- 🍨 本文为🔗365天深度学习训练营 中的学习记录博客
- 🍦 参考文章:365天深度学习训练营-第P1周:实现mnist手写数字识别(训练营内部成员可读)
- 🍖 原作者:K同学啊|接辅导、项目定制
目录
tf.config.list_physical_devices函数说明:
tf.config.experimental.set_memory_growth函数
tf.config.set_visible_devices函数
运行环境:
- 语言环境:Python3.8
- 编译器:jupyter notebook
- 深度学习环境:TensorFlow2.3
一、前期工作
1. 设置GPU
import tensorflow as tf
gpus = tf.config.list_physical_devices("GPU")
if gpus:
gpu0 = gpus[0] #如果有多个GPU,仅使用第0个GPU
tf.config.experimental.set_memory_growth(gpu0, True) #设置GPU显存用量按需使用
tf.config.set_visible_devices([gpu0],"GPU")tf.config.list_physical_devices函数说明:
tf.config.list_physical_devices(
device_type=None
)参数:
- device_type (可选字符串)仅包括与此设备类型匹配的设备。例如 "CPU" 或 "GPU"。
返回:
- 返回对主机运行时可见的物理设备列表。默认情况下,所有发现的 CPU 和 GPU 设备都被视为可见。此 API 允许在运行时初始化之前查询物理硬件资源。
tf.config.experimental.set_memory_growth函数
设置显存使用策略
默认情况下,TensorFlow 将使用几乎所有可用的显存,以避免内存碎片化所带来的性能损失。不过,TensorFlow 提供两种显存使用策略,让我们能够更灵活地控制程序的显存使用方式:
- 仅在需要时申请显存空间(程序初始运行时消耗很少的显存,随着程序的运行而动态申请显存);
- 限制消耗固定大小的显存(程序不会超出限定的显存大小,若超出的报错)。
可以通过 tf.config.experimental.set_memory_growth 将 GPU 的显存使用策略设置为 “仅在需要时申请显存空间”。以下代码将所有 GPU 设置为仅在需要时申请显存空间:
gpus = tf.config.list_physical_devices(device_type='GPU')
for gpu in gpus:
tf.config.experimental.set_memory_growth(device=gpu, enable=True)tf.config.set_visible_devices函数
通过 tf.config.set_visible_devices ,可以设置当前程序可见的设备范围(当前程序只会使用自己可见的设备,不可见的设备不会被当前程序使用)。
例如,如果在 4 卡的机器中我们需要限定当前程序只使用下标为 0、1 的两块显卡(GPU:0 和 GPU:1),可以使用以下代码:
gpus = tf.config.list_physical_devices(device_type='GPU')
tf.config.set_visible_devices(devices=gpus[0:2], device_type='GPU')2. 导入数据
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras import datasets, layers, models
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
(train_images, train_labels), (test_images, test_labels) = datasets.cifar10.load_data()3. 归一化
# 将像素的值标准化至0到1的区间内。
train_images, test_images = train_images / 255.0, test_images / 255.0
train_images.shape,test_images.shape,train_labels.shape,test_labels.shape4. 可视化
class_names = ['airplane', 'automobile', 'bird', 'cat', 'deer','dog', 'frog', 'horse', 'ship', 'truck']
plt.figure(figsize=(20,10))
for i in range(20):
plt.subplot(5,10,i+1)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
plt.grid(False)
plt.imshow(train_images[i], cmap=plt.cm.binary)
plt.xlabel(class_names[train_labels[i][0]])
plt.show()二、构建CNN网络
model = models.Sequential([
layers.Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu', input_shape=(32, 32, 3)), #卷积层1,卷积核3*3
layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)), #池化层1,2*2采样
layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='relu'), #卷积层2,卷积核3*3
layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)), #池化层2,2*2采样
layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='relu'), #卷积层3,卷积核3*3
layers.Flatten(), #Flatten层,连接卷积层与全连接层
layers.Dense(64, activation='relu'), #全连接层,特征进一步提取
layers.Dense(10) #输出层,输出预期结果
])
model.summary() # 打印网络结构二维卷积层:
tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(
filters, kernel_size, strides=(1, 1), padding='valid', data_format=None,
dilation_rate=(1, 1), activation=None, use_bias=True,
kernel_initializer='glorot_uniform', bias_initializer='zeros',
kernel_regularizer=None, bias_regularizer=None, activity_regularizer=None,
kernel_constraint=None, bias_constraint=None, **kwargs
)- filters ,kernel_size过滤器个数和卷积核尺寸,这两个没有默认值,必须给。
- 后面的那个多参数,都是关键字参数(有等于号的),都是有默认值的,可以不写。
参数filters:
这是第一个参数,位置是固定的,含义是过滤器个数,或者叫卷积核个数,这个与卷积后的输出通道数一样,比如下面filters为5的时候,卷积输出的通道数(最后一位)就是5
一个可选的关键字参数,input_shape:
当使用此层作为模型的第一层时,需要提供关键字参数input_shape(整数元组,不包括样本轴(不需要写batch_size))
例如,input_shape=(128, 128, 3)表示 128x128的 RGB 图像data_format="channels_last"
这个data_format参数是这样影响input_shape工作的。
- 如果不填写,默认是channels_last,否则可以填写channels_first。
- 前者的会把input_shape这个三元组给识别成(batch_size, height, width, channels),
-
- 通常在定义模型的时候,可以省略 batch_size 这个维度
- TensorFlow 在构建模型时允许忽略 batch_size 维度,只需要指定输入数据的形状,例如 (height, width, channels),然后它会自动处理批次大小这个维度。
- 后者则会识别成(batch_size, channels, height, width),不过样本轴不需要自己填写(不然反而会报错)
keras.layers.Flatten讲解
keras.layers.Flatten(input_shape=[])用于将输入层的数据压成一维的数据,一般用再卷积层和全连接层之间(因为全连接层只能接收一维数据,而卷积层可以处理二维数据,就是全连接层处理的是向量,而卷积层处理的是矩阵),原理如下:
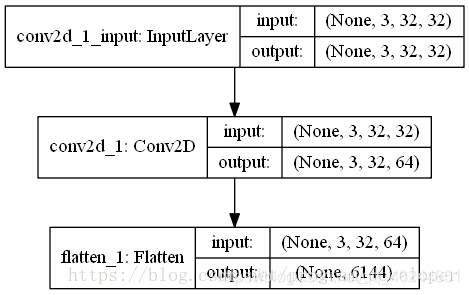
三、编译
model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True),
metrics=['accuracy'])四、训练模型
history = model.fit(train_images, train_labels, epochs=10,
validation_data=(test_images, test_labels))五、预测
通过模型进行预测得到的是每一个类别的概率,数字越大该图片为该类别的可能性越大
plt.imshow(test_images[1])import numpy as np
pre = model.predict(test_images)
print(class_names[np.argmax(pre[1])])六、模型评估
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.plot(history.history['accuracy'], label='accuracy')
plt.plot(history.history['val_accuracy'], label = 'val_accuracy')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('Accuracy')
plt.ylim([0.5, 1])
plt.legend(loc='lower right')
plt.show()
test_loss, test_acc = model.evaluate(test_images, test_labels, verbose=2)
























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








