的指针(BianrySortTreeNode)right;
- 创建一个BiarySortTree的类,把root节点作为类属性
- 编写addNode方法, 新增的Node作为参数; 如果判断新节点在BST中所在位置,进行添加操作
- 所有节点添加完成后,BST就已经构建完成
3.1.2 代码示例:
public void addNode(BinarySortTreeNode newNode) {
if (newNode == null) {
System.out.println("newNode is null!!");
return;
}
if (newNode.getVal() < this.getVal()) {
//新节点的值小于当前节点的值,挂载到左子树
if (this.getLeftChild() == null) {
this.setLeftChild(newNode);
} else {
//向左子树递归
this.leftChild.addNode(newNode);
}
} else {
//新节点的值大于当前节点,挂载到右子树
if (this.getRightChild() == null) {
this.setRightChild(newNode);
} else {
//向右递归
this.rightChild.addNode(newNode);
}
}
}
3.2 查找节点
3.2.1 查找节点的思路分析
- 若根结点的关键字值等于查找的关键字,成功
- 若小于根结点的关键字值,递归查左子树
- 若大于根结点的关键字值,递归查右子树
- 若子树为空,查找不成功
3.2.2 代码示例:
public BinarySortTreeNode searchNode(int val) {
if (this.getVal() == val) {
return this;
} else if (val < this.getVal()) {
if (this.leftChild == null) {
return null;
}
//向左递归查找
return this.leftChild.searchNode(val);
} else {
if (this.rightChild == null) {
return null;
}
//向右递归查找
return this.rightChild.searchNode(val);
}
}
3.3 删除节点
3.3.1 删除节点思路分析
删除节点的情况较复杂,有下面三种情况需要考虑
- 删除叶子节点
- 删除只有一颗子树的节点
- 删除有两颗子树的节点.
1. 删除叶子节点
-
先去找到要删除的结点targetNode
-
找到targetNode的父结点parentNode;
-
确定targetNode是parentNode的左子结点还是右子结点
- 如果是左子节点: ParentNode.left = null;
- 如果是右子节点:parentNode.right = null;
2. 删除只有一颗子树的节点
- 先去找到要删除的结点targetNode
- 找到targetNode的父结点parentNode
- 确定targetNode的子结点是左子结点还是右子结点
- 如果targetNode有左子结点:
-
如果targetNode是parentNode的左子节点:
- parentNode.left = targetNode.left;
-
如果targetNode是parentNode的右子节点:
- parentNode.right = targetNode.left;
-
- 如果targetNode有右子节点
-
如果targetNode是parentNode的左子节点:
- parentNode.left = targetNode.right;
-
如果targetNode是parentNode的右子节点:
- parentNode.right = targetNode.right;
-
3. 删除有两颗子树的节点
- 先去找到要删除的结点targetNode
- 找到targetNode的父结点parentNode
- 从targetNode的右子树找到最小的结点或者左子树中最小的节点
- 用一个临时变量,将最小结点的值保存temp
- 删除该最小结点
- targetNode.value=temp.value
3.3.2 代码实现
首先先定义两个方法:
- 查找父节点的方法
public BinarySortTreeNode searchParentNode(int val) {
if ((this.leftChild != null && this.leftChild.getVal() == val) || (this.rightChild != null && this.rightChild.getVal() == val)) {
return this;
} else if (val < this.getVal() && this.leftChild != null) {
//左递归
return this.leftChild.searchParentNode(val);
} else if (val > this.getVal() && this.rightChild != null) {
//有递归
return this.rightChild.searchParentNode(val);
} else {
return null;
}
}
- 查找左子树中最大值的方法
private int deleteMaxNode(BinarySortTreeNode node) {
BinarySortTreeNode temp = node;
if (temp == null) {
return -1;
}
while (temp.getRightChild() != null) {
temp = temp.getRightChild();
}
this.deleteNode(temp.getVal());
return temp.getVal();
}
删除节点代码实现
//删除节点
public void deleteNode(int val) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
BinarySortTreeNode targetNode = this.searchNode(val);
//没有找到节点
if (targetNode == null) {
return;
}
if (root.getLeftChild() == null && root.getRightChild() == null) {
//只有一个节点
root = null;
return;
}
//查找targetNode的父节点
BinarySortTreeNode parentNode = this.root.searchParentNode(val);
if (targetNode.getLeftChild() == null && targetNode.getRightChild() == null) {
//左右子树为null,说明是叶子节点
if (parentNode.getVal() > targetNode.getVal() && parentNode.getLeftChild() != null) {
//父节点val> 目标节点,说明目标在左侧
parentNode.setLeftChild(null);
