剑指–二叉树的镜像
1,题目:

2,思路:
方法一:递归:
递归解析:
- 1.终止条件: 当节点 root 为空时(即越过叶节点),则返回 null ;
- 2.开启递归 右子节点 mirrorTree(root.right) ,并将返回值作为 root 的 左子节点 。
- 3.开启递归 左子节点 mirrorTree(root.left) ,并将返回值作为 root 的 右子节点 。
- 4.返回值: 返回当前节点 root;
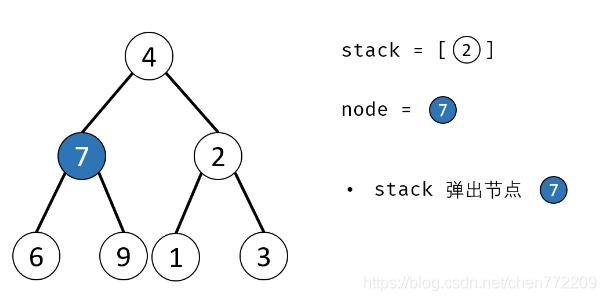
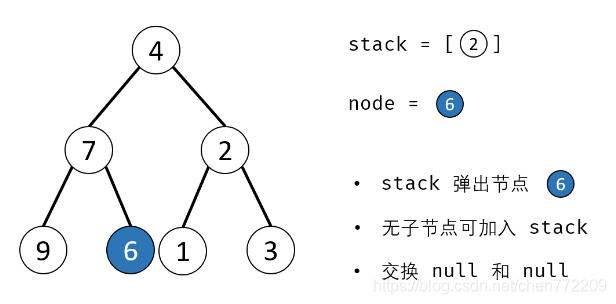
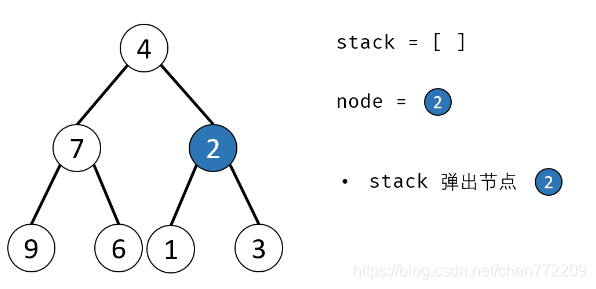
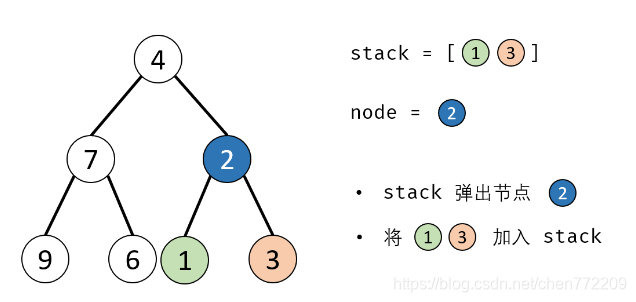
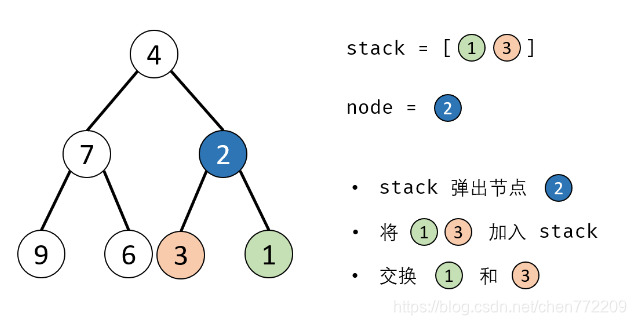
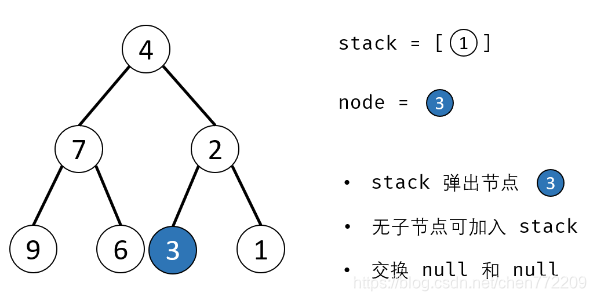
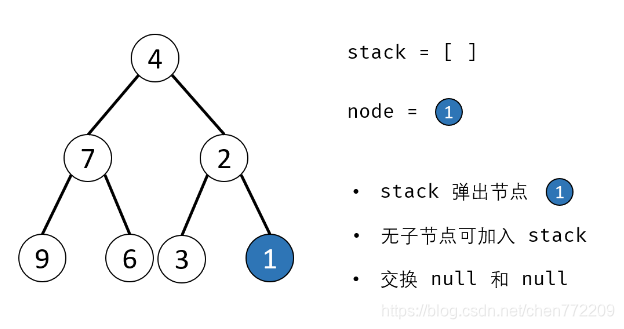
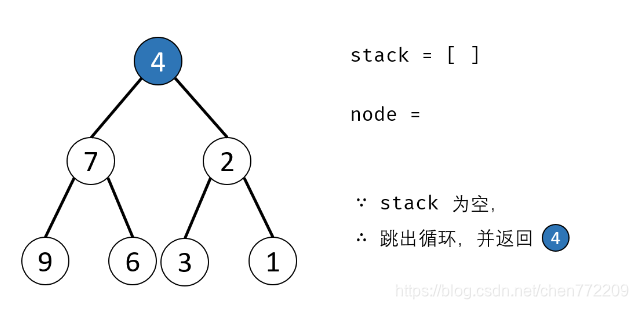
方法二:辅助栈(或队列)
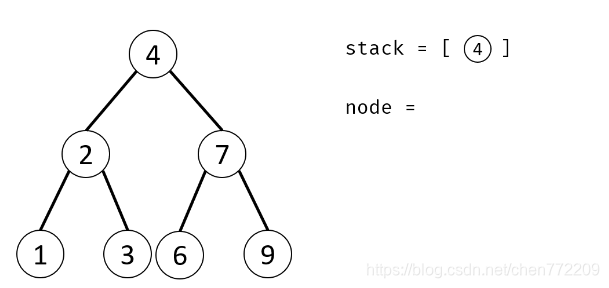
算法流程:
- 1.特例处理: 当 root 为空时,直接返回 null ;
- 2.初始化: 栈(或队列),本文用栈,并加入根节点 root 。
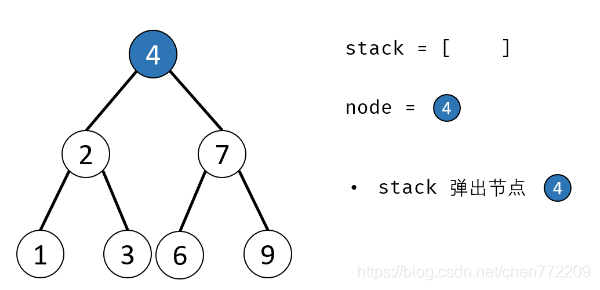
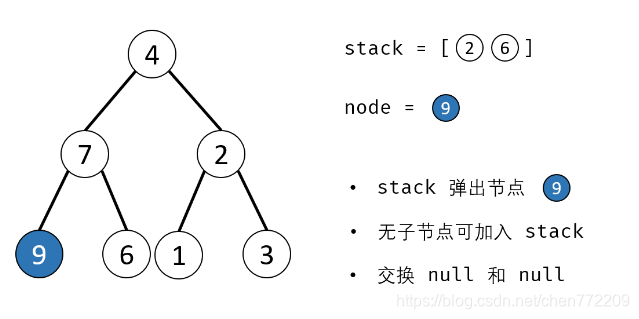
