官方文档还是很值得参考的,
上面的源码是参考这个git的
Shallow and Deep Convolutional Networks for Saliency Prediction
不过我改了训练集目前为止还没训练成功。。。就当是学习一下相关框架吧,以后如果训练成功了在更新
数据预处理
import cv2
import numpy as np
import cPickle as pickle
#PIC_PATH='/home/zcb/datasets/trainSet/Stimuli/Alldata/'
#SALMAP_PATH='/home/zcb/datasets/trainSet/FIXATIONMAPS/Alldata/'
PIC_PATH='/home/zcb/datasets/ecssd/images/'
SALMAP_PATH='/home/zcb/datasets/ecssd/ground_truth_mask/'
datalist = open(PIC_PATH+'list.txt','r')
namelist=[l.strip('\n') for l in datalist.readlines()]
sallist = open(SALMAP_PATH+'list.txt','r')
sallist=[l.strip('\n') for l in sallist.readlines()]
input_h=48
input_w=48
output_h=24
output_w=24
#NumSample=len(namelist)
NumSample=32
X1 = np.zeros((NumSample, 3,input_h, input_w), dtype='float32')
Y1 = np.zeros((NumSample, output_w*output_h), dtype='float32')
print NumSample
for i in range(NumSample):
img = cv2.imread(PIC_PATH+namelist[i], cv2.IMREAD_COLOR)
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
#print img.shape
img = cv2.resize(img,(input_w,input_h),interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
#print img.shape
#cv2.imshow('show',img)
img=img.astype(np.float32)
img = img /255.
#img -= 1.
if(cmp(img.shape , (input_h,input_w,3)) == 0):
img = img.transpose(2,0,1).reshape(3, input_h, input_w)
X1[i]=img
else:
print 'error'
#np.set_printoptions(threshold='nan')
label = cv2.imread(SALMAP_PATH+sallist[i],cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
#label = loadSaliencyMapSUN(names[i])
label = cv2.resize(label,(output_w,output_h),interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
#cv2.imshow('label',label)
#cv2.waitKey(0)
label = label.astype(np.float32)/255.
#label = misc.imresize(label,(48,48)) /
#label = label -1.
# print 'data',X1[i]
# print 'label',label
#Y1.append(label.reshape(1,48*48))
Y1[i]=label.reshape(1,output_h*output_w)
data_to_save = (X1, Y1)
f = file('data_ecssd_T.cPickle', 'wb')
pickle.dump(data_to_save, f, protocol=pickle.HIGHEST_PROTOCOL)
f.close()
训练代码
代码如下:
# add to kfkd.py
import lasagne
from lasagne.layers import *
from lasagne.updates import nesterov_momentum
from nolearn.lasagne import NeuralNet,BatchIterator
import os
import numpy as np
from sklearn.utils import shuffle
import cPickle as pickle
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import Image
import ImageOps
from scipy import misc
import scipy.io
import theano
import sys
sys.setrecursionlimit(10**8) # set the maximum depth
def load():
f = file('data_ecssd_T.cPickle', 'rb')
loaded_obj = pickle.load(f)
f.close()
X, y = loaded_obj
return X, y
def float32(k):
return np.cast['float32'](k)
class AdjustVariable(object):
def __init__(self, name, start=0.03, stop=0.001):
self.name = name
self.start, self.stop = start, stop
self.ls = None
def __call__(self, nn, train_history):
if self.ls is None:
self.ls = np.linspace(self.start, self.stop, nn.max_epochs)
epoch = train_history[-1]['epoch']
#if epoch > 200:
# getattr(nn, self.name).set_value(0.01)
#if epoch > 800:
# getattr(nn, self.name).set_value(0.005)
new_value = float32(self.ls[epoch - 1])
getattr(nn, self.name).set_value(new_value)
input_h=48
input_w=48
output_h=24
output_w=24
class FlipBatchIterator(BatchIterator):
def transform(self, Xb, yb):
Xb, yb = super(FlipBatchIterator, self).transform(Xb, yb)
# Flip half of the images in this batch at random:
bs = Xb.shape[0]
indices = np.random.choice(bs, bs / 2, replace=False)
Xb[indices] = Xb[indices, :, :, ::-1]
tmp = yb[indices].reshape(bs/2,1,output_h,output_w)
mirror = tmp[ :,:,:, ::-1]
yb[indices] = mirror.reshape(bs/2,output_w*output_h)
return Xb, yb
class EarlyStopping(object):
def __init__(self, patience=100):
self.patience = patience
self.best_valid = np.inf
self.best_valid_epoch = 0
self.best_weights = None
def __call__(self, nn, train_history):
current_valid = train_history[-1]['valid_loss']
current_epoch = train_history[-1]['epoch']
if current_valid < self.best_valid:
self.best_valid = current_valid
self.best_valid_epoch = current_epoch
self.best_weights = nn.get_all_params_values()
elif self.best_valid_epoch + self.patience < current_epoch:
print("Early stopping.")