} else if (parentNode.getVal() <= targetNode.getVal() && parentNode.getRightChild() != null) {
parentNode.setRightChild(null);
}
} else if (targetNode.getLeftChild() != null && targetNode.getRightChild() != null) {
//左右子树都存在. 从targetNode右子树中寻找最小的节点
/*int minNode = this.deleteMinNode(targetNode.getRightChild());
targetNode.setVal(minNode);*/
int maxNode = this.deleteMaxNode(targetNode.getLeftChild());
targetNode.setVal(maxNode);
} else {
//左右子树存在一个
if (targetNode.getLeftChild() != null) {
if (parentNode != null) {
//要删除的节点有左子节点
if (parentNode.getLeftChild().getVal() == val) {
parentNode.setLeftChild(targetNode.getLeftChild());
} else {
parentNode.setRightChild(targetNode.getLeftChild());
}
} else {
root = targetNode.getLeftChild();
}
} else {
//要删除的节点存在右子节点
if (parentNode != null) {
if (parentNode.getRightChild().getVal() == val) {
parentNode.setRightChild(targetNode.getRightChild());
} else {
parentNode.setLeftChild(targetNode.getRightChild());
}
} else {
root = targetNode.getRightChild();
}
}
}
}
4. 完整代码
public class BinarySortTree {
private BinarySortTreeNode root;
public BinarySortTree(BinarySortTreeNode root) {
this.root = root;
}
public BinarySortTree() {
}
public BinarySortTreeNode getRoot() {
return root;
}
public void setRoot(BinarySortTreeNode root) {
this.root = root;
}
//添加节点
public void addNode(BinarySortTreeNode node) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
this.root.addNode(node);
}
public void traverse() {
if (this.root == null) {
System.out.println("树为null 无法遍历");
return;
}
this.root.midOrderTraversal();
}
public BinarySortTreeNode searchNode(int val) {
return this.root.searchNode(val);
}
public BinarySortTreeNode searchParent(int val) {
return this.root.searchParentNode(val);
}
//删除节点
public void deleteNode(int val) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
BinarySortTreeNode targetNode = this.searchNode(val);
//没有找到节点
if (targetNode == null) {
return;
}
if (root.getLeftChild() == null && root.getRightChild() == null) {
//只有一个节点
root = null;
return;
}
//查找targetNode的父节点
BinarySortTreeNode parentNode = this.root.searchParentNode(val);
if (targetNode.getLeftChild() == null && targetNode.getRightChild() == null) {
//左右子树为null,说明是叶子节点
if (parentNode.getVal() > targetNode.getVal() && parentNode.getLeftChild() != null) {
//父节点val> 目标节点,说明目标在左侧
parentNode.setLeftChild(null);
} else if (parentNode.getVal() <= targetNode.getVal() && parentNode.getRightChild() != null) {
parentNode.setRightChild(null);
}
} else if (targetNode.getLeftChild() != null && targetNode.getRightChild() != null) {
//左右子树都存在. 从targetNode右子树中寻找最小的节点
/*int minNode = this.deleteMinNode(targetNode.getRightChild());
targetNode.setVal(minNode);*/
int maxNode = this.deleteMaxNode(targetNode.getLeftChild());
targetNode.setVal(maxNode);
} else {
//左右子树存在一个
if (targetNode.getLeftChild() != null) {
if (parentNode != null) {
//要删除的节点有左子节点
if (parentNode.getLeftChild().getVal() == val) {
parentNode.setLeftChild(targetNode.getLeftChild());
} else {
parentNode.setRightChild(targetNode.getLeftChild());
}
} else {
root = targetNode.getLeftChild();
}
} else {
//要删除的节点存在右子节点
if (parentNode != null) {
if (parentNode.getRightChild().getVal() == val) {
parentNode.setRightChild(targetNode.getRightChild());
} else {
parentNode.setLeftChild(targetNode.getRightChild());
}
} else {