- 3.循环交换: 当栈 stack 为空时跳出;
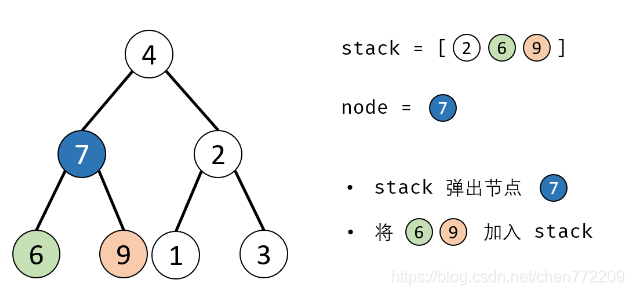
- 4.出栈: 记为 node ;
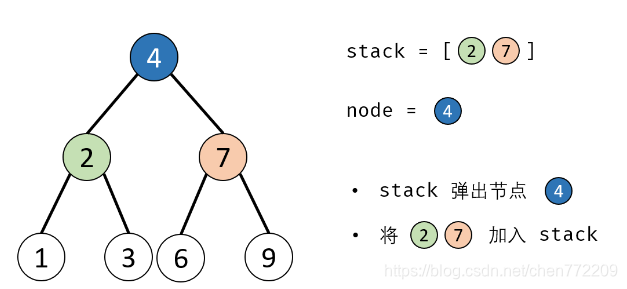
- 5.添加子节点: 将 node 左和右子节点入栈;
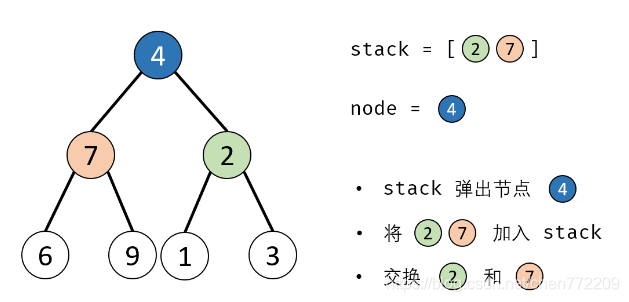
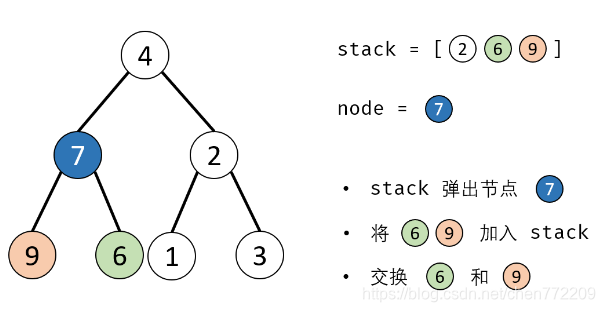
- 6.交换: 交换 node的左 / 右子节点。
- 7.返回值: 返回根节点 root。
下面是对应的图解:
3,代码:
方法一:递归:
class Solution {
public TreeNode mirrorTree(TreeNode root) {
//递归的方法
/*
递归解析:
1.终止条件: 当节点 root 为空时(即越过叶节点),则返回 null ;
2.递推工作:
3.开启递归 右子节点 mirrorTree(root.right) ,并将返回值作为 root 的 左子节点 。
4.开启递归 左子节点 mirrorTree(root.left) ,并将返回值作为 root 的 右子节点 。
5.返回值: 返回当前节点 root;
*/
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
TreeNode leftRoot = mirrorTree(root.right);
TreeNode rightRoot = mirrorTree(root.left);
root.left = leftRoot;
root.right = rightRoot;
return root;
}
}
方法二:辅助栈(或队列)
class Solution {
public TreeNode mirrorTree(TreeNode root) {
//方法二:辅助栈(或队列)
/*
算法流程:
1.特例处理: 当 root 为空时,直接返回 null ;
2.初始化: 栈(或队列),本文用栈,并加入根节点 root 。
3.循环交换: 当栈 stack 为空时跳出;
4.出栈: 记为 node ;
5.添加子节点: 将 node 左和右子节点入栈;
6.交换: 交换 node的左 / 右子节点。
7.返回值: 返回根节点 root。
*/
if(root == null) return null;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>() {{ add(root); }};
while(!stack.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
if(node.left != null) stack.add(node.left);
if(node.right != null) stack.add(node.right);
TreeNode tmp = node.left;
node.left = node.right;
node.right = tmp;
}
return root;
}
}






















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








