前言
\在2013年9月,苹果推出了iPhone5s,与此同时,iPhone5s配备了首个采用64位架构的A7双核处理器,为了节省内存和提高执行效率,苹果提出了Tagged Pointer的概念。对于64位程序,引入Tagged Pointer后,相关逻辑能减少一半的内存占用,以及3倍的访问速度提升,100倍的创建、销毁速度提升。本文从Tagged Pointer试图解决的问题入手,带领读者理解Tagged Pointer的实现细节和优势,最后指出了使用时的注意事项。
问题
\我们先看看原有的对象为什么会浪费内存。假设我们要存储一个NSNumber对象,其值是一个整数。正常情况下,如果这个整数只是一个NSInteger的普通变量,那么它所占用的内存是与CPU的位数有关,在32位CPU下占4个字节,在64位CPU下是占8个字节的。而指针类型的大小通常也是与CPU位数相关,一个指针所占用的内存在32位CPU下为4个字节,在64位CPU下也是8个字节。
\所以一个普通的iOS程序,如果没有Tagged Pointer对象,从32位机器迁移到64位机器中后,虽然逻辑没有任何变化,但这种NSNumber、NSDate一类的对象所占用的内存会翻倍。如下图所示:
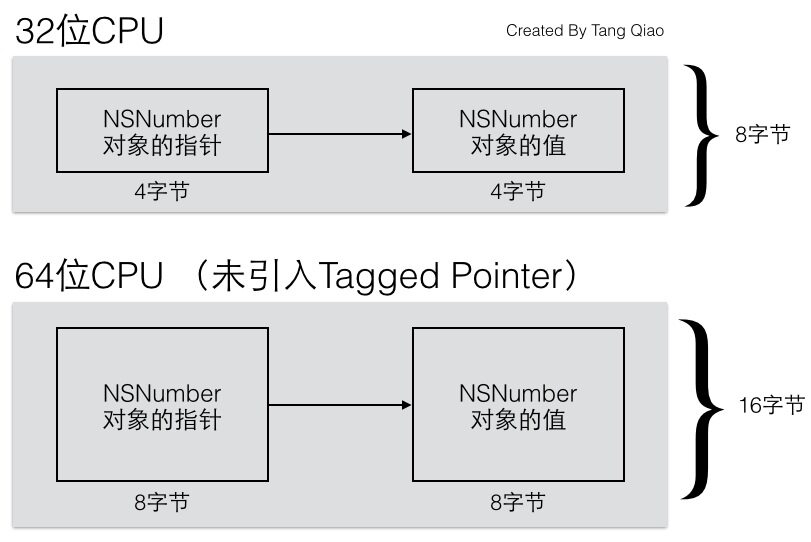
我们再来看看效率上的问题,为了存储和访问一个NSNumber对象,我们需要在堆上为其分配内存,另外还要维护它的引用计数,管理它的生命期。这些都给程序增加了额外的逻辑,造成运行效率上的损失。
\Tagged Pointer
\为了改进上面提到的内存占用和效率问题,苹果提出了Tagged Pointer对象。由于NSNumber、NSDate一类的变量本身的值需要占用的内存大小常常不需要8个字节,拿整数来说,4个字节所能表示的有符号整数就可以达到20多亿(注:2^31=2147483648,另外1位作为符号位),对于绝大多数情况都是可以处理的。
所以我们可以将一个对象的指针拆成两部分,一部分直接保存数据,另一部分作为特殊标记,表示这是一个特别的指针,不指向任何一个地址。所以,引入了Tagged Pointer对象之后,64位CPU下NSNumber的内存图变成了以下这样:
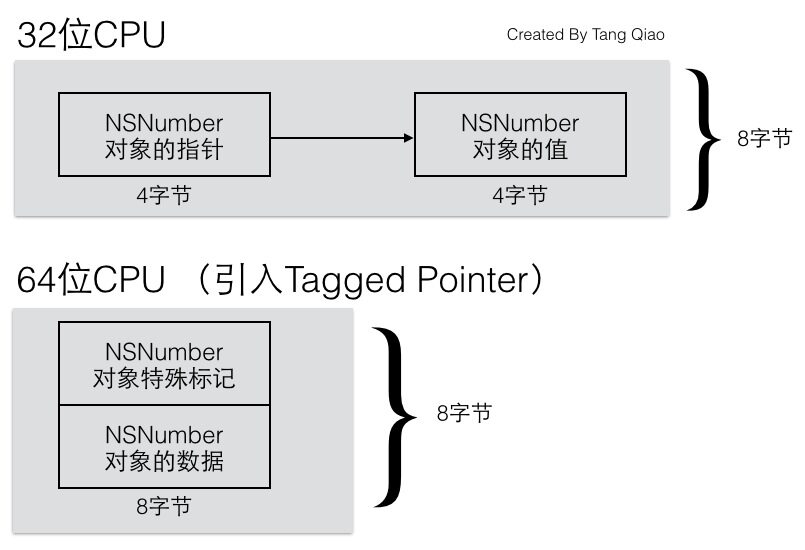
对此,我们也可以用 Xcode做实验来验证。我们的实验代码如下:
\\int main(int argc, char * argv[])\{\ @autoreleasepool {\ NSNumber *number1 = @1;\ NSNumber *number2 = @2;\ NSNumber *number3 = @3;\ NSNumber *numberFFFF = @(0xFFFF);\\ NSLog(@\"number1 pointer is %p\




 本文详细解析了TaggedPointer概念如何在64位程序中减少内存占用,提高访问速度及创建、销毁速度,通过实验代码验证了其效果,并指出了使用时的注意事项。
本文详细解析了TaggedPointer概念如何在64位程序中减少内存占用,提高访问速度及创建、销毁速度,通过实验代码验证了其效果,并指出了使用时的注意事项。
















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








