Chrome的在线自动字幕辅助工具
最近一直在使用Chrome上在线课程,在线字幕给了笔者很大帮助。但不知谷歌公司怎么想的(有可能是隐私问题),显示的字幕竟然不能下载,而且,字幕窗口展开后,最多是有8行,而且还不能向前滚动查看。趁前两天下午没啥事,用python写个字幕复制工具,主要解决以下几个问题:
- 字幕可以被复制
- 字幕可通过scroll bar前后滚动浏览
- 字幕可通过处理,自动实现分句。
思路
原来是想通过钩子程序截取字幕窗口写文字函数的,后来想想太复杂,有可能还有加密机制,因此,就偷懒,直接用Tesseract-OCR识别Chrome的字幕窗口,好在Chrome的字幕窗口本身是置顶的,只要能跳出字幕,文章本身非常清晰,Tesseract-OCR识别非常方便。基本思路如下:
1. 为不影响其他程序运行,识别过程须在一个单独的进程里
2. 获取字幕窗口,读取一行文字,OCR识别
3. 把识别的文字添加到Text控件中,这样文本就能滚动
4. 为与字幕速度尽可能保持一致,只对导出文字进行分句分句
主程序
QT控件比较丰富,这个工具没必要使用复杂控件,因此用了tkinter最为GUI,程序界面如下:
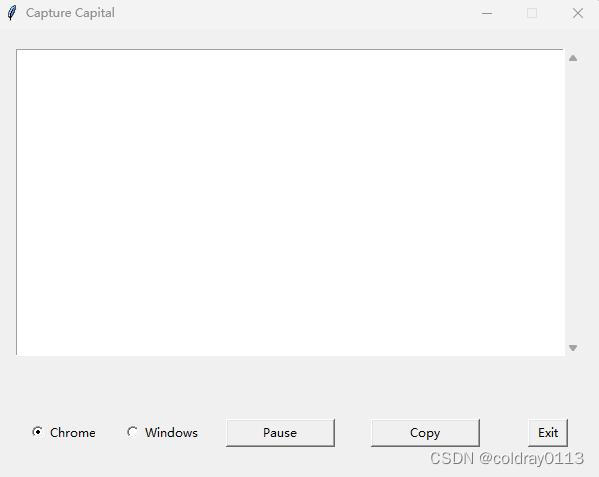
窗体的部分位置是通过PAGE来确定的,主要代码如下:
root = Tk()
root.title('Capture Capital')
root.attributes("-topmost",1) #置顶
v = IntVar()
place_x=int(root.winfo_screenwidth()-605) //2
place_y=int(root.winfo_screenheight()-450) // 2
root.geometry(f"605x450+{place_x}+{place_y}")
root.resizable(False, False)
panel=Frame(root) #建立一个panel,让Text和滚动条都在其上
panel.place(relx=0.033, rely=0.044, relheight=0.682, relwidth=0.934)
text=Text(panel)
scroll = Scrollbar(panel)
scroll.pack(side=RIGHT,fill=Y)
scroll.config(command=text.yview)
text.config(yscrollcommand=scroll.set)
text.pack()
text.config(spacing1=15) #行间距
text.configure(font =("Arial", 13))
Radiobutton1 = Radiobutton(root,text="Chrome", variable=v, value=0)
Radiobutton1.place(relx=0.06, rely=0.867, relheight=0.06, relwidth=0.104
Radiobutton2 = Radiobutton(root,text="Windows", variable=v, value=1)
Radiobutton2.place(relx=0.20, rely=0.867, relheight=0.06 , relwidth=0.152)
Button1 = Button(root)
Button1.place(relx=0.38, rely=0.867, height=28, width=109)
Button1.configure(text='Pause')
Button2 = Button(root)
Button2.place(relx=0.62, rely=0.867, height=28, width=109)
Button2.configure(text='Copy')
Button3 = Button(root)
Button3.place(relx=0.88, rely=0.867, height=28, width=40)
Button3.configure(text='Exit')```
然后为识别函数单独建立一个进程。由于正常语速1秒说4的单词顶天了,而Chrome的字幕一行能显示7-8个字符,为不独占CPU,考虑每0.5秒读一次字幕。图方便,直接用了threading.Thread建立进程。此部分代码如下:
def detect():
img0=Image.new('RGB',(512,30),(0,0,0)) #建一个空的截屏图像
while 1:
time.sleep(0.5)
...... #后面是截屏和OCR部分的代码
if __name__ == '__main__':
th0=threading.Thread(target=detect)
