一、ResNet网络简介
ResNet网络是在2015年由微软实验室中的何凯明等几位大神提出,是在CVPR 2016发表的一种影响深远的网络模型。在ImageNet的分类比赛上将网络深度直接提高到152层,前一年夺冠的VGG只有19层。斩获当年ImageNet竞赛中分类任务第一名,目标检测第一名。获得coco数据集中目标检测第一名,图像分割第一名,可以说ResNet的出现对深度神经网络来说具有重大的历史意义。原论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1512.03385
ResNet在cnn图像方面有着非常突出的表现,它利用 shortcut 短路连接,解决了深度网络中模型退化的问题。相比普通网络每两层/三层之间增加了短路机制,通过残差学习使深层的网络发挥出作用。
二、3D-ResNet网络简介
3D-ResNet是一种融合三维卷积(3D CNN)与残差学习(ResNet)的深度学习架构,专为处理时序空间数据(如视频、医学影像序列)设计,由日本产业技术综合研究所的Kensho Hara等人于CVPR 2018提出。
三、ResNet网络中的亮点
1)超深的网络结构(超过1000层);
2)提出Residual(残差结)模块;
3) 使用Batch Normalization加速训练。
采用Residual(残差结构)
在ResNet提出之前,所有的神经网络都是通过卷积层和池化层的单纯叠加组成的。人们普遍认为卷积层和池化层的层数越多,获取到的图片特征信息越全,学习效果也就越好。但是在实际的实验中发现,随着卷积层和池化层的叠加,不但没有出现学习效果越来越好的情况,反而出现梯度消失和梯度爆炸、以及退化问题。
梯度消失和梯度爆炸
梯度消失:若每一层的误差梯度小于1,反向传播时,网络越深,梯度越趋进与0
梯度爆炸:若每一层的误差梯度大于1,反向传播时,网络越深,梯度越来越大
退化问题
随着层数的增加,发现预测的效果反而越来越差。如下图(该图截取自原论文)
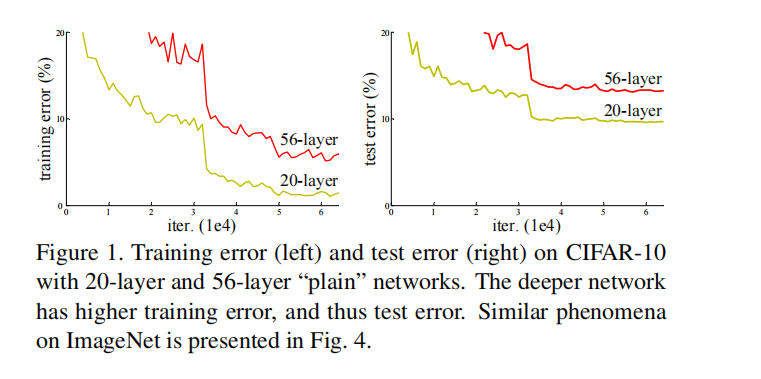
解决方法
ResNet论文提出通过数据的预处理以及在网络中使用 BN(Batch Normalization)层来解决。同时为了解决深层网络中的退化问题可以人为让神经网络某些层跳过下一层神经元的连接,隔层相连,弱化每层之间的强联系。这种神经网络被称为残差网络 (ResNets)。
ResNet论文提出了 residual结构(残差结构)来减轻退化问题,下图是使用residual结构的卷积网络,可以看到随着网络的不断加深,效果并没有变差,而是变的更好了。(虚线是train error,实线是test error)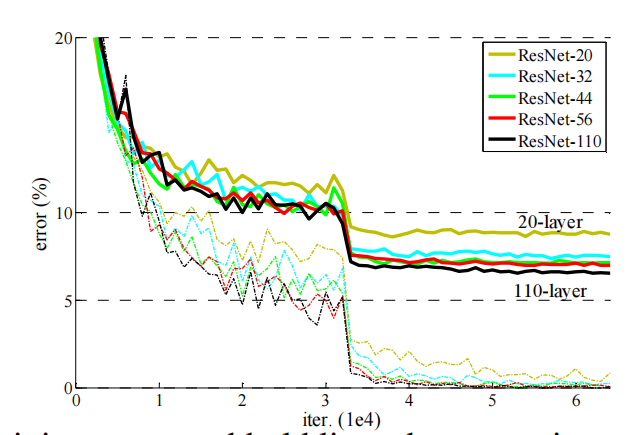
四、残差学习
残差及就是观测值与估计值之间的差。传统的CNN网络是一个串行任务。与传统的CNN网络相比ResNet网络增加了短路链接,如下图所示:
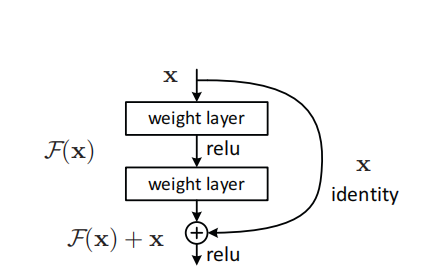
这就是残差块的关键点,添加了一个短路连接到第二层激活函数之前。那么激活函数的输入就由原来的输出H(x)=F(x)变为了H(x)=F(x)+x。这种输出称之为恒等映射。通过这种操作,使得网络在最差的情况下也能获取和输入一样的输出,使得网络不会出现退化问题。
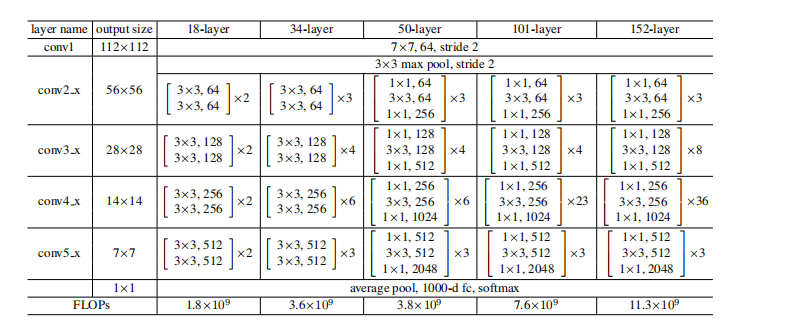
下图是论文给出的不同ResNet网络的层数需求:
五、ResNet代码示例:
model.py
#model.py
import torch.nn as nn
import torch
class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
expansion = 1
def __init__(self, in_channel, out_channel, stride=1, downsample=None, **kwargs):
super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channel, out_channels=out_channel,
kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channel, out_channels=out_channel,
kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel)
self.downsample = downsample
def forward(self, x):
identity = x
if self.downsample is not None:
identity = self.downsample(x)
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out += identity
out = self.relu(out)
return out
class Bottleneck(nn.Module):
expansion = 4
def __init__(self, in_channel, out_channel, stride=1, downsample=None,
groups=1, width_per_group=64):
super(Bottleneck, self).__init__()
width = int(out_channel * (width_per_group / 64.)) * groups
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channel, out_channels=width,
kernel_size=1, stride=1, bias=False) # squeeze channels
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(width)
# -----------------------------------------
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=width, out_channels=width, groups=groups,
kernel_size=3, stride=stride, bias=False, padding=1)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(width)
# -----------------------------------------
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=width, out_channels=out_channel*self.expansion,
kernel_size=1, stride=1, bias=False) # unsqueeze channels
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel*self.expansion)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.downsample = downsample
def forward(self, x):
identity = x
if self.downsample is not None:
identity = self.downsample(x)
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv3(out)
out = self.bn3(out)
out += identity
out = self.relu(out)
return out
class ResNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
block,
blocks_num,
num_classes=1000,
include_top=True,
groups=1,
width_per_group=64):
super(ResNet, self).__init__()
self.include_top = include_top
self.in_channel = 64
self.groups = groups
self.width_per_group = width_per_group
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, self.in_channel, kernel_size=7, stride=2,
padding=3, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(self.in_channel)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 64, blocks_num[0])
self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 128, blocks_num[1], stride=2)
self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 256, blocks_num[2], stride=2)
self.layer4 = self._make_layer(block, 512, blocks_num[3], stride=2)
if self.include_top:
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1)) # output size = (1, 1)
self.fc = nn.Linear(512 * block.expansion, num_classes)
