Java数据结构
学习内容来自mooc中华东师范大学课程《Java核心技术》
数组
数组是存放多个相同类型数据的容器,其:
- 元素按线性规则排列
- 可按照索引访问内容
- 声明时需要明确长度
Java数组定义和初始化
int a[]; // a 还没有new操作,实际上是null,也不知道内存位置
int[] b; // b 还没有new操作,实际上是null,也不知道内存位置
int[] c = new int[2]; // c 有两个元素,都是0
// 逐个初始化
c[0] = 1;
c[1] = 2;
int d[] = new int[]{1, 2, 4}; // d 有三个元素1,2,4,同时定义并初始化
int d1[] = {4,2,1}; // d1 有三个元素4,2,1,同时定义并初始化
int[][] a2 = {{1, 2, 3},{1, 23, 2}};
数组索引
- 数组的length表示数组长度
- 数组索引从 0 开始,至 length-1
- 数组索引不能越界,否则报错
数组遍历
两种方法:
- 自己控制
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {} - 无需控制
for(int i : nums) {},该方法又称 for-each 语句,不会出现越界访问
多维数组
可以理解为数组的数组。
规则数组:int[][] a = new int[2][3];,格局为:
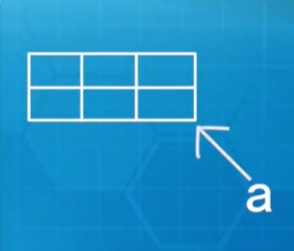
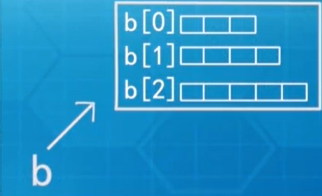
不规则数组:
int[][] b;
b = new int[3][];
b[0] = new int[3];
b[1] = new int[4];
b[2] = new int[5];
格局为:
小结
- 数组是一种确定大小的存储相同类型数据的容器
- 数组的初始化和两种遍历方法
JCF(Java Collection Framework)
容器:能够存放数据的空间结构
- 数组、多维数组,只能线性存放
- 列表、散列集、树……
容器框架:为表示和操作容器而规定的一种标准体系结构
- 对外的接口:容器中所能存放的数据结构类型
- 接口的实现:可复用的数据结构
- 算法:对数据的查找和排序
容器框架优点:提高数据存取效率
典型的容器框架:C++的STL、Java的JCF
JCF的集合接口是Collection
- add、contains、size、remove
- iterator
JCF的迭代器接口Iterator
- hasNext
- next
- remove
主要的数据结构实现类
- 列表(List,ArrayList, LinkedList)
- 集合(Set, HashSet,TreeSet,LinkedHashSet)
- 映射(Map,HashMap,TreeMap,LinkedHashMap)
主要的算法/工具类
- Arrays:对数组进行查找和排序等
- Collections:对Collection及其子类进行查找和排序等
列表List
List:列表
- 有序的Collection
- 允许重复元素
- 可以嵌套
List主要实现 - ArrayList(非同步的)
- LinkedList(非同步的)
- Vector(同步的)
ArrayList
- 以数组实现的列表,不支持同步
- 利用索引位置可以快速定位访问
- 不适合指定位置的插入、删除操作
- 适合变动不大,主要用于查询的数据
- 和Java数组相比,其容量可以动态调整
- ArrayList在元素填满容器时会自动扩充容器大小的50%,和StringBuffer中Capacity扩充方法类似
例子:
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> a1 = new ArrayList<Integer>();
a1.add(3); // ArrayList 只能装对象,即使这里是一个数字(int类型),也会装箱为Integer
a1.add(2);
a1.add(1);
a1.add(4);
a1.add(5);
a1.add(6);
a1.add(Integer.valueOf(6));
System.out.println("the third element is: " + a1.get(3)); // 4
a1.remove(3); // 删除该索引位置元素,其后元素前移
System.out.println("the third element is: " + a1.get(3)); // 5
a1.add(3,9); // 在该索引处插入元素,其后元素后移
System.out.println("the third element is: " + a1.get(3)); // 9
System.out.println("=======遍历方法=======");
ArrayList<Integer> a2 = new ArrayList<Integer>(100000);
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
a2.add(i);
}
traverseByIterator(a2);
traverseByIndex(a2);
traverseByForEach(a2);
}
public static void traverseByIterator(ArrayList<Integer> a1) {
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("========迭代器遍历========");
Iterator<Integer> iter1 = a1.iterator();
while (iter1.hasNext()) {
iter1.next();
}
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
long duration = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println(duration+"纳秒");
}
public static void traverseByIndex(ArrayList<Integer> a1) {
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("========随机索引遍历========");
for (int i = 0; i < a1.size(); i++) {
a1.get(i);
}
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
long duration = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println(duration+"纳秒");
}
public static void traverseByForEach(ArrayList<Integer> a1) {
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("========for-each 遍历========");
for (Integer i : a1) {
;
}
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
long duration = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println(duration+"纳秒");
}
输出结果:
the third element is: 4
the third element is: 5
the third element is: 9
=======遍历方法=======
========迭代器遍历========
10878000纳秒
========随机索引遍历========
5835300纳秒
========for-each 遍历========
6562000纳秒
LinkedList
- 以双向链表实现的列表,不支持同步
- 可被当做堆栈、队列和双端队列进行操作
- 顺序访问高效,随机访问性能差,中间插入和删除高效(和链表类似)
- 适用于经常变化的数据
例子:
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<Integer> l1 = new LinkedList<Integer>();
l1.add(3);
l1.add(2);
l1.add(5);
l1.add(6);
l1.add(6);
System.out.println(l1.size()); // 5
System.out.println(l1.peek()); // 3
l1.addFirst(9); // 在头部添加9
