1. 传统方式 Thread.join()
/**
* 使用传统方式启动线程,执行任务,实现阻塞
*
* @see Thread#join()
*
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
log.info("do something in Runnable");
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
thread.start();
log.info("is executing");
Thread.sleep(1000);
// 让当成线程停下来,等待thread线程执行完成,实现阻塞
thread.join();
log.info("Normal thread is done");
log.info(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": is done");
}
缺陷:
- 需要拿到线程的对象才能调用Thread.join(), 如果当前线程需要等待10个线程,代码变得十分复杂
- 无法定义和获得线程的返回值
2. 线程池 + AQS组件:CountDownLatch, 不获取返回值
2.1 等待一个线程
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 初始值,留给子线程递减
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(1);
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
executorService.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
log.info("runnable executed");
// 第一次执行 CountDownLatch 就减为0,相当于await() 只等待该线程执行一次;
countDownLatch.countDown();
}
}
// 让主线程阻塞
countDownLatch.await();
}
2.2 等待多个线程
使用while循环阻塞当前线程
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
// 注意计数是100以内,因为for循环是100次
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(100)
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// 第一次执行到这句话 CountDownLatch 的值变为99, 第100次到这刚好等于0
// 如果取值取101 甚至更大, 主线程则永远阻塞,因为CountDownLatch 最小只为 101-100 = 1,不符合唤醒规则
countDownLatch.countDown();
log.info(countDownLatch.getCount() + " ");
}
};
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
executorService.submit(runnable);
}
// 当 CountDownLatch 的值为0, await() 状态被唤醒,主线程继续执行
countDownLatch.await();
log.info("main thread is done");
executorService.shutdown();
}
缺陷:
- CountDownLatch对象只维护了计数器的递减,不能循环使用
- 需要明确阻塞前一共要执行几个线程
- 无法定义和获取线程的返回值
对比传统方式:
- 用一个全局的计数器,实现一个线程等待多个线程
- 将线程阻塞的任务委托给CountDownLatch来实现
3. AQS组件 FutureTask + Callable / Runnable, 获取返回值
3.1 预备知识 – 源码
- FutureTask 的构造方法
public FutureTask(Callable<V> callable) {
if (callable == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
this.callable = callable;
this.state = NEW;
}
public FutureTask(Runnable runnable, V result) {
this.callable = Executors.callable(runnable, result); // 内部将Runnable包装成Callable
this.state = NEW;
}
- 包装Runnable 为 Callable
传入Runnable的构造方法,实际上也是在使用Callable的特性 – 提供返回值
public static <T> Callable<T> callable(Runnable task, T result) {
if (task == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
return new RunnableAdapter<T>(task, result);
}
static final class RunnableAdapter<T> implements Callable<T> {
final Runnable task;
final T result;
RunnableAdapter(Runnable task, T result) {
this.task = task;
this.result = result;
}
public T call() {
task.run();
return result;
}
}
executorService.submit()返回值是 Future<> ,运行时生成的是FutureTask的对象
3.2 使用FutureTask + Runnable 实现等待多个线程,并获取线程返回值
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
log.info(" ");
}
};
// 可以使用链表优化,下一个例子优化
Stack<Future> stack = new Stack<>();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
Future<String> result = executorService.submit(runnable, "this result only instanceof String");
stack.push(result);
}
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
String result = (String) stack.pop().get();
sb.append(result);
}
log.info(sb.toString());
log.info("main thread is done");
executorService.shutdown();
}
- 缺陷
Runnable使用executorService.sumbit() 需要指定一个字符串类型的返回值
Runnable只能处理String类型的返回值,并且是统一处理,所有线程的返回值都在线程池接收时写死
需要用Callable 来解决这个返回值扩展的问题
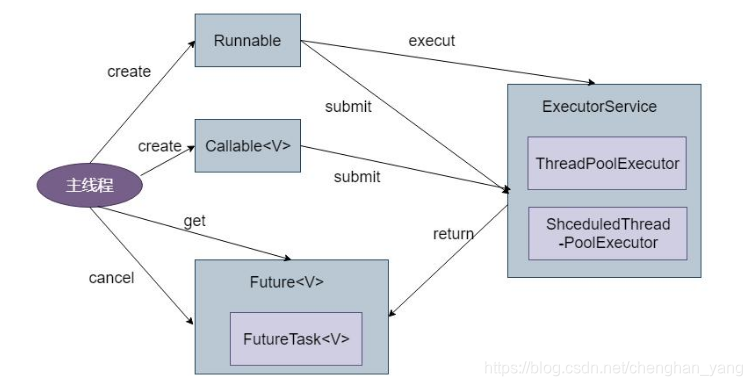
FutureTask.get() 阻塞得等待目标线程拿到返回值,拿到返回值的同时,线程执行完毕
3.3 使用FutureTask + Callable实现等待多个线程,并获取线程返回值
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
Callable<String> callable = new Callable<String>() {
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
log.info("callable is executing");
return "result N ";
}
};
LinkedList<Future> list = new LinkedList<>();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
Future<String> result = executorService.submit(callable);
list.addLast(result);
}
while (list.size() != 0) {
String o = (String) list.removeFirst().get();
sb.append(o);
}
log.info("result :{}", sb);
log.info("main thread is done");
executorService.shutdown();
}



























 1018
1018

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