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
def _make_layer(self, block, channel, block_num, stride=1):
downsample = None
if stride != 1 or self.in_channel != channel * block.expansion:
downsample = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(self.in_channel, channel * block.expansion, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(channel * block.expansion))
layers = []
layers.append(block(self.in_channel,
channel,
downsample=downsample,
stride=stride,
groups=self.groups,
width_per_group=self.width_per_group))
self.in_channel = channel * block.expansion
for _ in range(1, block_num):
layers.append(block(self.in_channel,
channel,
groups=self.groups,
width_per_group=self.width_per_group))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.maxpool(x)
x = self.layer1(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
x = self.layer3(x)
x = self.layer4(x)
if self.include_top:
x = self.avgpool(x)
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
x = self.fc(x)
return x
def resnet34(num_classes=1000, include_top=True):
# https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet34-333f7ec4.pth
return ResNet(BasicBlock, [3, 4, 6, 3], num_classes=num_classes, include_top=include_top)
def resnet50(num_classes=1000, include_top=True):
# https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet50-19c8e357.pth
return ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 6, 3], num_classes=num_classes, include_top=include_top)
def resnet101(num_classes=1000, include_top=True):
# https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet101-5d3b4d8f.pth
return ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 23, 3], num_classes=num_classes, include_top=include_top)
def resnext50_32x4d(num_classes=1000, include_top=True):
# https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnext50_32x4d-7cdf4587.pth
groups = 32
width_per_group = 4
return ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 6, 3],
num_classes=num_classes,
include_top=include_top,
groups=groups,
width_per_group=width_per_group)
def resnext101_32x8d(num_classes=1000, include_top=True):
# https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnext101_32x8d-8ba56ff5.pth
groups = 32
width_per_group = 8
return ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 23, 3],
num_classes=num_classes,
include_top=include_top,
groups=groups,
width_per_group=width_per_group)
train.py
#train.py
import sys
import json
from tqdm import tqdm
from pathlib import Path
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
from torchvision import datasets, transforms
from model import resnet50
class Config:
def __init__(self):
# 超参数
self.num_classes = 10
self.batch_size = 4
self.epochs = 300
self.lr = 1e-4
self.input_size = 128
self.device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
# 简洁路径配置
self.train_dir = r"F:\Window\Master's degree\ResNet_Moment\ResNet\datas\Plant_disease_and_insect\train"
self.val_dir = r"F:\Window\Master's degree\ResNet_Moment\ResNet\datas\Plant_disease_and_insect\val"
self.weights_path = "./runs/ResNet/best_model_plant_50.pth"
self.class_indices_path = "./plant_class_indices.json"
self.num_workers = 0
def get_data_transforms(input_size):
return {
"train": transforms.Compose([
transforms.RandomResizedCrop(input_size),
transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
]),
"val": transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize(input_size),
transforms.CenterCrop(input_size),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
])
}
def prepare_dataloaders(cfg, data_transform):
assert Path(cfg.train_dir).exists(), f"Train path not found: {cfg.train_dir}"
assert Path(cfg.val_dir).exists(), f"Val path not found: {cfg.val_dir}"
train_dataset = datasets.ImageFolder(cfg.train_dir, transform=data_transform["train"])
val_dataset = datasets.ImageFolder(cfg.val_dir, transform=data_transform["val"])
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
train_dataset, batch_size=cfg.batch_size, shuffle=True, num_workers=cfg.num_workers
)
val_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
val_dataset, batch_size=cfg.batch_size, shuffle=False, num_workers=cfg.num_workers
)
# 保存类别索引映射
class_dict = {v: k for k, v in train_dataset.class_to_idx.items()}
with open(cfg.class_indices_path, 'w') as f:
json.dump(class_dict, f, indent=4)
print(f"[INFO] Loaded {len(train_dataset)} training and {len(val_dataset)} validation samples.")
