当我们第一次发请求,对应的会触发init、service方法,第二次发送同样的请求就只会请求service方法了,上篇我们讲了init中DispatcherServlet的各个功能组件的初始化,这篇就来讲service方法,即当用户发送Http请求到服务器时,DispatcherServlet怎么来处理。由于service方法处理过程比较长,我们本篇先大致看下整体的调用路线,具体的操作留到下篇讲解。
首先请求到Tomcat,Tomcat会根据请求路径匹配到对应的Servlet来处理,Spring MVC中将所有的请求都交给DispatcherServlet来处理了,所以当我们请求的时候,Tomcat就匹配到DispatcherServlet了,然后调用DispatcherServlet的service方法,该方法由父类HttpServlet提供,该方法主要是将ServletRequest和ServletResponse转换成HttpServletRequest与HttpServletResponse,并调用了service的重载方法service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)。
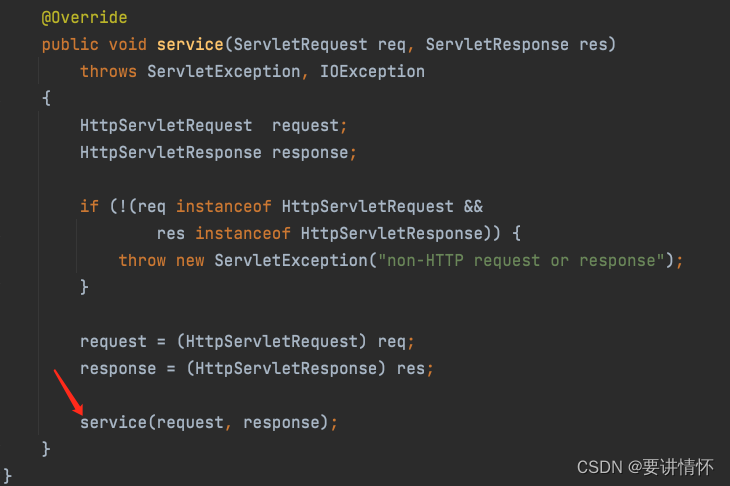
进入service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)方法,因为DispatcherServlet没有实现,所以调用的是父类FrameworkServlet的service方法。

