一 概述
将各自从小到大有序的两个链表head1 和head2 归并成一个从小到大有序链表。
二 Java代码实现
链表节点类(Node)
public class Node {
int data;
Node next;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
public int getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
public Node getNext() {
return next;
}
public void setNext(Node next) {
this.next = next;
}
}
合并有序链表类
public class MargeList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head1 = new Node(1);
Node n1 = new Node(3);
Node n2 = new Node(5);
head1.setNext(n1);
n1.setNext(n2);
Node head2 = new Node(2);
Node n4 = new Node(4);
Node n5 = new Node(6);
head2.setNext(n4);
n4.setNext(n5);
Node result = marge(head1,head2);
while (result!=null) {
System.out.print(result.getData()+ "");
result = result.getNext();
}
}
private static Node marge(Node head1,Node head2) {
//判断空
if(head1 == null || head2 == null) {
return head1 == null? head2 : head1;
}
//判断合并后头节点
Node node = head1.getData() <= head2.getData() ? head1:head2;
//使用head1和head2的副本
Node current1 = node == head1 ? head1:head2;
Node current2 = node == head1 ? head2:head1;
//使用临时空间
Node temp1 = null;
Node temp2 ;
//判断哪个先比较完
while(current1!=null&¤t2!=null){
if(current1.getData() <= current2.getData()){
//当副本current1的值小于等于副本current2中的值,将小值放入临时空间temp1
temp1 = current1;
//继续比较current1中下一个值
current1 = current1.getNext();
}else {
//使用临时空间temp2保存第一个元素小的副本current2的第二个节点及后续元素
temp2 = current2.getNext();
//将第一个值小的副本current2拷贝到临时空间temp1
temp1.setNext(current2);
//将较大值放入current2下一个节点
current2.setNext(current1);
//当副本current1的值不小于副本current2中的值,将小值放入临时空间temp1
temp1 = current2;
current2 = temp2;
}
}
temp1.setNext(current1 == null ? current2 : current1);
return node;
}
}
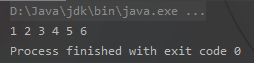
三 合并结果
链表一:1 3 5
链表二:2 4 6
合并结果
 有序链表合并算法
有序链表合并算法




















 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