return train_loader, val_loader
def create_model(cfg):
model = resnet50()
model.fc = nn.Linear(model.fc.in_features, cfg.num_classes)
return model.to(cfg.device)
def train_and_validate(model, train_loader, val_loader, cfg):
loss_fn = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=cfg.lr)
best_val_acc = 0.0
for epoch in range(cfg.epochs):
# === 训练 ===
model.train()
running_loss = 0.0
train_bar = tqdm(train_loader, file=sys.stdout, desc=f"[Train Epoch {epoch+1}/{cfg.epochs}]")
for images, labels in train_bar:
images, labels = images.to(cfg.device), labels.to(cfg.device)
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = model(images)
loss = loss_fn(outputs, labels)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
running_loss += loss.item()
train_bar.set_postfix(loss=loss.item())
avg_train_loss = running_loss / len(train_loader)
# === 验证 ===
model.eval()
correct = 0
with torch.no_grad():
val_bar = tqdm(val_loader, file=sys.stdout, desc=f"[Val Epoch {epoch+1}/{cfg.epochs}]")
for images, labels in val_bar:
images, labels = images.to(cfg.device), labels.to(cfg.device)
outputs = model(images)
preds = torch.argmax(outputs, dim=1)
correct += torch.eq(preds, labels).sum().item()
val_acc = correct / len(val_loader.dataset)
print(f"[Epoch {epoch+1}] Loss: {avg_train_loss:.4f} | Val Acc: {val_acc*100:.2f}%")
if val_acc > best_val_acc:
best_val_acc = val_acc
torch.save(model.state_dict(), cfg.weights_path)
print(f"[INFO] Saved new best model: {best_val_acc*100:.2f}%")
def main():
cfg = Config()
print(f"[INFO] Using device: {cfg.device}")
data_transform = get_data_transforms(cfg.input_size)
train_loader, val_loader = prepare_dataloaders(cfg, data_transform)
model = create_model(cfg)
train_and_validate(model, train_loader, val_loader, cfg)
print("[INFO]Training Complete!")
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
predict.py
#predict.py
import os
import json
import csv
from pathlib import Path
import torch
from PIL import Image
from torchvision import transforms
from model import resnet50
class Config:
def __init__(self):
self.device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
self.input_size = 128
self.weights_path = "./runs/ResNet/best_model_plant_50.pth"
self.class_indices_path = "./plant_class_indices.json"
self.data_dir = r"F:\Window\Master's degree\ResNet_Moment\ResNet\ResNet50_moment\datas\Noisy_15_plant"
self.csv_output = "predict_results_ResNet.csv"
def load_image_paths(root_dir, exts=(".jpg", ".png", ".jpeg",'.JPG')):
img_paths, true_labels = [], []
for subdir, _, files in os.walk(root_dir):
for file in files:
if file.lower().endswith(exts):
img_paths.append(os.path.join(subdir, file))
true_labels.append(os.path.basename(subdir))
return img_paths, true_labels
def get_transform(input_size):
return transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize(input_size),
transforms.CenterCrop(input_size),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
])
def load_model(cfg, num_classes):
model = resnet50(num_classes=num_classes).to(cfg.device)
assert os.path.exists(cfg.weights_path), f"Model weights not found: {cfg.weights_path}"
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(cfg.weights_path, map_location=cfg.device))
model.eval()
return model
# ---------------------------
# 主预测流程
# ---------------------------
def run_prediction():
cfg = Config()
print(f"[INFO] Using device: {cfg.device}")
# 加载类别索引
assert os.path.exists(cfg.class_indices_path), "class_indices.json not found!"
