
✅博主简介:本人擅长建模仿真、数据分析、论文写作与指导,项目与课题经验交流。项目合作可私信或扫描文章底部二维码。
1)易腐产品多工厂生产与配送集成优化建模和算法设计
- 随着物流发展和人们生活水平提高,易腐产品需求量增加,对新鲜度要求也更高。由于易腐产品易变质、难储存,生产与配送环节紧密联系,给企业经营决策带来困难。现有的易腐产品生产与配送集成优化研究存在价值损耗常以批次计算、多工厂集成优化研究少等问题。
- 以强时效易腐产品为主体,综合考虑保鲜期和价值损耗,保障产品新鲜度,对生产与配送环节进行集成优化。研究多工厂协同生产情形下的生产与配送集成优化,对离散生产和多回程多车辆配送进行集成,考虑车辆启用成本、行驶成本和价值损耗,以多个工厂的集成成本之和最小为目标建立非线性混合整数规划模型。
- 运用双层优化思想设计包含粒子群和遗传算法的双层启发式算法。第一层使用粒子群算法求解订单在工厂间的分配问题,通过不断调整粒子的位置和速度,寻找最优的订单分配方案,使得各个工厂的生产任务更加合理。第二层采用基于贪婪策略的遗传算法求解每个工厂的生产与配送集成优化,遗传算法通过模拟生物进化过程,不断优化生产与配送的具体方案,贪婪策略则有助于在局部范围内快速找到较好的解决方案,提高算法的效率。
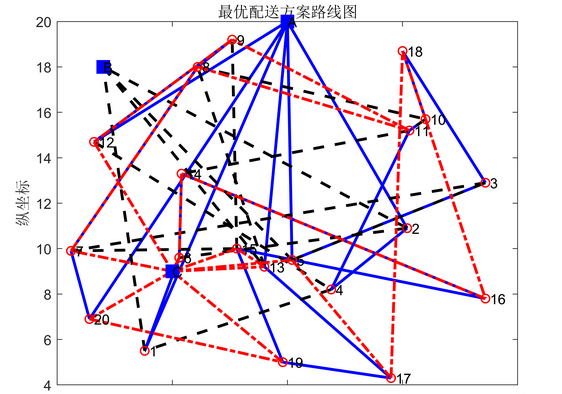
(2)易腐产品多工厂生产与配送集成优化算例分析
- 利用 Gurobi 求解器和设计的双层启发式算法求解小规模算例并进行比较,评估易腐产品多工厂集成优化模型和双层启发式算法的性能。通过对比两种方法的求解结果,可以了解模型的准确性和算法的有效性。
- 借鉴 Solomon 标准测试算例构造大规模问题算例,对不同订单规模问题进行求解并分析结果。研究不同订单规模下的生产与配送方案,了解模型在不同情况下的适用性和稳定性。同时研究工厂数量对集成成本的影响,分析多工厂生产模式下,工厂数量的变化对总成本的影响规律,为企业的生产决策提供参考。
- 通过仿真实验证明构建的模型能够求解易腐产品的订单分配和集成优化问题,同时设计的双层启发式算法具有良好的性能。对不同规模问题的求解结果表明,易腐企业采用多工厂生产不仅能接收更多订单,服务更多客户,还能降低每个工厂的集成成本,提高企业的经济效益。这说明多工厂生产与配送集成优化策略对于易腐产品企业具有重要的实际应用价值。
% 假设工厂数量
numFactories = 5;
% 假设车辆数量
numVehicles = 10;
% 假设订单数量
numOrders = 20;
% 随机生成工厂生产能力
factoryCapacity = rand(numFactories,1)*100;
% 随机生成订单需求
orderDemand = rand(numOrders,1)*50;
% 随机生成车辆启用成本
vehicleStartupCost = rand(numVehicles,1)*100;
% 随机生成车辆行驶成本系数
vehicleTravelCostCoeff = rand(1)*10;
% 随机生成价值损耗系数
valueDecayCoeff = rand(1)*0.1;
% 随机生成工厂与订单之间的距离矩阵
distanceMatrix = rand(numFactories,numOrders)*100;
% 计算总成本函数
costFunction = @(solution) calculateTotalCost(solution,factoryCapacity,orderDemand,vehicleStartupCost,vehicleTravelCostCoeff,valueDecayCoeff,distanceMatrix);
% 粒子群算法参数设置
numParticles = 50;
numIterationsPSO = 100;
inertiaWeight = 0.5;
c1 = 1;
c2 = 1;
% 初始化粒子群
particles = zeros(numParticles,numFactories*numOrders);
velocities = zeros(numParticles,numFactories*numOrders);
pBest = particles;
pBestCost = inf(numParticles,1);
for i = 1:numParticles
particles(i,:) = randperm(numFactories*numOrders);
pBestCost(i) = costFunction(particles(i,:));
end
gBest = particles(find(min(pBestCost),1),:);
gBestCost = min(pBestCost);
% 粒子群算法迭代过程
for iteration = 1:numIterationsPSO
for i = 1:numParticles
% 更新速度
velocities(i,:) = inertiaWeight*velocities(i,:) + c1*rand(1)*(pBest(i,:)-particles(i,:)) + c2*rand(1)*(gBest-particles(i,:));
% 更新位置
particles(i,:) = particles(i,:) + velocities(i,:);
particles(i,:) = mod(particles(i,:),numFactories*numOrders);
% 计算适应度
currentCost = costFunction(particles(i,:));
if currentCost < pBestCost(i)
pBest(i,:) = particles(i,:);
pBestCost(i) = currentCost;
end
if currentCost < gBestCost
gBest = particles(i,:);
gBestCost = currentCost;
end
end
end
% 将粒子群算法得到的订单分配结果传递给遗传算法
orderAllocation = reshape(gBest,numOrders,numFactories);
% 遗传算法参数设置
populationSize = 50;
numGenerationsGA = 100;
mutationRate = 0.1;
% 初始化遗传算法种群
population = zeros(populationSize,numOrders*numFactories);
for i = 1:populationSize
for j = 1:numFactories
factoryOrders = find(orderAllocation(:,j)>0);
population(i,(j-1)*numOrders+1:j*numOrders) = factoryOrders(randperm(numel(factoryOrders)));
end
end
% 遗传算法迭代过程
for generation = 1:numGenerationsGA
% 计算适应度
fitness = zeros(populationSize,1);
for i = 1:populationSize
fitness(i) = calculateFactoryCost(population(i,:),factoryCapacity,orderDemand,vehicleStartupCost,vehicleTravelCostCoeff,valueDecayCoeff,distanceMatrix);
end
% 选择操作
selectedIndices = tournamentSelection(fitness,populationSize);
selectedPopulation = population(selectedIndices,:);
% 交叉操作
newPopulation = crossover(selectedPopulation);
% 变异操作
for i = 1:size(newPopulation,1)