th0.start()
mainloop() #这是tkinter的主循环
截屏
中文版Chrome字幕窗口的标题是’实时字幕’,所以很容易截屏。Chrome的字幕窗口虽然是有些透明度,但透的不是深,Tesseract-OCR能直接识别。而且,一般情况下字幕窗口的倒数第二行单词是稳定的,所有读字幕窗口的倒数第二行就可以了,这样压缩窗口和展开窗口截屏的代码都一样。
def subRect(s,t):
'''
本程序通过字幕窗口左下角进行倒数第二行截屏窗口的定位,s为字幕窗口的Rect,t截取图形在字幕窗口的左上角坐
、宽和高。经测量,取这个值比较合适:chromePackedWindow=(22,30,534,60)
'''
global ifChromeCaption #以Chrome的字幕窗口进行识别
if ifChromeCaption:
return(s[2]-28-(t[2]-t[0]),s[3]-62-(t[3]-t[1]),s[2]-28,s[3]-62) #28,62为截屏图像右下角到字幕窗口右下角的距离
def detect():
....... #接上面进程主循环
hwnd=0
hwnd = win32gui.FindWindow(None, title)
if hwnd!=0 and win32gui.IsWindowVisible(hwnd)==True:
rect=win32gui.GetWindowRect(hwnd)
img1 = ImageGrab.grab(subRect(rect,rectW))
为加快识别,这里要做个截屏图像筛选,若图像没啥变化,截完屏就不进行OCR了。
flag=False # 当前读取的截屏与上次读取的行图形是否稳定
for i in range(img0.size[0]):
for j in range(img0.size[1]):
s=img0.getpixel((i,j))
t=img1.getpixel((i,j))
dr=abs(s[0]-t[0])
db=abs(s[1]-t[1])
dg=abs(s[2]-t[2])
#threshold这个阈值,程序中取100,主要是考虑到字幕窗口移动的因素
if dr>threshold and db>threshold and dg>threshold:
flag=True
break
if flag:
break
解析文字
没啥好说的,一行
code = pytesseract.image_to_string(img1, lang='eng')
有时,在长句中,倒数第二行字幕显示后仍会发生改变,这个改变需要进行句法分析,代表这个变化行与刚才那行是同一行,只是显示上的变化。
code = pytesseract.image_to_string(img1, lang='eng')
code = code.replace('\n','')
if len(code)>10: #当前文字是否太短,太短可能不是实时的字幕内容
#data = pytesseract.image_to_data(img1,lang='eng')
#本次解析的文字与上次解析的文字是否相似
diff_result = difflib.SequenceMatcher(None, code, lastcode).ratio()
然后把文字送到Text中:
if diff_result<Diff: #不相似,说明是新的内容
'''
chrome生成的文字倒数第二行可行会有变化,本程序解析的文字是最长的一行
那样,此最长行与下一行可能在衔接处有重复文字。
'''
#把上次解析的文字和本次解析的文字拆分成两个列表,把本次解析行重复的文字删除
lastword=tokenizer.tokenize(lastcode)
word=tokenizer.tokenize(code)
for i in range(len(lastword)):
if lastword[-i-1]==word[i]:
word.pop()
else:
break
code=combineSentence(word)
lastcode=code
appendText(lastcode,0)
text.update()
else: #相似,输出最长的句子
if len(code)>len(lastcode):
lastcode=code
appendText(lastcode,1)
text.update()
导出
这里是按键点下,复制到剪贴板。由于原来Chrome的字幕是不分句的,所以句子挤在一起,所以这里要有个分句函数。这个函数国外论坛上找的1,比较好用:
def split_into_sentences(text): #英语分句
alphabets= "([A-Za-z])"
prefixes = "(Mr|St|Mrs|Ms|Dr)[.]"