with open(cfg.class_indices_path, "r") as f:
class_indict = json.load(f)
class_name_to_index = {v: int(k) for k, v in class_indict.items()}
# 加载模型
model = load_model(cfg, num_classes=len(class_indict))
transform = get_transform(cfg.input_size)
# 加载图片路径和标签
img_paths, true_labels = load_image_paths(cfg.data_dir)
total = len(img_paths)
correct = 0
# 开始预测并保存到CSV
with open(cfg.csv_output, mode="w", newline='') as f:
writer = csv.writer(f)
writer.writerow(["ImagePath", "TrueLabel", "PredictedLabel", "Probability"])
for img_path, true_label in zip(img_paths, true_labels):
try:
img = Image.open(img_path).convert("RGB")
except Exception as e:
print(f"[WARNING] Failed to load {img_path}: {e}")
continue
img_tensor = transform(img).unsqueeze(0).to(cfg.device)
with torch.no_grad():
output = model(img_tensor)
prob = torch.softmax(output, dim=1)
pred_idx = torch.argmax(prob, dim=1).item()
pred_label = class_indict[str(pred_idx)]
confidence = prob[0][pred_idx].item()
if pred_label == true_label:
correct += 1
writer.writerow([img_path, true_label, pred_label, round(confidence, 4)])
acc = correct / total
print("[RESULT]")
print(f" Total Images: {total}")
print(f" Correct Predictions: {correct}")
print(f" Accuracy: {acc:.4f}")
print(f" Results saved to: {cfg.csv_output}")
if __name__ == '__main__':
run_prediction()
六、3DResNet示例:
3维数据集(.nii文件)简介
NIfTI格式是一种用于神经影像学数据的文件格式,最初是为神经影像学发明的。它包含两个能够将每个体素的索引(i,j,k)和它的空间位置(x,y,z)关联起来的仿射坐标。NIfTI格式具有四个维度,包括x、y、z和时间。它的体素大小和数据类型通常是以int16或double形式存储的。Extension部分可以由用户自定义数据,但通常不会被通用软件使用。NIfTI-1格式是基于ANALYZE 7.5格式发展而来的,具有一些新的特性。
nii.gz:这是NIfTI格式的一种压缩版本,通过gzip算法进行压缩,以减少文件大小和存储需求。
本示例采用ModelNet10数据集来进行实验测试。数据集链接:https://github.com/SomTambe/ModelNet10-dataset
该数据集为.off格式,本示例对其进行了对于的转换,转换代码如下:
import os
import trimesh
import numpy as np
import nibabel as nib
from tqdm import tqdm
import multiprocessing as mp
def repair_mesh(mesh):
"""修复网格问题,确保水密性"""
if not mesh.is_watertight:
# 填充孔洞
mesh.fill_holes()
# 修复法线方向
mesh.fix_normals()
return mesh
def process_file(args):
"""处理单个文件的函数,用于多进程"""
input_path, output_path, pitch = args
try:
# 加载.off文件
mesh = trimesh.load(input_path)
# 网格修复(确保水密性)
mesh = repair_mesh(mesh)
# 体素化处理
voxel_grid = mesh.voxelized(pitch=pitch)
voxel_array = voxel_grid.matrix.astype(np.uint16)
# 创建NIfTI图像
affine = np.eye(4)
nifti_img = nib.Nifti1Image(voxel_array, affine)
# 保存
nib.save(nifti_img, output_path)
return True, output_path
except Exception as e:
return False, f"{input_path}: {str(e)}"
def convert_off_to_nifti(input_folder, output_folder, pitch=1.0, num_workers=None):
if not os.path.exists(output_folder):
os.makedirs(output_folder)
print(f"✅ 创建输出文件夹: {output_folder}")
off_files = [f for f in os.listdir(input_folder) if f.lower().endswith('.off')]
print(f"🔍 找到 {len(off_files)} 个.off文件")
if not off_files:
print("⚠️ 未找到.off文件,请检查输入路径")
return
# 准备参数列表
tasks = []
for filename in off_files:
input_path = os.path.join(input_folder, filename)
output_path = os.path.join(output_folder, filename.replace('.off', '.nii'))
tasks.append((input_path, output_path, pitch))
# 设置进程数
if num_workers is None:
num_workers = mp.cpu_count()
print(f"🚀 使用 {num_workers} 个进程进行转换...")
# 使用进程池处理
results = []
with mp.Pool(num_workers) as pool:
with tqdm(total=len(tasks), desc="转换进度") as pbar:
for i, (success, msg) in enumerate(pool.imap_unordered(process_file, tasks)):
if success:
pbar.update()
results.append(True)
else:
pbar.update()
results.append(False)
print(f"\n⚠️ 转换失败: {msg}")
success_count = sum(results)
fail_count = len(off_files) - success_count
print(f"\n🎉 转换完成!成功: {success_count}, 失败: {fail_count}")
print(f"输出目录: {os.path.abspath(output_folder)}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
INPUT_FOLDER = r"F:\Window\Master's degree\Deep_learn\deep-learning-for-image-processing-master\data_set\ModelNet10_off\train\bed"
OUTPUT_FOLDER = r"F:\Window\Master's degree\Deep_learn\deep-learning-for-image-processing-master\data_set\ModelNet10_nii\train\bed"
VOXEL_SIZE = 1.0
NUM_WORKERS = 4
convert_off_to_nifti(INPUT_FOLDER, OUTPUT_FOLDER, VOXEL_SIZE, num_workers=NUM_WORKERS)model.py
import torch.nn as nn
import torch
class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
expansion = 1 #18层和34层对应的结构
def __init__(self, in_channel, out_channel, stride=1, downsample=None, **kwargs):
super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv3d(in_channels=in_channel, out_channels=out_channel,
kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm3d(out_channel)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.conv2 = nn.Conv3d(in_channels=out_channel, out_channels=out_channel,
kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm3d(out_channel)
self.downsample = downsample
#正向传播
def forward(self, x):
identity = x
if self.downsample is not None:
identity = self.downsample(x)
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out += identity
out = self.relu(out)
return out
class Bottleneck(nn.Module):
expansion = 4
def __init__(self, in_channel, out_channel, stride=1, downsample=None,
groups=1, width_per_group=64):
super(Bottleneck, self).__init__()
width = int(out_channel * (width_per_group / 64.)) * groups
self.conv1 = nn.Conv3d(in_channels=in_channel, out_channels=width,
kernel_size=1, stride=1, bias=False) # squeeze channels
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm3d(width)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv3d(in_channels=width, out_channels=width, groups=groups,
kernel_size=3, stride=stride, bias=False, padding=1)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm3d(width)
self.conv3 = nn.Conv3d(in_channels=width, out_channels=out_channel * self.expansion,
kernel_size=1, stride=1, bias=False) # unsqueeze channels
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm3d(out_channel * self.expansion)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.downsample = downsample
def forward(self, x):
identity = x
if self.downsample is not None:
identity = self.downsample(x)
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv3(out)
out = self.bn3(out)
out += identity #可以替换成对应矩的方式
out = self.relu(out)
return out
class ResNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
block,
blocks_num,
num_classes=1000, #分类的种类
include_top=True,
groups=1,
width_per_group=64,
in_channels=3):
super(ResNet, self).__init__()
self.include_top = include_top
self.in_channel = 64
self.groups = groups
self.width_per_group = width_per_group
self.conv1 = nn.Conv3d(in_channels, self.in_channel, kernel_size=7, stride=2,
padding=3, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm3d(self.in_channel)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool3d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 64, blocks_num[0])
self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 128, blocks_num[1], stride=2)