if rand() < mutationRate
newPopulation(i,:) = mutate(newPopulation(i,:));
end
end
% 更新种群
population = newPopulation;
end
% 选择最优解
[~,bestIndex] = min(fitness);
bestSolution = population(bestIndex,:);
% 显示最优解
disp('最优订单分配和生产配送方案:');
disp(bestSolution);
% 计算总成本函数
function totalCost = calculateTotalCost(solution,factoryCapacity,orderDemand,vehicleStartupCost,vehicleTravelCostCoeff,valueDecayCoeff,distanceMatrix)
numFactories = size(factoryCapacity,1);
numOrders = size(orderDemand,1);
orderAllocation = reshape(solution,numOrders,numFactories);
totalCost = 0;
for i = 1:numFactories
factoryOrders = find(orderAllocation(:,i)>0);
factoryCost = calculateFactoryCost(solution((i-1)*numOrders+1:i*numOrders),factoryCapacity(i),orderDemand(factoryOrders),vehicleStartupCost,vehicleTravelCostCoeff,valueDecayCoeff,distanceMatrix(i,factoryOrders));
totalCost = totalCost + factoryCost;
end
return totalCost;
end
% 计算单个工厂的成本函数
function factoryCost = calculateFactoryCost(factorySolution,factoryCapacity,orderDemand,vehicleStartupCost,vehicleTravelCostCoeff,valueDecayCoeff,distanceMatrix)
numOrders = length(orderDemand);
vehicleRoutes = generateVehicleRoutes(factorySolution);
factoryCost = 0;
for j = 1:length(vehicleRoutes)
routeCost = vehicleStartupCost(j) + vehicleTravelCostCoeff*sum(distanceMatrix(vehicleRoutes{j}));
for k = 1:length(vehicleRoutes{j})
orderIndex = vehicleRoutes{j}(k);
routeCost = routeCost + valueDecayCoeff*distanceMatrix(orderIndex)*orderDemand(orderIndex);
end
factoryCost = factoryCost + routeCost;
end
return factoryCost;
end
% 生成车辆路线函数
function vehicleRoutes = generateVehicleRoutes(factorySolution)
numOrders = length(factorySolution);
visitedOrders = false(numOrders,1);
vehicleRoutes = cell(1);
routeIndex = 1;
while ~all(visitedOrders)
currentRoute = [];
currentCapacity = 0;
for i = 1:numOrders
if ~visitedOrders(i) && currentCapacity + find(factorySolution==i) <= 1
currentRoute = [currentRoute,factorySolution(i)];
visitedOrders(i) = true;
currentCapacity = currentCapacity + find(factorySolution==i);
end
end
vehicleRoutes{routeIndex} = currentRoute;
routeIndex = routeIndex + 1;
end
return vehicleRoutes;
end
% 锦标赛选择函数
function selectedIndices = tournamentSelection(fitness,populationSize)
numTournaments = populationSize;
tournamentSize = 5;
selectedIndices = zeros(numTournaments,1);
for i = 1:numTournaments
tournamentIndices = randperm(populationSize,tournamentSize);
tournamentFitness = fitness(tournamentIndices);
[~,bestIndex] = min(tournamentFitness);
selectedIndices(i) = tournamentIndices(bestIndex);
end
return selectedIndices;
end
% 交叉操作函数
function newPopulation = crossover(selectedPopulation)
numParents = size(selectedPopulation,1);
newPopulation = zeros(numParents,size(selectedPopulation,2));
for i = 1:2:numParents
parent1 = selectedPopulation(i,:);
parent2 = selectedPopulation(i+1,:);
crossoverPoint = randi(size(parent1,2)-1)+1;
child1 = [parent1(1:crossoverPoint);parent2(crossoverPoint+1:end)];
child2 = [parent2(1:crossoverPoint);parent1(crossoverPoint+1:end)];
newPopulation(i,:) = child1;
newPopulation(i+1,:) = child2;
end
return newPopulation;
end
% 变异操作函数
function mutatedSolution = mutate(solution)
numOrders = length(solution);
mutationPoint1 = randi(numOrders);
mutationPoint2 = randi(numOrders);
temp = solution(mutationPoint1);
solution(mutationPoint1) = solution(mutationPoint2);
solution(mutationPoint2) = temp;
return solution;
end





















 1044
1044

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










