Framework and Implementation application – with example
Type: Application Structure
Introduction
In this post you see the basics about framework and implementation application in Pega.
The primary focus of any application will be to increase the maximum re-usability as well as support scalability.
Consider, Amazon organization. They have 3 divisions:
- Sales
- Service
- Marketing
Amazon plans to provide Pega CRM solution to Sales division and if it is a success, then they may want to expand the solution to other divisions.
Here, we will be creating a framework application and implementation application for sales.
Business may have some common features for all the 3 divisions. You can bring those to framework application so that it can be reused whenever we extend to other divisions.
Implementation application contains rules and business specific to Sales division.
How do you start building an application?
If we are going to built any application, say java application what will we do?
- We need Java Development Kit (JDK).
- We will import the required packages and start create project by coding.
For a Pega application,
- We need to buy the licensed Pega product from Pegasystems.
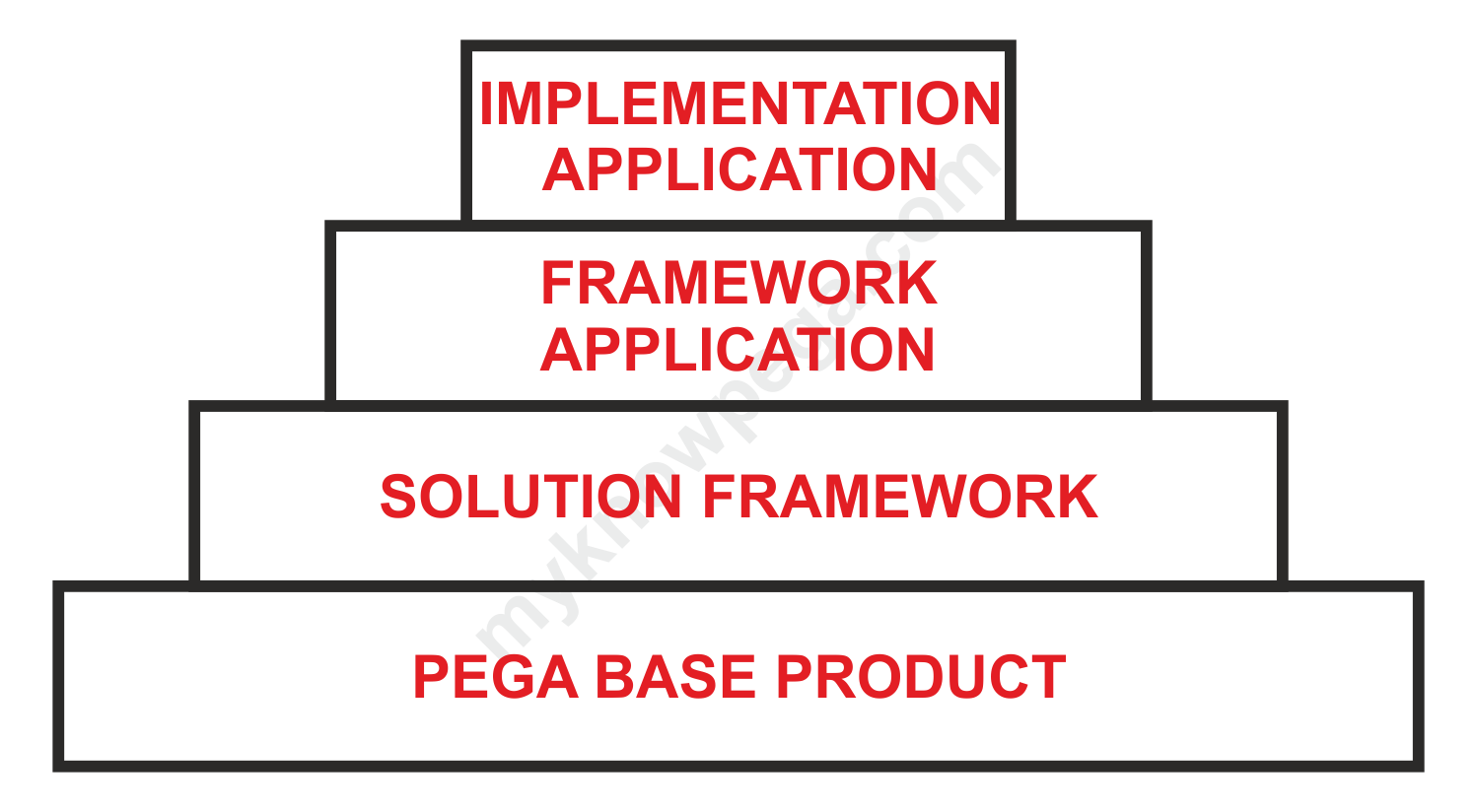
- Initial Pega product contains configuration files along with ‘PegaRules’ application.
- We can call it as a framework application. But we won’t. We call it as Pega base application.
- All the standard OOTB rules like CreateAddWork, UpdateStatus, some standard UI will be included in the PegaRules application.
Solution Framework
Pegasystems not only provide the base product, they built framework application for specific business requirements.
Say for a call center CRM application, Pegasystems builds a CPM framework application over base product. We can purchase the CPM Framework, a licensed product and use it as a framework.
We call it as solution framework. Solution framework can be used 70% to complete application which we can extend to satisfy our requirement.
Let us walk through an example,
Imagine 2 brothers bought a single land. They planned to live together. They decided to build a 2 storeys building.
- Ground floor – Common hall and kitchen.
- First floor – Individual home for brothers.
First they decided to build a single home in the first floor and planned to extend the first floor in future.

I am going to compare the house building with Pega Application building.
Step 1: You are going to buy a land.
Pega: Buy a Pega Licensed product –PegaRules application.
Step 2: You have an option to buy the land with the basement laid.
Pega: You can buy a Solution framework based on your business.
Step 3: You need to build the ground floor. Remember ground floor contains the common rooms like kitchen and hall.
Pega: Build a framework application extending solution framework or PegaRules. Bring all the common rules under framework application.
Step 4: Now you will build a room in the first floor extending ground floor. This room will house the things that belongs to a particular brother.
Pega: Build an implementation application extending framework application. Bring all the rules specific to that division in the implementation application.
- Implementation application can use the rules in framework, solution framework, Pegarules application.
- Framework application can use rules in Solution framework as well as PegaRules, but not in Implementation application.
These rule resolution are based on class inheritance which we will see in the next post ‘Enterprise class structure’
Hope you got the basics about framework and implementation application
Summary
Tip: 现在的Framework已经用的不多了. Pega建议用户使用Application layer去使用.




 文章介绍了在Pega中构建框架应用和实施应用的概念,以提高可重用性和支持扩展性。以亚马逊组织为例,说明如何为销售部门创建框架和实施应用。Pega提供基础产品和特定业务的解决方案框架,允许用户根据需求扩展。框架应用包含通用规则,而实施应用则包含特定部门的规则。文章通过建造房屋的比喻解释了这一过程。
文章介绍了在Pega中构建框架应用和实施应用的概念,以提高可重用性和支持扩展性。以亚马逊组织为例,说明如何为销售部门创建框架和实施应用。Pega提供基础产品和特定业务的解决方案框架,允许用户根据需求扩展。框架应用包含通用规则,而实施应用则包含特定部门的规则。文章通过建造房屋的比喻解释了这一过程。
















 1597
1597

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