self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 256, blocks_num[2], stride=2)
self.layer4 = self._make_layer(block, 512, blocks_num[3], stride=2)
if self.include_top:
# self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1)) # output size = (1, 1)
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool3d((1, 1,1)) # output size = (1, 1,1)
self.fc = nn.Linear(512 * block.expansion, num_classes)
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv3d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
def _make_layer(self, block, channel, block_num, stride=1):
downsample = None
if stride != 1 or self.in_channel != channel * block.expansion:
downsample = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv3d(self.in_channel, channel * block.expansion, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm3d(channel * block.expansion))
layers = []
layers.append(block(self.in_channel,
channel,
downsample=downsample,
stride=stride,
groups=self.groups,
width_per_group=self.width_per_group))
self.in_channel = channel * block.expansion
for _ in range(1, block_num):
layers.append(block(self.in_channel,
channel,
groups=self.groups,
width_per_group=self.width_per_group))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.maxpool(x)
x = self.layer1(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
x = self.layer3(x)
x = self.layer4(x)
if self.include_top:
x = self.avgpool(x)
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
x = self.fc(x)
return x
# def resnet34(num_classes=1000, include_top=True):
# # https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet34-333f7ec4.pth
# return ResNet(BasicBlock, [3, 4, 6, 3], num_classes=num_classes, include_top=include_top)
def resnet34(num_classes=1000, include_top=True):
model = ResNet(BasicBlock, [3, 4, 6, 3], num_classes=num_classes, include_top=include_top)
model.conv1 = nn.Conv3d(1, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3, bias=False)
return model
def resnet50(num_classes=1000, include_top=True):
# https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet50-19c8e357.pth
return ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 6, 3], num_classes=num_classes, include_top=include_top)
def resnet101(num_classes=1000, include_top=True):
# https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet101-5d3b4d8f.pth
return ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 23, 3], num_classes=num_classes, include_top=include_top)
def resnext50_32x4d(num_classes=1000, include_top=True):
# https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnext50_32x4d-7cdf4587.pth
groups = 32
width_per_group = 4
return ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 6, 3],
num_classes=num_classes,
include_top=include_top,
groups=groups,
width_per_group=width_per_group)
def resnext101_32x8d(num_classes=1000, include_top=True):
# https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnext101_32x8d-8ba56ff5.pth
groups = 32
width_per_group = 8
return ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 23, 3],
num_classes=num_classes,
include_top=include_top,
groups=groups,
width_per_group=width_per_group)
train.py
import argparse
import os
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import numpy as np
import torch.optim as optim
from torch.cuda.amp import GradScaler, autocast
from torch.testing._internal.common_utils import args
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader, Dataset
import SimpleITK as sitk
import sys
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
from tqdm import tqdm
from functools import partial
import nibabel as nib # 用于检查NIfTI文件头信息
from model import resnet34
# 自定义转换函数
def resize_transform(x, size=(128, 128, 128)):
# (batch, channel, depth, height, width)
if x.dim() == 4:
x = x.unsqueeze(0)
# 获取当前空间维度
current_dims = x.shape[2:]
# 如果维度不匹配,调整目标尺寸
if len(current_dims) != len(size):
# 使用最大维度作为基准
max_dim = max(current_dims)
scale = size[0] / max_dim
new_size = [int(d * scale) for d in current_dims]
# 如果目标尺寸仍然是3D,但输入是2D,复制深度维度
if len(new_size) == 2 and len(size) == 3:
new_size = [size[0]] + new_size
size = tuple(new_size)
interpolated = nn.functional.interpolate(
x,
size=size,
mode='trilinear' if len(size) == 3 else 'bilinear',
align_corners=False
)
if interpolated.dim() == 5 and interpolated.shape[0] == 1:
interpolated = interpolated.squeeze(0)
return interpolated
def normalize_transform(x):
if torch.min(x) == torch.max(x):
return x
# 归一化到0-1范围
normalized = (x - torch.min(x)) / (torch.max(x) - torch.min(x))
# 确保数值稳定性
normalized = torch.clamp(normalized, 0.0, 1.0)
return normalized
# 自定义3D数据集类
class Nifti3DDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, root_dir, transform=None, cache=False, min_dim=3):
self.root_dir = root_dir
self.transform = transform
self.cache = cache
self.min_dim = min_dim # 最小维度要求
self.cache_dict = {}
self.classes, self.class_to_idx = self._find_classes()
self.samples = self._make_dataset()
# 检查样本维度
self.validate_dimensions()
def _find_classes(self):
classes = [d.name for d in os.scandir(self.root_dir) if d.is_dir()]
classes.sort()
class_to_idx = {cls_name: i for i, cls_name in enumerate(classes)}
return classes, class_to_idx
def _make_dataset(self):
samples = []
for target_class in self.classes:
class_idx = self.class_to_idx[target_class]
target_dir = os.path.join(self.root_dir, target_class)
for root, _, fnames in os.walk(target_dir):
for fname in sorted(fnames):
if fname.endswith(('.ni', '.nii', '.nii.gz')):
path = os.path.join(root, fname)
samples.append((path, class_idx))
return samples
def validate_dimensions(self):
"""验证所有文件是否符合维度要求"""
invalid_files = []
for path, _ in self.samples:
try:
img = nib.load(path)
dim = img.header['dim'][0]
if dim < self.min_dim + 1: # dim[0]包括通道信息
invalid_files.append(path)
except:
invalid_files.append(path)
if invalid_files:
print(f"Warning: Found {len(invalid_files)} files with invalid dimensions")
for i, fpath in enumerate(invalid_files[:5]): # 显示前5个
print(f" {i + 1}. {fpath}")
if len(invalid_files) > 5:
print(f" ... and {len(invalid_files) - 5} more")
def __len__(self):
return len(self.samples)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
path, label = self.samples[idx]
# 检查缓存
if self.cache and idx in self.cache_dict:
return self.cache_dict[idx]
try:
# 使用SimpleITK读取NIfTI文件
img = sitk.ReadImage(path)
data = sitk.GetArrayFromImage(img) # 获取NumPy数组 (Z, Y, X)
# 转换数据类型并归一化
if data.dtype == np.uint16:
data = data.astype(np.float32) / 65535.0
elif data.dtype == np.uint8:
data = data.astype(np.float32) / 255.0
elif data.dtype == np.int16:
data = data.astype(np.float32) / 32767.0
else:
data = data.astype(np.float32)
# 处理不同维度的数据
if data.ndim == 2: # 2D图像 (H, W)
# 添加通道和深度维度 (C=1, D=1, H, W)
data = data[np.newaxis, np.newaxis, ...]