System.out.println(l1.peek()); // 9
l1.add(3, 7);
System.out.println(l1.get(3)); // 7
l1.remove(3);
System.out.println(l1.get(3)); // 5
LinkedList<Integer> l2 = new LinkedList<Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
l2.add(i);
}
traverseByIterator(l2);
traverseByIndex(l2);
traverseByForEach(l2);
}
public static void traverseByIterator(LinkedList<Integer> a1) {
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("========迭代器遍历========");
Iterator<Integer> iter1 = a1.iterator();
while (iter1.hasNext()) {
iter1.next();
}
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
long duration = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println(duration+"纳秒");
}
public static void traverseByIndex(LinkedList<Integer> a1) {
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("========随机索引遍历========");
for (int i = 0; i < a1.size(); i++) {
a1.get(i);
}
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
long duration = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println(duration+"纳秒");
}
public static void traverseByForEach(LinkedList<Integer> a1) {
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("========for-each 遍历========");
for (Integer i : a1) {
;
}
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
long duration = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println(duration+"纳秒");
}
输出结果:
5
3
9
7
5
========迭代器遍历========
1639900纳秒
========随机索引遍历========
78414300纳秒
========for-each 遍历========
1053800纳秒
例子3,对ArrayList和LinkedList进行性能对比:
public static void main(String[] args) {
int times = 10 * 1000;
ArrayList<Integer> arrayList = new ArrayList<Integer>();
LinkedList<Integer> linkedList = new LinkedList<Integer>();
System.out.println("Test times = " + times);
System.out.println("---------------------");
// ArrayList add
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
for (int i = 0; i < times; i++) {
arrayList.add(0, i);
}
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
long duration = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println("ArrayList add time -> " + duration);
// LinkedList add
startTime = System.nanoTime();
for (int i = 0; i < times; i++) {
linkedList.add(0, i);
}
endTime = System.nanoTime();
duration = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println("LinkedList add time -> " + duration);
System.out.println("---------------------");
// ArrayList get
startTime = System.nanoTime();
for (int i = 0; i < times; i++) {
arrayList.get(i);
}
endTime = System.nanoTime();
duration = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println("ArrayList get time -> " + duration);
// LinkedList get
startTime = System.nanoTime();
for (int i = 0; i < times; i++) {
linkedList.get(i);
}
endTime = System.nanoTime();
duration = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println("LinkedList get time -> " + duration);
System.out.println("---------------------");
// ArrayList remove
startTime = System.nanoTime();
for (int i = 0; i < times; i++) {
arrayList.remove(0);
}
endTime = System.nanoTime();
duration = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println("ArrayList remove time -> " + duration);
// LinkedList remove
startTime = System.nanoTime();
for (int i = 0; i < times; i++) {
linkedList.remove(0);
}
endTime = System.nanoTime();
duration = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println("LinkedList remove time -> " + duration);
}
输出结果:
Test times = 10000
---------------------
ArrayList add time -> 7764700
LinkedList add time -> 2554400
---------------------
ArrayList get time -> 1086600
LinkedList get time -> 73014300
---------------------
ArrayList remove time -> 6343400
LinkedList remove time -> 1578800
可见:
- 对于插入和删除来说,LinkedList性能更优
- 对于索引的顺序访问来说,ArrayList性能更优
Vector
- 是一个同步类
- 个ArrayList类似,可变数组实现的列表
- Vector同步,适合在多线程下使用
- 原先不属于JCF框架,属于最早的java数组结构,性能较差
- 从JDK1.2开始被重写,加入JCF
- 官方建议在非同步情况下,使用ArrayList
例子:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Vector<Integer> vec = new Vector<Integer>();