我们主要对GET、POST等常见的请求类型进行分析,所以对于PATCH请求我们就不过多关注,有兴趣的可以自行了解,接着进入父类HttpServlet的service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)方法中:
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException {
//先获取请求类型
String method = req.getMethod();
//如果是GET请求,会去判断下浏览器是否
//客户端在请求一个文件的时候,发现自己缓存的文件有 Last Modified ,
//那么在请求中会包含 If Modified Since ,这个时间就是缓存文件的 Last Modified 。
//因此,如果请求中包含 If Modified Since,就说明已经有缓存在客户端。
//服务端只要判断这个时间和当前请求的文件的修改时间就可以确定是返回 304 还是 200
//返回304就是自从上次请求后,请求的网页未修改过。服务器返回此响应时,不会返回网页内容。
//节省带宽和开销。
//参考文章:https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/gwdgwd123/article/details/82384716
if (method.equals(METHOD_GET)) {
long lastModified = getLastModified(req);
if (lastModified == -1) {
// 如果servlet不支持 if-modified-since,直接调用doGet
doGet(req, resp);
} else {
//如果servlet支持if-modified-since,就从header中获取时间,判断
//时间最后一次修改时间是否大于当前请求时间,则直接调用doGet,小于的话就
//直接设置响应为304返回给浏览器
long ifModifiedSince;
try {
ifModifiedSince = req.getDateHeader(HEADER_IFMODSINCE);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException iae) {
// Invalid date header - proceed as if none was set
ifModifiedSince = -1;
}
if (ifModifiedSince < (lastModified / 1000 * 1000)) {
// If the servlet mod time is later, call doGet()
// Round down to the nearest second for a proper compare
// A ifModifiedSince of -1 will always be less
maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified);
doGet(req, resp);
} else {
resp.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_MODIFIED);
}
}
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_HEAD)) {
//如果客户端只想获取响应的headers内容,如Content-Type、Content-Length
//使用HEAD请求,我们平常一般不关注
long lastModified = getLastModified(req);
maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified);
doHead(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_POST)) {
//如果是POST请求
doPost(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_PUT)) {
//如果是PUT请求
doPut(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_DELETE)) {
//如果是DELETE请求
doDelete(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_OPTIONS)) {
//如果是OPTIONS请求
doOptions(req,resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_TRACE)) {
//如果是TRACE请求
doTrace(req,resp);
} else {
//返回异常信息,标志无法处理该请求
String errMsg = lStrings.getString("http.method_not_implemented");
Object[] errArgs = new Object[1];
errArgs[0] = method;
errMsg = MessageFormat.format(errMsg, errArgs);
resp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_IMPLEMENTED, errMsg);
}
}我们直接进入doGet方法,因为DispatcherServlet没有实现,所以调用的是父类FrameworkServlet的doGet方法
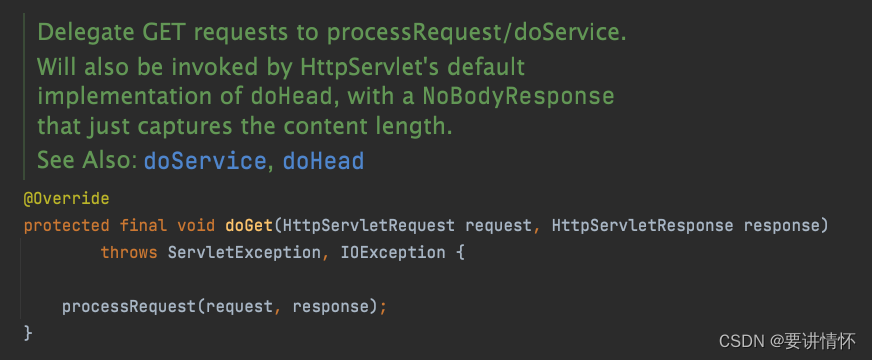
可以看到FrameworkServlet的doGet直接调用了processRequest
protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Throwable failureCause = null;
//在该方法处理中需要重新设置LocalContext属性,所以先拿到,并在方法执行完后在finally重新set进去
//恢复到之前的配置,不影响当前请求处理后LocalContext属性值
LocaleContext previousLocaleContext = LocaleContextHolder.getLocaleContext();
LocaleContext localeContext = buildLocaleContext(request);
//同LocaleContext处理方式一样
RequestAttributes previousAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = buildRequestAttributes(request, response, previousAttributes);
//异步处理,主要用作SPI,通常不被应用程序类直接使用
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptor(FrameworkServlet.class.getName(), new RequestBindingInterceptor());
//将当前的LocaleContext和RequestAttributes绑定到当前线程里,当请求方法执行完后会
//在finally中将线程的这两个属性重新初始化到之前的previousLocaleContext和previousAttributes
initContextHolders(request, localeContext, requestAttributes);
try {
//交给doService处理
doService(request, response);
}
catch (ServletException | IOException ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw new NestedServletException("Request processing failed", ex);
}
finally {
resetContextHolders(request, previousLocaleContext, previousAttributes);
if (requestAttributes != null) {
requestAttributes.requestCompleted();
}
logResult(request, response, failureCause, asyncManager);
publishRequestHandledEvent(request, response, startTime, failureCause);
}
}进入doService方法中发现没有看到我们想要的核心逻辑,而是调用doDispatch方法处理
@Override
protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
logRequest(request);
//同processRequest方法中的LocaleContext处理一样,先把原始的request属性存起来,等请求处理完毕之后
//再在finally方法中恢复,不影响后续的流程调用
Map<String, Object> attributesSnapshot = null;
if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) {
attributesSnapshot = new HashMap<>();
Enumeration<?> attrNames = request.getAttributeNames();
while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement();
if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PREFIX)) {
attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName));
}
}
}
// 设置相关的处理器属性
request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext());
request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource());
if (this.flashMapManager != null) {
FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response);
if (inputFlashMap != null) {
request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap));
}
request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap());
request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager);
}
try {
//分发请求
doDispatch(request, response);
}
finally {
if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Restore the original attribute snapshot, in case of an include.
if (attributesSnapshot != null) {
restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot);
}
}
}
}继续进入doDispatch方法中一探究竟
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
//检查是否是MultipartContent的请求,如果是的话就会转换为MultipartHttpServletRequest
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// Determine handler for the current request.
//为本次request请求寻找一个具体的Handler,并封装成一个执行器链
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// 为当前的handler寻找一个具体的HandlerAdapter,因为HandlerMapping有多个实现类
// 需要适配器来提供一个统一供外部调用的方法入口
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
//如果支持last-modified,则处理
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
//拦截器前置处理
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// 真正调用Controller的地方
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
//视图转换
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
//拦截器后置处理
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well,
// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios.
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
//处理程序调用的结果,即ModelAndView或要解析为ModelAndView的异常
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
} 深入理解SpringMVCDispatcherServlet的service方法处理流程
深入理解SpringMVCDispatcherServlet的service方法处理流程





 当用户发送HTTP请求到服务器时,Tomcat会匹配到DispatcherServlet并调用其service方法。这个方法首先由HttpServlet提供,主要负责将请求和响应转化为标准HTTP对象。对于GET请求,它会检查IfModifiedSince头来决定是否返回304状态码。接着,请求会被转发到doGet方法,进一步处理。在doService方法中,DispatcherServlet调用doDispatch来找到合适的处理器和适配器来执行实际的业务逻辑。
当用户发送HTTP请求到服务器时,Tomcat会匹配到DispatcherServlet并调用其service方法。这个方法首先由HttpServlet提供,主要负责将请求和响应转化为标准HTTP对象。对于GET请求,它会检查IfModifiedSince头来决定是否返回304状态码。接着,请求会被转发到doGet方法,进一步处理。在doService方法中,DispatcherServlet调用doDispatch来找到合适的处理器和适配器来执行实际的业务逻辑。
















 3475
3475

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