elif data.ndim == 3: # 3D图像 (D, H, W)
# 添加通道维度 (C=1, D, H, W)
data = data[np.newaxis, ...]
elif data.ndim == 4: # 可能是(C, D, H, W)或(D, H, W, T)
# 取前三个通道,如果是时间维度则压缩
if data.shape[3] == 1: # 单时间点
data = data[:, :, :, 0] # 移除时间维度
else:
data = data[0] # 取第一个通道
data = data[np.newaxis, ...] # 确保有通道维度
# 转换为张量
data = torch.from_numpy(np.ascontiguousarray(data))
if self.transform:
data = self.transform(data)
# 更新缓存
if self.cache:
self.cache_dict[idx] = (data, label)
return data, label
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error loading {path}: {str(e)}")
return self.load_dummy_sample(label) # 返回替代样本
def load_dummy_sample(self, label):
"""生成替代样本防止训练中断"""
# 创建随机3D体积 (C=1, D=64, H=64, W=64)
dummy_data = torch.rand(1, 64, 64, 64)
return dummy_data, label
# 配置训练参数
class Config:
def __init__(self):
self.data_path = "datas/ModelNet10_nii"
self.batch_size = 4
self.accumulation_steps = 4
self.num_epochs = 100
self.num_workers = 0
self.learning_rate = 1e-4
self.num_classes = 10 #分类个数
self.pretrained_path = "model/pretrain/resnet_34.pth"
# 数据预处理 - 使用更智能的调整大小
self.transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Lambda(partial(resize_transform, size=(96, 96, 96))), # 减小尺寸节省显存
transforms.Lambda(normalize_transform)
])
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--model_path', type=str, default='best.pt')
args = parser.parse_args()
# 自定义collate函数处理异常
def collate_fn(batch):
filtered_batch = []
for item in batch:
if item is not None:
# 检查数据维度是否有效
data, label = item
if data.dim() >= 4: # 至少是(C, D, H, W)
filtered_batch.append(item)
if not filtered_batch:
# 如果整个batch都无效,创建一个虚拟batch
dummy_data = torch.rand(1, 1, 64, 64, 64)
dummy_label = torch.tensor([0])
return dummy_data, dummy_label
return torch.utils.data.dataloader.default_collate(filtered_batch)
# 主训练函数
def main():
# 初始化配置
config = Config()
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
print(f"Using device: {device}")
# 设置混合精度训练
device_type = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
use_amp = True if device_type == "cuda" else False
print(f"Using AMP: {use_amp}")
# 构建数据集
train_dataset = Nifti3DDataset(
root_dir=os.path.join(config.data_path, "train"),
transform=config.transform,
cache=False,
min_dim=3 # 要求至少3维数据
)
val_dataset = Nifti3DDataset(
root_dir=os.path.join(config.data_path, "val"),
transform=config.transform,
cache=False,
min_dim=3
)
print(f"Train dataset size: {len(train_dataset)}")
print(f"Validation dataset size: {len(val_dataset)}")
# 创建数据加载器
train_loader = DataLoader(
train_dataset,
batch_size=config.batch_size,
shuffle=True,
num_workers=config.num_workers,
pin_memory=True,
collate_fn=collate_fn
)
val_loader = DataLoader(
val_dataset,
batch_size=config.batch_size,
shuffle=False,
num_workers=config.num_workers,
collate_fn=collate_fn
)
# 初始化模型
model = resnet34(num_classes=config.num_classes).to(device)
# 加载预训练权重
if os.path.exists(config.pretrained_path):
try:
model_dict = model.state_dict()
pretrained_dict = torch.load(config.pretrained_path, map_location=device)
# 过滤不匹配的键
matched_dict = {}
for k, v in pretrained_dict.items():
if k in model_dict and v.shape == model_dict[k].shape:
matched_dict[k] = v
else:
print(f"Skipping layer: {k} (shape mismatch)")
model_dict.update(matched_dict)
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(args.model_path, map_location=device, weights_only=True))
print(f"Loaded {len(matched_dict)}/{len(pretrained_dict)} layers from pretrained weights")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error loading pretrained weights: {str(e)}")
else:
print(f"Pretrained weights not found at {config.pretrained_path}")
# 损失函数和优化器
loss_function = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=config.learning_rate)
scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.StepLR(optimizer, step_size=30, gamma=0.1)
scaler = GradScaler(enabled=use_amp)
# 训练参数
best_acc = 0.0
save_path = "./runs/ResNet/best_model.pth"
# 训练循环
for epoch in range(config.num_epochs):
# ----------------- 训练阶段 -----------------
model.train()
running_loss = 0.0
train_bar = tqdm(train_loader, file=sys.stdout, desc=f"Epoch {epoch + 1}/{config.num_epochs}")
# 优化器梯度清零移到循环内部
optimizer.zero_grad()