root = targetNode.getRightChild();
}
}
}
}
//删除并且返回最小节点的值
private int deleteMinNode(BinarySortTreeNode node) {
BinarySortTreeNode temp = node;
if (temp == null) {
return -1;
}
while (temp.getLeftChild() != null) {
temp = temp.getLeftChild();
}
this.deleteNode(temp.getVal());
return temp.getVal();
}
//删除并返回左子树中最大的那个节点的值
private int deleteMaxNode(BinarySortTreeNode node) {
BinarySortTreeNode temp = node;
if (temp == null) {
return -1;
}
while (temp.getRightChild() != null) {
temp = temp.getRightChild();
}
this.deleteNode(temp.getVal());
return temp.getVal();
}
}
class BinarySortTreeNode implements TreeTraversal {
private Integer val; //节点值
private BinarySortTreeNode leftChild; //左子树
private BinarySortTreeNode rightChild; //右子树
public BinarySortTreeNode(Integer val) {
this.val = val;
this.leftChild = null;
this.rightChild = null;
}
public Integer getVal() {
return val;
}
public void setVal(Integer val) {
this.val = val;
}
public BinarySortTreeNode getLeftChild() {
return leftChild;
}
public void setLeftChild(BinarySortTreeNode leftChild) {
this.leftChild = leftChild;
}
public BinarySortTreeNode getRightChild() {
return rightChild;
}
public void setRightChild(BinarySortTreeNode rightChild) {
this.rightChild = rightChild;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "BinarySortTreeNode{" +
"val=" + val +
'}';
}
public void addNode(BinarySortTreeNode newNode) {
if (newNode == null) {
System.out.println("newNode is null!!");
return;
}
if (newNode.getVal() < this.getVal()) {
//新节点的值小于当前节点的值,挂载到左子树
if (this.getLeftChild() == null) {
this.setLeftChild(newNode);
} else {
//向左子树递归
this.leftChild.addNode(newNode);
}
} else {
//新节点的值大于当前节点,挂载到右子树
if (this.getRightChild() == null) {
this.setRightChild(newNode);
} else {
//向右递归
this.rightChild.addNode(newNode);
}
}
}
@Override
public void preOrderTraversal() {
System.out.println(this);
if (this.leftChild != null) {
this.leftChild.preOrderTraversal();
}
if (this.rightChild != null) {
this.rightChild.preOrderTraversal();
}
}
@Override
public void midOrderTraversal() {
if (this.leftChild != null) {
this.leftChild.midOrderTraversal();
}
System.out.println(this);
if (this.rightChild != null) {
this.rightChild.midOrderTraversal();
}
}
//查找节点
public BinarySortTreeNode searchNode(int val) {
if (this.getVal() == val) {
return this;
} else if (val < this.getVal()) {
if (this.leftChild == null) {
return null;
}
//向左递归查找
return this.leftChild.searchNode(val);
} else {
if (this.rightChild == null) {
return null;
}
//向右递归查找
return this.rightChild.searchNode(val);
}
}
//查找父节点
public BinarySortTreeNode searchParentNode(int val) {
if ((this.leftChild != null && this.leftChild.getVal() == val) || (this.rightChild != null && this.rightChild.getVal() == val)) {
return this;
} else if (val < this.getVal() && this.leftChild != null) {
//左递归
return this.leftChild.searchParentNode(val);
} else if (val > this.getVal() && this.rightChild != null) {
//有递归
return this.rightChild.searchParentNode(val);
} else {
return null;
}
}
}
5. 总结
BST中给定值的比较次数等于给定值节点在二叉排序树中的层数。如果二叉排序树是平衡的,则n个节点的二叉排序树的高度为Log 2n+1,其查找效率为O(Log 2n),近似于折半查找。如果二叉排序树完全不平衡,则其深度可达到n,查找效率为O(n),退化为顺序查找。一般的,二叉排序树的查找性能在O(Log 2n)到O(n)之间。因此,为了获得较好的查找性能,就要构造一棵平衡的二叉排序树。























 1524
1524

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