suffixes = "(Inc|Ltd|Jr|Sr|Co)"
starters = "(Mr|Mrs|Ms|Dr|He\s|She\s|It\s|They\s|Their\s|Our\s|We\s|But\s|However\s|That\s|This\s|Wherever)"
acronyms = "([A-Z][.][A-Z][.](?:[A-Z][.])?)"
websites = "[.](com|net|org|io|gov)"
digits = "([0-9])"
text = " " + text + " ." #此行是我加的,因为这个函数最后一句若认为不是句子,就自动把内容扔了。加了句号,让它强制识别为句子
text = text.replace("\n"," ")
text = re.sub(prefixes,"\\1<prd>",text)
text = re.sub(websites,"<prd>\\1",text)
text = re.sub(digits + "[.]" + digits,"\\1<prd>\\2",text)
if "..." in text: text = text.replace("...","<prd><prd><prd>")
if "Ph.D" in text: text = text.replace("Ph.D.","Ph<prd>D<prd>")
text = re.sub("\s" + alphabets + "[.] "," \\1<prd> ",text)
text = re.sub(acronyms+" "+starters,"\\1<stop> \\2",text)
text = re.sub(alphabets + "[.]" + alphabets + "[.]" + alphabets + "[.]","\\1<prd>\\2<prd>\\3<prd>",text)
text = re.sub(alphabets + "[.]" + alphabets + "[.]","\\1<prd>\\2<prd>",text)
text = re.sub(" "+suffixes+"[.] "+starters," \\1<stop> \\2",text)
text = re.sub(" "+suffixes+"[.]"," \\1<prd>",text)
text = re.sub(" " + alphabets + "[.]"," \\1<prd>",text)
if "”" in text: text = text.replace(".”","”.")
if "\"" in text: text = text.replace(".\"","\".")
if "!" in text: text = text.replace("!\"","\"!")
if "?" in text: text = text.replace("?\"","\"?")
text = text.replace(".",".<stop>")
text = text.replace("?","?<stop>")
text = text.replace("!","!<stop>")
text = text.replace("<prd>",".")
sentences = text.split("<stop>")
sentences = sentences[:-1]
sentences = [s.strip() for s in sentences]
sentences[-1]=sentences[-1][0:-2] #把句号再删了
return sentences
复制到剪贴板:
def onCopy():
txt=text.get(1.0,END) #行号以1开始,列号以0开始,返回从第1行1列至文末所有内容
lst=txt.split('\n')
sentence=combineSentence(lst)
tmp=split_into_sentences(sentence)
sentence='\n'.join(tmp)
subprocess.run(['clip.exe'], input=sentence.strip().encode('utf-16'), check=True)
结语
程序基本上基本满足自己的功能,由于截屏只截取了字幕窗口最后第二行,因此字幕窗口最后一行会没有识别,但这个已经不影响使用了。
实际代码多线程没做优化,退出程序必须按Exit键;Windonws11据说也有内部的实时字幕,估计也差不多,我没有去实现,留了个空。际的代码中还增加了些功能:Text窗口只读,但能使用CTRL+C复制;按a键可以添加一个红色的标签;暂停取词;清空Text。
家若有什么想法可以给我写邮件(coldraymagic@gmail.com) ,我再增加功能。谢谢。
最后,附上全部代码。







 本文介绍了一款使用Python编写的工具,该工具能够捕获并处理Chrome浏览器中的自动字幕,实现字幕的滚动浏览、复制及自动分句。
本文介绍了一款使用Python编写的工具,该工具能够捕获并处理Chrome浏览器中的自动字幕,实现字幕的滚动浏览、复制及自动分句。

















 3万+
3万+