for step, (images, labels) in enumerate(train_bar):
images, labels = images.to(device), labels.to(device)
# 确保输入数据有正确的维度 (N, C, D, H, W)
if images.dim() == 4:
images = images.unsqueeze(1) # 添加通道维度
elif images.dim() == 5 and images.shape[1] == 1:
pass # 已经是正确格式
else:
print(f"Invalid input shape: {images.shape}, skipping batch")
continue
# 混合精度训练 - 使用新版API
with torch.amp.autocast(device_type=device.type, enabled=use_amp):
logits = model(images)
loss = loss_function(logits, labels)
loss = loss / config.accumulation_steps # 梯度累积的损失归一化
# 反向传播和梯度累积
scaler.scale(loss).backward() # 缩放损失并反向传播
# 梯度累积步骤
if (step + 1) % config.accumulation_steps == 0 or (step + 1) == len(train_loader):
scaler.step(optimizer) # 更新参数
scaler.update()
optimizer.zero_grad() # 清空梯度
# 统计损失(乘以累积步数恢复原始损失值)
running_loss += loss.item() * config.accumulation_steps
# 更新进度条描述
train_bar.set_description(
f"Train Epoch [{epoch + 1}/{config.num_epochs}] Loss: {loss.item() * config.accumulation_steps:.4f}"
)
# 计算平均训练损失
epoch_loss = running_loss / len(train_loader)
# ----------------- 验证阶段 -----------------
model.eval()
correct = 0
total = 0
val_loss = 0.0
with torch.no_grad():
val_bar = tqdm(val_loader, file=sys.stdout, desc="Validating")
for val_images, val_labels in val_bar:
val_images, val_labels = val_images.to(device), val_labels.to(device)
if val_images.dim() == 4:
val_images = val_images.unsqueeze(1)
# 验证阶段也使用混合精度
with torch.amp.autocast(device_type=device.type, enabled=use_amp):
outputs = model(val_images)
loss_val = loss_function(outputs, val_labels)
_, predicted = torch.max(outputs.data, 1)
total += val_labels.size(0)
correct += (predicted == val_labels).sum().item()
val_loss += loss_val.item()
val_bar.set_description(f"Val Acc: {100 * correct / total:.2f}%")
# 计算验证准确率和平均损失
val_accurate = correct / total
avg_val_loss = val_loss / len(val_loader)
# 输出完整epoch统计信息
print(f'Epoch [{epoch + 1}/{config.num_epochs}] '
f'Train Loss: {epoch_loss:.4f} | '
f'Val Loss: {avg_val_loss:.4f} | '
f'Val Acc: {100 * val_accurate:.2f}%')
scheduler.step(avg_val_loss)
# 保存最佳模型 - 基于验证准确率
if val_accurate > best_acc:
best_acc = val_accurate
torch.save(model.state_dict(), save_path)
print(f"Saved best model with accuracy: {100 * best_acc:.2f}%")
# 清理GPU缓存
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
print('Finished Training')
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
predict.py
import json
import os
import torch
import numpy as np
import SimpleITK as sitk
import torch.nn as nn
from torchvision import transforms
import nibabel as nib
from model import resnet34
import argparse
from functools import partial
# 自定义转换函数(与训练脚本一致)
def resize_transform(x, size=(96, 96, 96)):
if x.dim() == 4:
x = x.unsqueeze(0)
current_dims = x.shape[2:]
if len(current_dims) != len(size):
max_dim = max(current_dims)
scale = size[0] / max_dim
new_size = [int(d * scale) for d in current_dims]
if len(new_size) == 2 and len(size) == 3:
new_size = [size[0]] + new_size
size = tuple(new_size)
interpolated = nn.functional.interpolate(
x,
size=size,
mode='trilinear' if len(size) == 3 else 'bilinear',
align_corners=False
)
if interpolated.dim() == 5 and interpolated.shape[0] == 1:
interpolated = interpolated.squeeze(0)
return interpolated
def normalize_transform(x):
"""归一化转换函数"""
if torch.min(x) == torch.max(x):
return x
normalized = (x - torch.min(x)) / (torch.max(x) - torch.min(x))
return torch.clamp(normalized, 0.0, 1.0)
# 数据预处理管道
transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Lambda(partial(resize_transform, size=(96, 96, 96))),
transforms.Lambda(normalize_transform)
])
def load_and_preprocess_nii(file_path):
try:
# 加载图像
img = sitk.ReadImage(file_path)
data = sitk.GetArrayFromImage(img) # (Z, Y, X)
# 转换数据类型
if data.dtype == np.uint16:
data = data.astype(np.float32) / 65535.0
elif data.dtype == np.uint8:
data = data.astype(np.float32) / 255.0
elif data.dtype == np.int16:
data = data.astype(np.float32) / 32767.0
else:
data = data.astype(np.float32)
# 处理不同维度的数据
if data.ndim == 2: # 2D图像
data = data[np.newaxis, np.newaxis, ...]
elif data.ndim == 3: # 3D图像
data = data[np.newaxis, ...]
elif data.ndim == 4: # 4D数据
if data.shape[3] == 1:
data = data[:, :, :, 0]
else:
data = data[0]
data = data[np.newaxis, ...]