vec.add(1);
vec.add(2);
vec.add(3);
vec.remove(2);
System.out.println(vec.size());
System.out.println(vec.get(1));
vec.add(1,5);
System.out.println(vec.get(1));
System.out.println("=======遍历方法=======");
Vector<Integer> v = new Vector<Integer>(100000);
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
v.add(i);
}
traverseByIterator(v);
traverseByIndex(v);
traverseByForEach(v);
traverseByEnumeration(v);
}
public static void traverseByIterator(Vector<Integer> a1) {
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("========迭代器遍历========");
Iterator<Integer> iter1 = a1.iterator();
while (iter1.hasNext()) {
iter1.next();
}
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
long duration = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println(duration+"纳秒");
}
public static void traverseByIndex(Vector<Integer> a1) {
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("========索引遍历========");
for (int i = 0; i < a1.size(); i++) {
a1.get(i);
}
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
long duration = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println(duration+"纳秒");
}
public static void traverseByForEach(Vector<Integer> a1) {
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("========for-each 遍历========");
for (Integer i : a1) {
;
}
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
long duration = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println(duration+"纳秒");
}
public static void traverseByEnumeration(Vector<Integer> a1) {
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("========Enumeration遍历========");
for (Enumeration enu = a1.elements(); enu.hasMoreElements(); ) {
enu.nextElement();
}
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
long duration = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println(duration+"纳秒");
}
输出结果:
2
2
5
=======遍历方法=======
========迭代器遍历========
7247799纳秒
========索引遍历========
5681400纳秒
========for-each 遍历========
7368599纳秒
========Enumeration遍历========
7732800纳秒
小结
- 同步采用Vector
- 非同步情况下,根据数据操作特点选择ArrayList/LinkedList
集合Set
特点:
- 确定性:对任意对象都能判定其是否属于某一个集合
- 互异性:集合内每个元素互不相同,不存在重复元素
- 无序性:集合内的元素顺序无关
和数学中的集合概念类似。
Java中的集合接口Set:
- HashSet:基于散列函数的集合,无序,不支持同步
- TreeSet:基于树结构的集合,可排序,不支持同步
- LinkedHashSet:基于散列函数和双向链表的集合,可排序的,不支持同步
HashSet
- 基于HashMap实现的,可以容纳null元素,不支持同步
- add
- clear 清除整个HashSet
- contains
- remove
- retainAll 计算两个集合交集
例子:
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet<Integer> hs = new HashSet<Integer>();
hs.add(null);
hs.add(10000);
hs.add(20);
hs.add(3);
hs.add(40000);
hs.add(5660000);
hs.add(102300);
hs.add(10);
hs.add(null); // 重复了
System.out.println(hs.size());
if(!hs.contains(6)) {
hs.add(6);
}
System.out.println(hs.size());
hs.remove(3);
System.out.println(hs.size());
System.out.println("========遍历========");
for(Integer i : hs) {
System.out.println(i);
}
System.out.println("=======交集测试=======");
HashSet<Integer> s1 = new HashSet<Integer>();
HashSet<Integer> s2 = new HashSet<Integer>();
s1.add(1);
s1.add(2);
s1.add(3);
s2.add(3);
s2.add(4);
s2.add(5);
s1.retainAll(s2);
System.out.println("交集长度:" + s1.size());
System.out.println("=======速度测试=======");
HashSet<Integer> hs2 = new HashSet<Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
hs2.add(i);
}
traverseByForEach(hs2);
traverseByIterator(hs2);
}
public static void traverseByForEach(HashSet<Integer> a1) {
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("========for-each 遍历========");
for (Integer i : a1) {
;
}
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
long duration = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println(duration+"纳秒");
}
public static void traverseByIterator(HashSet<Integer> a1) {
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("========迭代器遍历========");
Iterator<Integer> iter1 = a1.iterator();
while (iter1.hasNext()) {
iter1.next();
}
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
