在java中基于socket的网络通信主要是使用ServerSocket及Socket来分别构建服务端和客户端,双方通过发送和接收字节数组来实现数据的交换,其通信流程如下:
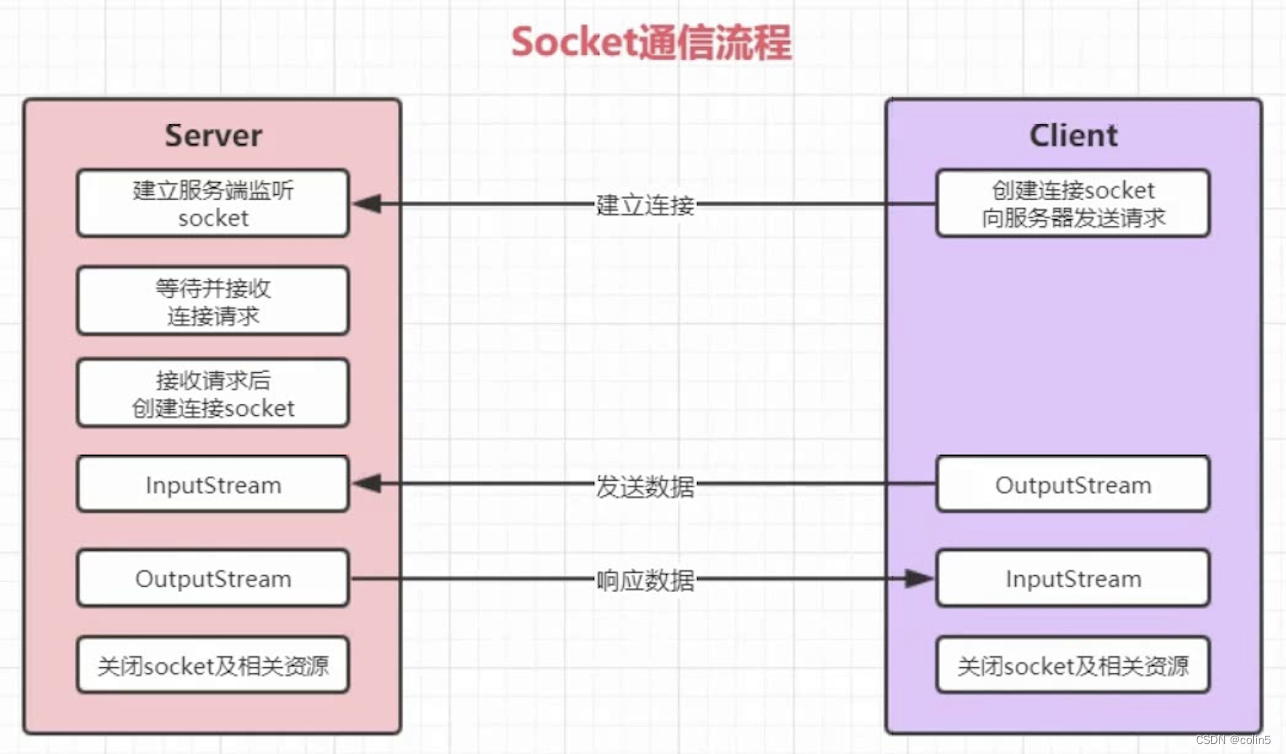
示例代码如下:
服务端Server.java
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(9999);
System.out.println("server started...");
while (true) {
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
System.out.println("client connected...");
executorService.execute(() -> {
process(socket);
});
}
}
public static void process(Socket socket) {
long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println("thread id:" + threadId + ", thread name:" + threadName);
InputStream inputStream = null;
OutputStream outputStream = null;
try {
inputStream = socket.getInputStream();
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int read = inputStream.read(bytes);
System.out.println("client:" + new String(bytes, 0, read));
outputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
outputStream.write("hello client".getBytes());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
inputStream.close();
outputStream.close();
socket.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
客户端Client.java
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
while (true) {
Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 9999);
OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
System.out.println("Please input string:");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String msg = scanner.nextLine();
outputStream.write(msg.getBytes());
InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream();
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int read = inputStream.read(bytes);
System.out.println("Message from server:" + new String(bytes, 0, read).trim());
socket.close();
}
}
}




 本文介绍了Java中使用ServerSocket和Socket进行网络通信的基本流程,包括服务端和客户端的创建,以及字节数组数据交换的过程。示例代码展示了如何实现简单的Socket通信。
本文介绍了Java中使用ServerSocket和Socket进行网络通信的基本流程,包括服务端和客户端的创建,以及字节数组数据交换的过程。示例代码展示了如何实现简单的Socket通信。
















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