# 转换为张量并应用预处理
data = torch.from_numpy(np.ascontiguousarray(data))
data = transform(data)
# 添加批次维度 (1, C, D, H, W)
if data.dim() == 4: # (C, D, H, W)
data = data.unsqueeze(0)
return data
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error processing file {file_path}: {str(e)}")
return None
def predict(model, image_tensor, device, class_names):
"""对图像张量进行预测"""
if image_tensor is None:
print("Invalid input tensor. Skipping prediction.")
return None
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
# 确保正确的维度 (N, C, D, H, W)
if image_tensor.dim() == 4: # (C, D, H, W)
image_tensor = image_tensor.unsqueeze(0)
# 移动到设备
image_tensor = image_tensor.to(device)
# 获取模型输出
outputs = model(image_tensor)
# 应用softmax获取概率
probabilities = torch.softmax(outputs, dim=1)
# 获取预测结果
_, predicted_idx = torch.max(outputs, 1)
predicted_class = class_names[predicted_idx.item()]
# 转换为numpy数组
probs = probabilities.cpu().numpy().flatten()
return predicted_class, predicted_idx.item(), probs
def main():
# 设置默认参数(根据您的需求配置)
default_model_path = "runs/ResNet/best_model.pth"
default_input_path = "datas/ModelNet10_nii_Test/test"
# 解析命令行参数
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="3D Medical Image Classification Prediction")
parser.add_argument("--model-path", type=str, default=default_model_path,
help="Path to trained model weights (.pth file)")
parser.add_argument("--input", type=str, default=default_input_path,
help="Input file (.nii, .nii.gz) or directory")
parser.add_argument("--class-names-json", type=str,
default="3D_class_indices.json",
help="Path to JSON file containing class names")
args = parser.parse_args()
# 设置设备
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
print(f"Using device: {device}")
# 新代码(JSON文件读取):
try:
with open(args.class_names_json, 'r') as f:
class_data = json.load(f)
class_names = class_data["classes"]
print(f"Loaded {len(class_names)} classes from {args.class_names_json}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error loading class names JSON: {str(e)}")
class_names = ["bathtub", "bed"] # 默认回退值
num_classes = len(class_names)
# 加载模型
model = resnet34(num_classes=num_classes).to(device)
# 加载训练好的权重
if os.path.exists(args.model_path):
try:
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(args.model_path, map_location=device, weights_only=True))
print(f"Loaded model weights from {args.model_path}")
model.eval()
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error loading model weights: {str(e)}")
return
else:
print(f"Model weights not found at {args.model_path}")
return
# 收集输入文件
input_files = []
if os.path.isfile(args.input):
input_files.append(args.input)
elif os.path.isdir(args.input):
for root, _, files in os.walk(args.input):
for file in files:
if file.endswith(('.nii', '.nii.gz', '.ni')):
input_files.append(os.path.join(root, file))
if not input_files:
print(f"No valid .nii files found in {args.input}")
return
print(f"Found {len(input_files)} files for prediction")
# 预测结果列表
results = []
# 逐个预测每个文件
for file_path in input_files:
print(f"\nProcessing: {os.path.basename(file_path)}")
# 加载并预处理图像
tensor = load_and_preprocess_nii(file_path)
if tensor is None:
print(f"Skipping due to processing error: {file_path}")
continue
# 预测
predicted_class, class_idx, probs = predict(model, tensor, device, class_names)
# 显示结果
print(f" Predicted class: {predicted_class}")
print(f" Confidence: {probs[class_idx]:.4f}")
print(" Class probabilities:")
for i, (cls, prob) in enumerate(zip(class_names, probs)):
print(f" {cls}: {prob:.4f}")
# 保存结果
results.append({
"file": os.path.basename(file_path),
"predicted_class": predicted_class,
"class_idx": class_idx,
"max_prob": float(probs[class_idx]),
"probabilities": probs.tolist()
})
# 准确率评估:真实标签是文件名去掉编号后的部分
correct = 0
total = 0
for r in results:
base = r['file'].replace('.nii.gz', '').replace('.nii', '').replace('.mat', '')
parts = base.split('_')
if len(parts) > 1 and parts[-1].isdigit():
true_label = '_'.join(parts[:-1]).lower()
else:
true_label = base.lower()
pred_label = r['predicted_class'].lower()
if true_label == pred_label:
correct += 1
else:
print(f"[错] 文件: {r['file']} → 真实: {true_label}, 预测: {pred_label}")
total += 1
accuracy = correct / total if total > 0 else 0.0
print(f"\n✅ 模型准确率: {accuracy:.4f} ({correct}/{total})")
# 计算平均最大预测置信度
if results:
avg_max_prob = sum(r['max_prob'] for r in results) / len(results)
print(f"\n📈 所有样本的平均最高置信度: {avg_max_prob:.4f}")
else:
print("\n⚠️ 无预测结果,无法计算平均最高置信度。")
# 保存结果到CSV
csv_path = "prediction_results.csv"
with open(csv_path, "w") as f:
f.write("Filename,Predicted Class,Confidence")
for cls in class_names:
f.write(f",{cls} Probability")
f.write("\n")
for res in results:
f.write(f"{res['file']},{res['predicted_class']},{res['probabilities'][res['class_idx']]:.4f}")
for prob in res['probabilities']:
f.write(f",{prob:.4f}")
f.write("\n")
print(f"\nPrediction results saved to {csv_path}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()




















 2842
2842

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