long duration = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println(duration+"纳秒");
}
输出结果:
8
9
8
========遍历========
null
10000
40000
20
5660000
6
10
102300
=======交集测试=======
交集长度:1
=======速度测试=======
========for-each 遍历========
5839600纳秒
========迭代器遍历========
4755300纳秒
LinkedHashSet
- 继承HashSet,也是基于HashMap实现的,可以容纳null,不支持同步
- 方法和HashSet基本一致
- 通过一个双向链表维护插入顺序
TreeSet
- 基于TreeMap实现,不可以容纳null,不支持同步
- 基本方法和HashSet一致
- 根据CompareTo方法或指定Comparator排序
对比
若使用for-each遍历方法遍历三种集合:
- HashSet是无序的
- LinkedHashSet是和输入顺序一致的
- TreeSet默认是从小到大排序
HashSet,LinkedHashSet,TreeSet的元素都是对象
HashSet和LinkedHashSet判断元素重复的原则:
- 判断两个元素的hashCode返回值是否相同,若不同,返回false
- 若相同,判定equals方法,若不同,返回false;若相同,返回true
- hashCode和equals方法是所有类都有的,因为Object类有
TreeSet判断元素重复的原则:
- 需要元素继承自Comparator接口
- 比较两个元素的compareTo方法
例子:
先定义两个类
public class Cat {
private int size;
public Cat(int size) {
this.size = size;
}
}
public class Dog {
private int size;
public Dog(int size) {
this.size = size;
}
public int getSize() {
return size;
}
// 重写了equals方法
public boolean equals(Object obj2) {
System.out.println("Dog equals() ~~~~~~~~~~~~");
if (0 == size - ((Dog)obj2).getSize()) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
// 重写了hashCode方法
public int hashCode() {
System.out.println("Dog hashCode() ~~~~~~~~~~~~~");
return size;
}
// 重写了toString方法
public String toString() {
System.out.println("Dog toString() ~~~~~~~~~~~~~");
return size + "";
}
}
注意,equals(), hashCode(), toString() 三个方法三位一体,一般改写其中一个,就需要三个都改写。也就是说,如果该类的 equals() 方法判定两个对象是相同的,那么两个对象的 hashCode() 和 toString() 方法返回的值也是相同的。
对比结果:
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("========Cat HashSet========");
HashSet<Cat> hs = new HashSet<Cat>();
hs.add(new Cat(2));
hs.add(new Cat(1));
hs.add(new Cat(3));
hs.add(new Cat(5));
hs.add(new Cat(4));
hs.add(new Cat(4));
System.out.println(hs.size()); // 6
// 即HashSet不会判断后两个对象为相同对象
// 也就是size相同的Cat对象的hashCode或者equals方法返回值不同
LinkedHashSet<Cat> ls = new LinkedHashSet<Cat>();
ls.add(new Cat(2));
ls.add(new Cat(1));
ls.add(new Cat(3));
ls.add(new Cat(5));
ls.add(new Cat(4));
ls.add(new Cat(4));
System.out.println(ls.size()); // 6
HashSet<Dog> hs2 = new HashSet<Dog>();
hs2.add(new Dog(2));
hs2.add(new Dog(1));
hs2.add(new Dog(3));
hs2.add(new Dog(5));
hs2.add(new Dog(4));
hs2.add(new Dog(4));
System.out.println(hs2.size()); // 5
// 在该类的重写方法中,保证了size相同的对象为同一对象,所以只会有一个size为4的Dog
}
再重写一个类:
public class Tiger implements Comparable{
private int size;
public Tiger(int size) {
this.size = size;
}
public int getSize() {
return size;
}
// 重写了compareTo
public int compareTo(Object o) {
System.out.println("Tiger compareTo() ~~~~~~~~~~");
return size - ((Tiger) o).getSize();
}
}
Tiger 实现 Comparable 接口,必须重写 compareTo() 方法来比较大小。该方法具体规则为:
- int a = obj1.compareTo(obj2);
- 如果 a >0,则 obj1 > obj2
- 如果 a == 0,则 obj1 == obj2
- 如果 a <0,则 obj1 < obj2
对其测试:
HashSet<Tiger> hs3 = new HashSet<Tiger>();
hs3.add(new Tiger(2));
hs3.add(new Tiger(1));
hs3.add(new Tiger(3));
hs3.add(new Tiger(5));
hs3.add(new Tiger(4));
hs3.add(new Tiger(4));
System.out.println(hs3.size()); // 6
// 也就是说HashSet的判定不会关心compareTo()方法
也就是刚刚提到的:
HashSet和LinkedHashSet判断元素重复的原则:
- 判断两个元素的hashCode返回值是否相同,若不同,返回false
- 若相同,判定equals方法,若不同,返回false;若相同,返回true
接下来测试TreeSet。
首先需要说明,TreeSet的对象必须实现Comparable接口,即实现compareTo方法。
基本类型基本上都实现了compareTo方法。
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 添加到TreeSet的对象必须实现Comparable接口,即实现compareTo方法
TreeSet<Tiger> hs3 = new TreeSet<Tiger>();
hs3.add(new Tiger(2));
hs3.add(new Tiger(1));
hs3.add(new Tiger(3));
hs3.add(new Tiger(5));
hs3.add(new Tiger(4));
hs3.add(new Tiger(4));
System.out.println(hs3.size()); // 5
// 在TreeSet添加元素的过程中,会不断的调用compareTo方法和已有的元素对比
}
于是,就像我们之前提到的:
TreeSet判断元素重复的原则:
- 需要元素继承自Comparator接口
- 比较两个元素的compareTo方法
小结
- 本节介绍了 HashSet、LinkedHashSet 和 TreeSet,分别具有各自的特点
- 注意不同 Set 判断元素是否重复的原则
映射
Map 映射(和键值对的定义差不多)
- 数学定义:两个集合之间元素的对应关系
- 一个输入对应到一个输出
- {Key, Value} 键值对
Java中的Map
- Hashtable,同步,慢,数据量小
- HashMap,不支持同步,快,数据量大
