文章目录
- 一、`int pthread_create(pthread_t *thread, pthread_attr_t *attr, void *(*start_routine)(void *), void *arg);`
- 二、`int pthread_join(pthread_t tid, void **thread_return);`
- 三、`int pthread_detach(pthread_t tid);`
- 四、`void pthread_exit(void *retval);`
- 五、`int pthread_setcancelstate(int state, int *oldstate);`
- 六、`int pthread_cancel(pthread_t tid);`
- 七、
一、int pthread_create(pthread_t *thread, pthread_attr_t *attr, void *(*start_routine)(void *), void *arg);
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
void *thread_fun(void* arg)
{
int num = *((int*)arg);
printf("int the new thread: num = %d\n", num);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
pthread_t tid;
int test = 100;
pthread_create(&tid, NULL, thread_fun, (void *)&test);
while(1);
return 0;
}
二、int pthread_join(pthread_t tid, void **thread_return);
等待线程结束并回收线程资源,此函数会阻塞,类似进程的 wait() 函数。如果线程已经结束,那么该函数会立即返回
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
void *thead_fun(void *arg)
{
static int ret = 5; // thread_join.cpp:7:13: warning: address of local variable ‘ret’ returned [-Wreturn-local-addr]
sleep(1);
pthread_exit((void*)&ret);
//return (void*)&ret;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
pthread_t tid;
void *ret = NULL;
pthread_create(&tid, NULL, thead_fun, NULL);
pthread_join(tid, &ret);
printf("ret = %d\n", *((int*)ret));
return 0;
}
三、int pthread_detach(pthread_t tid);
在默认情况下,线程的终止状态会保存到对该线程调用 pthread_join,然后才释放底层存储资源
如果线程处于分离状态,线程资源的回收工作交由系统完成,此函数不会阻塞
对分离状态的线程进行 pthread_join 调用会立即返回失败,返回 EINVAL
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
void *thead_fun(void *arg)
{
for(int i=0; i<3; i++)
{
printf("thread is runing\n");
sleep(1);
}
return NULL;
}
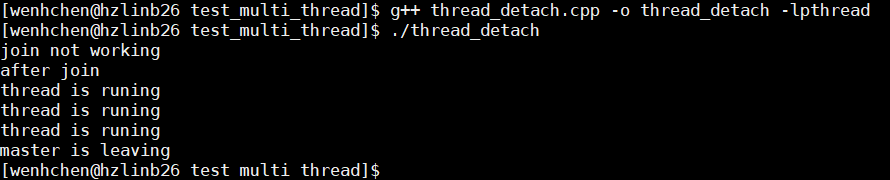
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
pthread_t tid;
pthread_create(&tid, NULL, thead_fun, NULL);
pthread_detach(tid);
if (pthread_join(tid, NULL)) // 立即返回,调用失败
{
printf("join not working\n");
}
printf("after join\n");
sleep(5);
printf("master is leaving\n");
return 0;
}
四、void pthread_exit(void *retval);
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
void *thead_fun(void *arg)
{
static int ret = 5; // thread_join.cpp:7:13: warning: address of local variable ‘ret’ returned [-Wreturn-local-addr]
sleep(1);
pthread_exit((void*)&ret);
//return (void*)&ret;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
pthread_t tid;
void *ret = NULL;
pthread_create(&tid, NULL, thead_fun, NULL);
pthread_join(tid, &ret);
printf("ret = %d\n", *((int*)ret));
return 0;
}
五、int pthread_setcancelstate(int state, int *oldstate);
state:
PTHREAD_CANCEL_ENABLE 允许线程接收取消请求;
PTHREAD_CANCEL_DISABLE忽略取消请求
oldstate:
获取先前的取消状态
六、int pthread_cancel(pthread_t tid);
在默认的情况下,pthread_cancel 函数会使由 tid 标识的线程的行为表现为如同调用了参数为PTHEAD_CANCELED 的 pthread_exit 函数
pthread_cancel 并不等待线程终止,它仅仅提出请求,线程可以设置忽略 cancel 请求
七、
线程终止方法:
- return:线程执行结束正常退出
- pthread_cancel:被同一进程中其它线程取消
- pthread_exit:线程自己调用
pthread_exit退出
多线程编译:
线程函数在 pthread 库中,故链接时要加上参数 -lpthread,如:
g++ test.cpp -o test -lpthread





 本文详细介绍了POSIX线程编程中的关键函数,包括`pthread_create`用于创建线程,`pthread_join`等待线程结束并回收资源,`pthread_detach`使线程在结束时自动清理,`pthread_exit`线程退出方式,`pthread_setcancelstate`和`pthread_cancel`用于线程取消。通过示例代码展示了这些函数的使用方法。
本文详细介绍了POSIX线程编程中的关键函数,包括`pthread_create`用于创建线程,`pthread_join`等待线程结束并回收资源,`pthread_detach`使线程在结束时自动清理,`pthread_exit`线程退出方式,`pthread_setcancelstate`和`pthread_cancel`用于线程取消。通过示例代码展示了这些函数的使用方法。
















 737
737

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








