README
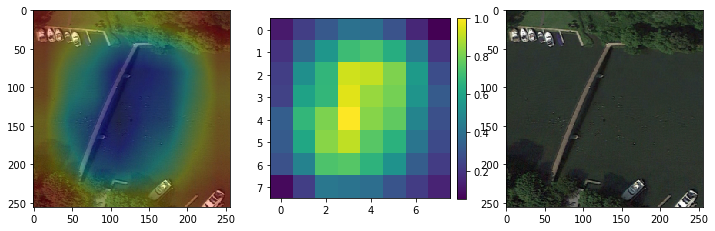
对网络的注意力可视化,可以很快的看出网络存在的问题以及可以改进的空间
refer: https://medium.com/@stepanulyanin/implementing-grad-cam-in-pytorch-ea0937c31e82
attention可视化的思路:
- 通过hook获得特征层的grad,维度是(batch, 2048, 8, 8)
- 然后对每个channel的grad求平均,维度是(batch, 2048)
- 计算前向传播得到的特征图,维度是(batch, 2048, 8, 8)
- 将第三步得到的特征图和第二步得到的平均后的grad做个加权求和,维度是(batch, 2048, 8, 8)
- 将第四步加权求和后的(batch, 2048, 8, 8)按channel做平均,维度是(batch, 8, 8),然后缩小到[0,1] 就是heatmap
源代码
https://github.com/CarryHJR/remote-sense-quickstart
模型部分承接scene-classification-quickstart.ipynb
定义用于计算卷积的模块
net_single = list(net.children())[0]
from torchvision import models
class ResNetCam(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(ResNetCam, self).__init__()
# get the pretrained VGG19 network
self.resnet = net_single
# disect the network to access its last convolutional layer
self.features_conv = nn.Sequential(*list(self.resnet.children())[:8])
# get the max pool of the features stem
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1))
# get the classifier of the vgg19
self.fc = self.resnet.fc
# placeholder for the gradients
self.gradients = None
# hook for the gradients of the activations
def activations_hook(self, grad):
self.gradients = grad
def forward(self, x):
x = self.features_conv(x)
print(x.shape)
# register the hook
h = x.register_hook(self.activations_hook)
# apply the remaining pooling
x = self.avgpool(x)
x = x.view((1, -1))
x = self.fc(x)
return x
# method for the gradient extraction
def get_activations_gradient(self):
return self.gradients
# method for the activation exctraction
def get_activations(self, x):
return self.features_conv(x)
resNetCam = ResNetCam()
_ = resNetCam.eval()
attention可视化
img, _ = next(dataiter_val)
# get the most likely prediction of the model
pred = resNetCam(img.cuda())
index = pred.argmax(dim=1).item()
pred[:, index].backward()
# 通过hook获得特征层的grad,维度是(batch, 2048, 8, 8)
gradients = resNetCam.get_activations_gradient()
# 然后对每个channel的grad求平均,维度是(batch, 2048)
pooled_gradients = torch.mean(gradients, dim=[0, 2, 3])
# 计算前向传播得到的特征图,维度是(batch, 2048, 8, 8)
activations = resNetCam.get_activations(img.cuda()).detach()
# 将第三步得到的特征图和第二步得到的平均后的grad做个加权求和,维度是(batch, 2048, 8, 8)
for i in range(activations.shape[1]):
activations[:, i, :, :] *= pooled_gradients[i]
# 将第四步加权求和后的(batch, 2048, 8, 8)按channel做平均,维度是(batch, 8, 8),然后缩小到[0,1] 就是heatmap
heatmap = torch.mean(activations, dim=1).squeeze()
# relu on top of the heatmap
# expression (2) in https://arxiv.org/pdf/1610.02391.pdf
heatmap = heatmap.cpu()
heatmap = np.maximum(heatmap, 0)
# normalize the heatmap
heatmap /= torch.max(heatmap)
image = img[0].numpy().transpose((1, 2, 0))
image = np.array(std) * image + np.array(mean)
image = np.clip(image, 0, 1)
image = np.uint8(255*image)
import cv2
heatmap_resize = cv2.resize(heatmap.numpy(), (image.shape[1], image.shape[0]))
heatmap_resize = np.uint8(255 * heatmap_resize)
heatmap_resize = cv2.applyColorMap(heatmap_resize, cv2.COLORMAP_JET)
superimposed_img = heatmap_resize * 0.4 + image
superimposed_img = superimposed_img / np.max(superimposed_img)
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1,3,figsize=(12,4))
axes[0].imshow(superimposed_img)
tmp = heatmap.squeeze().numpy()
im = axes[1].imshow(tmp, interpolation='nearest')
axes[1].figure.colorbar(im, ax=axes[1], fraction=0.046, pad=0.04)
axes[2].imshow(image)
print(idx_to_class[index])









 本文介绍了一种名为Grad-CAM的技术,用于可视化深度学习模型的注意力机制。通过计算特征图与梯度的加权平均,Grad-CAM能生成热力图,显示模型在进行预测时关注的图像区域。此方法有助于理解模型决策过程,识别潜在问题并提供改进方向。
本文介绍了一种名为Grad-CAM的技术,用于可视化深度学习模型的注意力机制。通过计算特征图与梯度的加权平均,Grad-CAM能生成热力图,显示模型在进行预测时关注的图像区域。此方法有助于理解模型决策过程,识别潜在问题并提供改进方向。
















 5万+
5万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