- Properties,同步,文件形式,数据量小
Hashtable
- K-V对,K和V都不允许为null
- 同步,多线程安全
- 无序的
- 适合小数据量
- 主要方法:clear, contains/containsValue, containsKey, get, put, remove, size
例子:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Hashtable<Integer, String> ht = new Hashtable<Integer, String>();
ht.put(1000, "aaa");
ht.put(2, "bbb");
ht.put(30000, "ccc");
System.out.println(ht.contains("aaa")); // true
System.out.println(ht.containsValue("aaa")); // true
System.out.println(ht.containsKey(1000)); // true
System.out.println(ht.get(1000)); // aaa
ht.put(1000, "ddd");
System.out.println(ht.get(1000)); // ddd
ht.remove(2);
System.out.println(ht.size()); // 2
ht.clear();
System.out.println(ht.size()); // 0
Hashtable<Integer, String> ht2 = new Hashtable<Integer, String>();
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
ht2.put(i, "aaa");
}
traverseByEntry(ht2);
traverseByKeySet(ht2);
traverseByKeyEnumeration(ht2);
}
public static void traverseByEntry(Hashtable<Integer, String> ht) {
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("==========Entry迭代器遍历==========");
Integer key;
String value;
Iterator<Entry<Integer, String>> iter = ht.entrySet().iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry = iter.next();
// 获取key
key = entry.getKey();
// 获取value
value = entry.getValue();
}
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
long duration = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println(duration + "纳秒");
}
public static void traverseByKeySet(Hashtable<Integer, String> ht) {
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("==========KeySet迭代器遍历==========");
Integer key;
String value;
Iterator<Integer> iter = ht.keySet().iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
// 获取key
key = iter.next();
// 获取value
value = ht.get(key);
}
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
long duration = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println(duration + "纳秒");
}
public static void traverseByKeyEnumeration(Hashtable<Integer, String> ht) {
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("==========Enumeration迭代器遍历==========");
Integer key;
String value;
Enumeration<Integer> iter = ht.keys();
while (iter.hasMoreElements()) {
// 获取key
key = iter.nextElement();
// 获取value
value = ht.get(key);
}
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
long duration = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println(duration + "纳秒");
}
输出结果:
true
true
true
aaa
ddd
2
0
==========Entry迭代器遍历==========
26371200纳秒
==========KeySet迭代器遍历==========
19081800纳秒
==========Enumeration迭代器遍历==========
10092700纳秒
其中:
- Enumeration是只读的,速度更快(理论上 )
- Iterator可以做删除,功能更强大
HashMap
- K-V对,K和V都允许为null
- 不同步,多线程不安全
- 无序的
- 主要方法:clear, containsValue, containsKey, get, put, remove, size
例子:
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<Integer, String> hm = new HashMap<Integer, String>();
hm.put(1, null);
hm.put(null, "abc");
hm.put(1000, "aaa");
hm.put(2, "bbb");
hm.put(30000, "ccc");
System.out.println(hm.containsValue("aaa")); // true
System.out.println(hm.containsKey(1000)); // true
System.out.println(hm.get(1000)); // aaa
hm.put(1000, "ddd");
System.out.println(hm.get(1000)); // ddd
hm.remove(2);
System.out.println(hm.size()); // 4
hm.clear();
System.out.println(hm.size()); // 0
HashMap<Integer, String> hm2 = new HashMap<Integer, String>();
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
hm2.put(i, "aaa");
}
traverseByEntry(hm2);
traverseByKeySet(hm2);
}
public static void traverseByEntry(HashMap<Integer, String> hm) {
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("==========Entry迭代器遍历==========");
Integer key;
String value;
Iterator<Entry<Integer, String>> iter = hm.entrySet().iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry = iter.next();
// 获取key
key = entry.getKey();
// 获取value
value = entry.getValue();
}
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
long duration = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println(duration + "纳秒");
