给你二叉树的根节点 root ,返回它节点值的 前序 遍历。
示例 1:
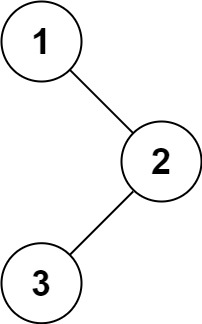
输入:root = [1,null,2,3] 输出:[1,2,3]
文章讲解:代码随想录
视频讲解:每次写递归都要靠直觉? 这次带你学透二叉树的递归遍历!| LeetCode:144.前序遍历,145.后序遍历,94.中序遍历_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
第一印象:不会,二叉树是我的知识盲区,一刷属于是扫盲了。
看完讲解:清晰明了,注意点是写递归的时候思路要清晰,我觉得也是需要反复练习的。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
// 二叉树的前序递归遍历
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
preorder(root, result);
return result;
}
public void preorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> result) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
result.add(root.val);
preorder(root.left, result);
preorder(root.right, result);
}
}
// 二叉树的前序迭代遍历
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) return result;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
result.add(node.val);
if (node.right != null) {
stack.push(node.right);
}
if (node.left != null) {
stack.push(node.left);
}
}
return result;
}
}
// 二叉树的中序递归遍历
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
inorder(root, result);
return result;
}
public void inorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> result) {
if (root == null) return;
inorder(root.left, result);
result.add(root.val);
inorder(root.right, result);
}
}
// 二叉树的中序迭代遍历
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) return result;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode node = root;
while (node != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while (node != null) {
stack.push(node);
node = node.left;
}
node = stack.pop();
result.add(node.val);
node = node.right;
}
return result;
}
}
// 二叉树的后续递归遍历
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
postorder(root, result);
return result;
}
public void postorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> result) {
if (root == null) return;
postorder(root.left, result);
postorder(root.right, result);
result.add(root.val);
}
}
// 二叉树的后序迭代遍历
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) return result;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode node = root;
stack.push(node);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
node = stack.pop();
result.add(node.val);
if (node.left != null) {
stack.push(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
stack.push(node.right);
}
}
Collections.reverse(result);
return result;
}
}今日小结:说真的欠的实在是太多了,最近也很忙倒是真的,我希望gap的这段时间能够沉下心来学习,计算机是个很卷的地方,我觉得要摆正心态。




 本文介绍了如何通过递归和迭代的方式实现二叉树的前序遍历,包括代码示例和重要注意事项,强调了在编程中的实践与心态调整。
本文介绍了如何通过递归和迭代的方式实现二叉树的前序遍历,包括代码示例和重要注意事项,强调了在编程中的实践与心态调整。
















 728
728

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








