在Linux环境编程中,经常要对文件进行操作,比如打开,关闭,读,写,定位操作,本篇记录open, close, read, write, lseek函数的使用。
首先通过man 2 open命令查看帮助文档
1.open函数打开文件
| 函数名 | open |
| 相关函数 | close |
| 表头文件 |
#include <sys/types.h> |
| 函数定义 |
int open(const char *pathname, int flags); |
| 函数说明 | 打开由路径名指定的文件, pathname绝对路径文件名, flags打开标志,例如:O_RDONLY(只读),O_WRONLY (只写),O_CREAT(创建),O_APPEND(追加)等,返回类型为int。 |
| 返回值 | 返回值0表示成功,非零表示失败。 |
2.close函数关闭打开的文件
| 函数名 | close |
| 相关函数 | open |
| 表头文件 |
#include <unistd.h> |
| 函数定义 | int close(int fd); |
| 函数说明 | 关闭打开的文件fd,返回类型为int。 |
| 返回值 | 返回值0表示成功,非零表示失败。 |
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
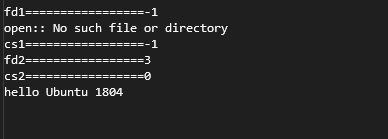
int fd1 = open("/home/scott/projects/linuxAPI/main2.cpp", O_RDONLY); //成功大于0的fd, 失败返回-1
cout << "fd1=================" << fd1 << endl;
if (fd1 == -1)
{
perror("open:");
}
int cs1 = close(fd1);
cout << "cs1=================" << cs1 << endl;
int fd2 = open("/home/scott/projects/linuxAPI/main.cpp", O_RDONLY); //成功大于0的fd, 失败返回-1
cout << "fd2=================" << fd2 << endl;
if (fd2 == -1)
{
perror("open:");
}
int cs2 = close(fd2);
cout << "cs2=================" << cs2 << endl;
cout << "hello Ubuntu 1804" << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
3.read函数读取打开文件的内容
| 函数名 | read |
| 相关函数 | write |
| 表头文件 | #include <unistd.h> |
| 函数定义 | ssize_t read(int fd, void *buf, size_t count); |
| 函数说明 | 从fd文件标识符中读取内容到buf中,返回类型为ssize_t。 |
| 返回值 | 成功返回读取的字符数,失败返回-1。 |
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char buf1[1024];
char buf2[1024];
//打开文件
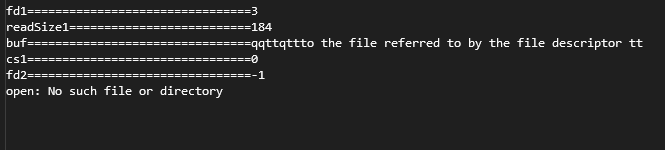
int fd1 = open("/home/scott/projects/linuxAPI/aa.txt", O_RDONLY);
cout << "fd1================================" << fd1 << endl;
if (fd1 == -1)
{
perror("open:");
return 1;
}
//读取文件
size_t readSize1 = read(fd1, buf1, sizeof(buf1) - 1);
cout << "readSize1==========================" << readSize1 << endl;
if (readSize1 > 0)
{
cout << "buf================================" << buf1 << endl;
//确保字符串末尾以'\0'结束
buf1[readSize1] = '\0';
}
int cs1 = close(fd1);
cout << "cs1================================" << cs1 << endl;
//打开文件
int fd2 = open("/home/scott/projects/linuxAPI/aa2.txt", O_RDONLY);
cout << "fd2================================" << fd2 << endl;
if (fd2 == -1)
{
perror("open");
return 1;
}
//读取文件
size_t readSize2 = read(fd2, buf2, sizeof(buf2) - 1);
cout << "readSize1==========================" << readSize2 << endl;
if (readSize2 > 0)
{
cout << "buf2================================" << buf2 << endl;
//确保字符串末尾以'\0'结束
buf2[readSize2] = '\0';
}
int cs2 = close(fd2);
cout << "cs2================================" << cs2 << endl;
cout << "hello Ubuntu 1804" << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
4.read函数读取打开文件的内容
| 函数名 | write |
| 相关函数 | read |
| 表头文件 | #include <unistd.h> |
| 函数定义 | ssize_t write(int fd, const void *buf, size_t count); |