}
public static void traverseByKeySet(HashMap<Integer, String> hm) {
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("==========KeySet迭代器遍历==========");
Integer key;
String value;
Iterator<Integer> iter = hm.keySet().iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
// 获取key
key = iter.next();
// 获取value
value = hm.get(key);
}
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
long duration = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println(duration + "纳秒");
}
输出结果:
true
true
aaa
ddd
4
0
==========Entry迭代器遍历==========
29238600纳秒
==========KeySet迭代器遍历==========
12736300纳秒
LinkedHashMap
- 基于双向链表的维持插入顺序的HashMap
例子:
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedHashMap<Integer, String> hm = new LinkedHashMap<Integer, String>();
hm.put(1, null);
hm.put(null, "abc");
hm.put(1000, "aaa");
hm.put(2, "bbb");
hm.put(30000, "ccc");
System.out.println(hm.containsValue("aaa")); // true
System.out.println(hm.containsKey(1000)); // true
System.out.println(hm.get(1000)); // aaa
hm.put(1000, "ddd");
System.out.println(hm.get(1000)); // ddd
hm.remove(2);
System.out.println(hm.size()); // 4
System.out.println("遍历开始====================");
Integer key;
String value;
Iterator<Entry<Integer, String>> iter = hm.entrySet().iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry = iter.next();
// 获取key
key = entry.getKey();
// 获取value
value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println("Key:" + key + ", Value:" + value);
}
System.out.println("遍历结束====================");
LinkedHashMap<Integer, String> hm2 = new LinkedHashMap<Integer, String>();
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
hm2.put(i, "aaa");
}
traverseByEntry(hm2);
traverseByKeySet(hm2);
}
public static void traverseByEntry(LinkedHashMap<Integer, String> hm) {
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("==========Entry迭代器遍历==========");
Integer key;
String value;
Iterator<Entry<Integer, String>> iter = hm.entrySet().iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry = iter.next();
// 获取key
key = entry.getKey();
// 获取value
value = entry.getValue();
}
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
long duration = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println(duration + "纳秒");
}
public static void traverseByKeySet(LinkedHashMap<Integer, String> hm) {
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("==========KeySet迭代器遍历==========");
Integer key;
String value;
Iterator<Integer> iter = hm.keySet().iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
// 获取key
key = iter.next();
// 获取value
value = hm.get(key);
}
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
long duration = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println(duration + "纳秒");
}
输出结果:
true
true
aaa
ddd
4
遍历开始====================
Key:1, Value:null
Key:null, Value:abc
Key:1000, Value:ddd
Key:30000, Value:ccc
遍历结束====================
==========Entry迭代器遍历==========
20681900纳秒
==========KeySet迭代器遍历==========
18043300纳秒
TreeMap
- 和TreeMap很相似
- 基于红黑树的Map,可以根据key的自然排序或者compareTo方法进行排序输出
- 键不可以为null,值可以
例子:
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeMap<Integer, String> hm = new TreeMap<Integer, String>();
hm.put(1, null);
// hm.put(null, "abc");
hm.put(1000, "aaa");
hm.put(2, "bbb");
hm.put(30000, "ccc");
System.out.println(hm.containsValue("aaa")); // true
System.out.println(hm.containsKey(1000)); // true
System.out.println(hm.get(1000)); // aaa
hm.put(1000, "ddd");
System.out.println(hm.get(1000)); // ddd
hm.remove(2);
System.out.println(hm.size()); // 4
System.out.println("遍历开始====================");
Integer key;
String value;
Iterator<Entry<Integer, String>> iter = hm.entrySet().iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry = iter.next();
// 获取key
key = entry.getKey();
// 获取value
value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println("Key:" + key + ", Value:" + value);
}
System.out.println("遍历结束====================");
TreeMap<Integer, String> hm2 = new TreeMap<Integer, String>();
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
hm2.put(i, "aaa");
}
traverseByEntry(hm2);
traverseByKeySet(hm2);
}
public static void traverseByEntry(TreeMap<Integer, String> hm) {
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("==========Entry迭代器遍历==========");
Integer key;
String value;
Iterator<Entry<Integer, String>> iter = hm.entrySet().iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry = iter.next();
// 获取key
key = entry.getKey();
// 获取value
value = entry.getValue();
}
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
long duration = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println(duration + "纳秒");
}
public static void traverseByKeySet(TreeMap<Integer, String> hm) {
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("==========KeySet迭代器遍历==========");
Integer key;
String value;
Iterator<Integer> iter = hm.keySet().iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
// 获取key
key = iter.next();
// 获取value
value = hm.get(key);
}
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
long duration = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println(duration + "纳秒");
}
输出结果:
true
true
aaa
ddd
3
遍历开始====================
Key:1, Value:null
Key:1000, Value:ddd
Key:30000, Value:ccc
遍历结束====================
==========Entry迭代器遍历==========
15293800纳秒
==========KeySet迭代器遍历==========
24155700纳秒
Properties
- 继承于Hashtable
- 可以将K-V对保存在文件中
- 适用于数据量少的配置文件
- Hashtable的方法都继承
- 还有加载文件的load方法,写文件的store方法
- 获取属性的getProperty,设置属性的setProperty
例子:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
System.out.println("写入Test.properties===============");
WriteProperties("Test.properties", "name", "12345");
System.out.println("加载Test.properties===============");
GetAllProperties("Test.properties");
System.out.println("从Test.properties加载=============");
String value = GetValueByKey("Test.properties", "name");
System.out.println("name is " + value);
}
public static void WriteProperties(String filePath, String pKey, String pValue) throws IOException {
File file = new File(filePath);
if (!file.exists()) {
file.createNewFile();
}
Properties pps = new Properties();
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(filePath);
// 从输入流中读取属性列表(键和元素对)
pps.load(in);
// 调用 Hashtable 的方法put。使用 getProperty 提供并行性
// 强制要求属性的键和值使用字符串。返回值是 Hashtable 调用 put 的结果
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(filePath);
pps.setProperty(pKey, pValue);
// 以适合使用 load 方法加载到 Properties 表中的格式
// 将此 Properties 表中的属性列表(键和元素对)写入输入流
pps.store(out, "Update " + pKey + " name");
out.close();
}
public static void GetAllProperties(String filePath) throws IOException {
Properties pps = new Properties();
InputStream in = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(filePath));
pps.load(in); // 加载所有的K-V对
Enumeration en = pps.propertyNames(); // 得到配置文件的KeySet
while (en.hasMoreElements()) {
String strKey = (String) en.nextElement();
String strValue = pps.getProperty(strKey);
}
}
public static String GetValueByKey(String filePath, String key) {
Properties pps = new Properties();
try {
InputStream in = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(filePath));
pps.load(in);
String value = pps.getProperty(key);
return value;
}
catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
小结
- HashMap 是最常用的映射结构
- 如需要排序,考虑 LinkedHashMap 或者 TreeMap
- 如需要将 K-V 存储为文件,可采用 Properties 类
JCF的工具类
- 不存储数据,而是在数据容器上,实现高效操作。如排序、搜索
- Arrays类
- Collections类
Arrays
处理对象是数组
- 排序:对数组排序,sort/parallelSort
- 查找:从数组中查找一个元素,binarySearch
- 批量拷贝:从源数组批量复制元素到目标数组,copyOf
- 批量赋值:对数组进行批量赋值,fill
- 等价性比较:判定两个数组内容是否相同,equals
- 最大、最小值:Arrays.stream(array).max()
例子:
public static void main(String[] args) {
testSort();
testSearch();
testCopy();
testFill();
testEquality();
}
public static void testSort() {
Random r = new Random();
int[] a = new int[10];
for (int i = 0 ; i < 10; i++) {
a[i] = r.nextInt(100);