| 函数说明 | 向文件描述符fd中写入数据,buf指向要写入的数据的缓冲区,count写入数据的大小,返回类型ssize_t。 |
| 返回值 | 成功返回实际写入的字节数,失败返回-1。 |
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
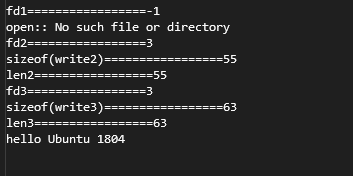
int fd1 = open("/home/scott/projects/linuxAPI/aa.txt", O_WRONLY); //成功大于0的fd, 失败返回-1 文件不存在
cout << "fd1=================" << fd1 << endl;
if (fd1 == -1)
{
perror("open:");
}
else
{
//写内容 如果文件存在会覆盖之前的内容
char write1[] = "write() writes up to count bytes from the buffer starting at ";
size_t textLen1 = sizeof(write1);
size_t len1 = write(fd1, write1, sizeof(write1));
cout << "sizeof(write1)=================" << textLen1 << endl;
cout << "len1=================" << len1 << endl;
}
close(fd1);
int fd2 = open("/home/scott/projects/linuxAPI/aa.txt", O_WRONLY | O_CREAT, 0644); //成功大于0的fd, 失败返回-1 文件不存在,则创建
cout << "fd2=================" << fd2 << endl;
if (fd2 == -1)
{
perror("open:");
}
else
{
//写内容
char write2[] = "buf to the file referred to by the file descriptor fd.";
size_t textLen2 = sizeof(write2);
size_t len2 = write(fd2, write2, sizeof(write2));
cout << "sizeof(write2)=================" << textLen2 << endl;
cout << "len2=================" << len2 << endl;
}
close(fd2);
int fd3 = open("/home/scott/projects/linuxAPI/aa.txt", O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_APPEND, 0644); //成功大于0的fd, 失败返回-1 文件不存在,则创建
cout << "fd3=================" << fd3 << endl;
if (fd3 == -1)
{
perror("open:");
}
else
{
//写内容, 存在这追加内容
char write3[] = "write() writes up to count bytes from the buffer starting at .";
size_t textLen3 = sizeof(write3);
size_t len3 = write(fd3, write3, sizeof(write3));
cout << "sizeof(write3)=================" << textLen3 << endl;
cout << "len3=================" << len3 << endl;
}
close(fd3);
cout << "hello Ubuntu 1804" << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
5.lseek函数读取打开文件的内容
| 函数名 | lseek |
| 相关函数 | fseek |
| 表头文件 | #include <sys/types.h> #include <unistd.h> |
| 函数定义 | off_t lseek(int fd, off_t offset, int whence); |
| 函数说明 | 将打开文件描述的文件偏移重新定位。
fd:文件描述符 offset:字节数,以whence参数为基点解释offset(偏移量) whence:解释offset参数的基点 SEEK_SET:文件偏移量设置为offset(开头) SEEK_CUR:文件偏移量设置为当前文件偏移量加上offset,offset可以为 负数(末尾) SEEK_END:文件偏移量设置为文件长度加上 offset,offset可以为负数 |
| 返回值 | 成功返回偏移值,失败返回-1。 |
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
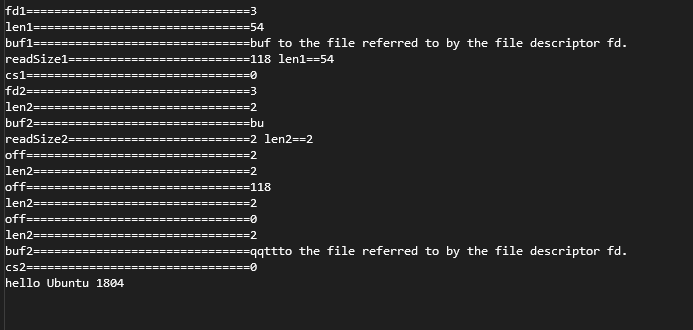
int main()
{
char buf1[1024];
//打开文件
int fd1 = open("/home/scott/projects/linuxAPI/aa.txt", O_RDONLY);
cout << "fd1================================" << fd1 << endl;
if (fd1 == -1)
{
perror("open:");
return 1;
}
//读取文件
size_t readSize1 = read(fd1, buf1, sizeof(buf1) - 1);
size_t len1 = strlen(buf1); //计算到以'\0'结尾
cout << "len1===============================" << len1 << endl;
if (readSize1 > 0)
{
//原文
cout << "buf1===============================" << buf1 << endl;
//确保字符串末尾以'\0'结束
buf1[readSize1] = '\0';
}
len1 = strlen(buf1); //计算到以'\0'结尾
cout << "readSize1==========================" << readSize1 << " len1==" << len1 << endl;
int cs1 = close(fd1);
cout << "cs1================================" << cs1 << endl;
//====================================================================
char buf2[1024];
//打开文件
int fd2 = open("/home/scott/projects/linuxAPI/aa.txt", O_RDWR);
cout << "fd2================================" << fd2 << endl;
if (fd2 == -1)
{
perror("open2:");
return 1;
}
//读取文件
size_t readSize2 = read(fd2, buf2, 2);
size_t len2 = strlen(buf2); //计算到以'\0'结尾
cout << "len2===============================" << len2 << endl;
if (readSize2 > 0)
{
cout << "buf2===============================" << buf2 << endl;
//确保字符串末尾以'\0'结束
buf2[readSize2] = '\0';
}
len2 = strlen(buf2); //计算到以'\0'结尾
cout << "readSize2==========================" << readSize2 << " len2==" << len2 << endl;
int off = lseek(fd2, 0, SEEK_CUR); //获取文件指针当前位置
cout << "off================================" << off << endl;
//从off位置开始写入tt两个字符, 前面读到的位置是2,因此这里在第3个位置写入tt
char write1[3] = "tt";
len2 = write(fd2, write1, len2);
cout << "len2===============================" << len2 << endl;
off = lseek(fd2, 0, SEEK_END); //获取文件长度, 同时文件指针移到了末尾
cout << "off================================" << off << endl;
//从off位置开始写入ss两个字符,即在文件末尾添加ss与两个字符
char write2[3] = "ss";
len2 = write(fd2, write2, len2);
cout << "len2===============================" << len2 << endl;
off = lseek(fd2, 0, SEEK_SET); //文件指针移动头部 off = 0
cout << "off================================" << off << endl;
//从off位置开始写入aa两个字符, 即在文件开头位置写入qq
char write3[3] = "qq";
len2 = write(fd2, write3, len2);
cout << "len2===============================" << len2 << endl;
//把指针移到头部
off = lseek(fd2, 0, SEEK_SET);
//读取全文
readSize2 = read(fd2, buf2, sizeof(buf2) - 1);
cout << "buf2===============================" << buf2 << endl;
int cs2 = close(fd2);
cout << "cs2================================" << cs2 << endl;
cout << "hello Ubuntu 1804" << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
参考:
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/m0_74091159/article/details/142263395
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/2091075
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/m0_74091159/article/details/142261052
https://www.cnblogs.com/codemagiciant/p/17662930.html
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/m0_74091159/article/details/142261980
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/m0_68250740/article/details/139015396








 本文介绍了用于获取文件系统状态信息的C语言API:statfs和fstatfs函数。这两个函数可以提供诸如文件系统的块大小、可用块数、总节点数等关键数据。此外,还详细展示了statfs结构体中各个字段的含义及其用途。
本文介绍了用于获取文件系统状态信息的C语言API:statfs和fstatfs函数。这两个函数可以提供诸如文件系统的块大小、可用块数、总节点数等关键数据。此外,还详细展示了statfs结构体中各个字段的含义及其用途。
















 1504
1504

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