}
System.out.println("测试排序~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~");
System.out.println("before~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~");
for (int i = 0; i < 10 ;i++) {
System.out.print(a[i] + ", ");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("after sorting~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~");
Arrays.sort(a);
for (int i = 0; i < 10 ;i++) {
System.out.print(a[i] + ", ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void testSearch() {
Random r = new Random();
int[] a = new int[10];
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
a[i] = r.nextInt(100);
}
a[a.length - 1] = 10000;
System.out.println("测试Search~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~");
System.out.println("10000的位置是:" + Arrays.binarySearch(a, 10000));
}
public static void testCopy() {
Random r = new Random();
int[] a = new int[10];
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
a[i] = r.nextInt(100);
}
int[] b = Arrays.copyOf(a, 5);
System.out.println("测试拷贝前五个元素~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~");
System.out.println("源数组~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~");
for (int i = 0; i < 10 ;i++) {
System.out.print(a[i] + ", ");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("新数组~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~");
for (int i = 0; i < 5 ;i++) {
System.out.print(b[i] + ", ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void testFill() {
int[] a = new int[10];
Arrays.fill(a, 123);
Arrays.fill(a, 2, 8, 666);
System.out.println("数组~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~");
for (int i = 0; i < 10 ;i++) {
System.out.print(a[i] + ", ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void testEquality() {
int[] a = new int[10];
int[] b = new int[10];
Arrays.fill(a, 666);
Arrays.fill(b, 666);
System.out.println(Arrays.equals(a, b));
b[3] = 777;
System.out.println(Arrays.equals(a, b));
}
Collections
处理对象是Collection及其子类
- 排序:sort
- 搜索:binarySearch
- 批量赋值:fill
- 最大、最小:max、min
- 反序:reverse
对象比较
对象实现Comparable接口(需要修改对象类)
- compareTo方法,>返回1,==返回0,<返回-1
- Arrays 和 Collections 在进行对象sort时,自动调用该方法
新建Comparator(适用于对象类不可更改的情况)
- compare方法,>返回1,==返回0,<返回-1
- Comparator比较器将作为参数提交给工具类的sort方法
例子1:
// 实现Comparable接口
public class Person implements Comparable<Person>{
String name;
int age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
// 重写compareTo方法
public int compareTo(Person b) {
int i = 0;
i = name.compareTo(b.name);
if (i == 0) {
return age - b.age;
}
else {
return i;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person[] ps = new Person[3];
ps[0] = new Person("Tom", 20);
ps[1] = new Person("Mike", 18);
ps[2] = new Person("Mike", 20);
Arrays.sort(ps);
for (Person p :ps) {
System.out.println(p.getName() + ", " + p.getAge());
}
}
}
例子2:
public class Person2 {
private String name;
private int age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public Person2(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person2[] ps = new Person2[3];
ps[0] = new Person2("Tom", 20);
ps[1] = new Person2("Mike", 18);
ps[2] = new Person2("Mike", 20);
// 使用一个匿名类实现Comparator
Arrays.sort(ps, new Comparator<Person2>(){
public int compare(Person2 a, Person2 b) {
int i = 0;
i = a.getName().compareTo(b.getName());
if (i == 0) {
return a.getAge() - b.getAge();
}
return i;
}
});
for (Person2 p : ps) {
System.out.println(p.getName() + ", " + p.getAge());
}
}
小结
- Arrays 和 Collections 功能强大,包含许多常用方法
- 对象比较方法Comparable/Comparator





 本文详细介绍了Java中的数组概念、定义与初始化,以及数组索引、遍历方法,并深入剖析了JCF(Java Collection Framework)中的List、Set和Map等容器及其子类,包括ArrayList、LinkedList、HashSet、TreeSet和HashMap等,同时涵盖了工具类Arrays和Collections的实用功能。
本文详细介绍了Java中的数组概念、定义与初始化,以及数组索引、遍历方法,并深入剖析了JCF(Java Collection Framework)中的List、Set和Map等容器及其子类,包括ArrayList、LinkedList、HashSet、TreeSet和HashMap等,同时涵盖了工具类Arrays和Collections的实用功能。


















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