print("Best valid loss was {:.6f} at epoch {}.".format(
self.best_valid, self.best_valid_epoch))
nn.load_params_from(self.best_weights)
raise StopIteration()
def my_loss(a,b):
return theano.tensor.abs_(a-b)
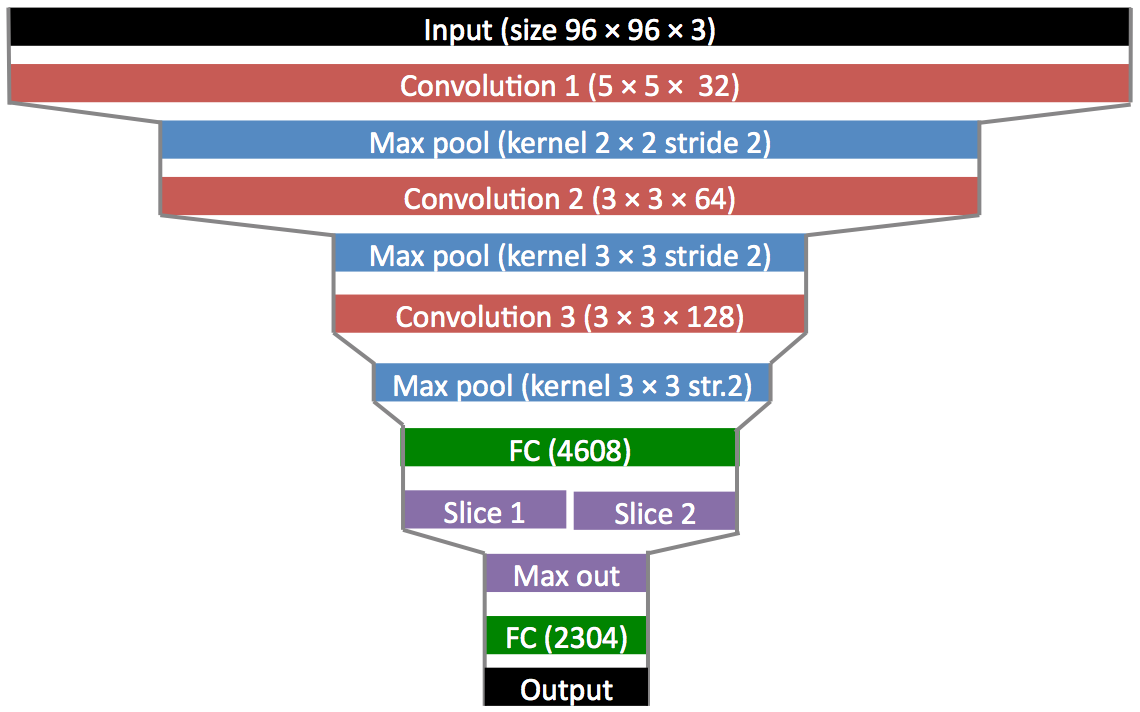
layers0 = [
# layer dealing with the input data
(InputLayer, {'shape':(None, 3, input_h, input_w)}),
# first stage of our convolutional layers
(Conv2DLayer, {'num_filters':32 , 'filter_size': 5,'pad':1,'W':lasagne.init.Uniform()}),
#(Conv2DLayer, {'num_filters':32 , 'filter_size': 7,'pad':1,'W':lasagne.init.Uniform()}),
(MaxPool2DLayer, {'pool_size': 2}),
# second stage of our convolutional layers
(Conv2DLayer, {'num_filters':64 , 'filter_size': 3,'pad':1,'W':lasagne.init.Uniform()}),
#(Conv2DLayer, {'num_filters':16 , 'filter_size': 3,'pad':1,'W':lasagne.init.Uniform()}),
(MaxPool2DLayer, {'pool_size': 2}),
# third stage of our convolutional layers
(Conv2DLayer, {'num_filters': 128, 'filter_size': 3,'pad':1,'W':lasagne.init.Uniform()}),
#(Conv2DLayer, {'num_filters': 32, 'filter_size': 3,'pad':1,'W':lasagne.init.Uniform()}),
(MaxPool2DLayer, {'pool_size': 2}),
#(Conv2DLayer, {'num_filters': 32, 'filter_size': 3,'pad':1,'W':lasagne.init.Uniform()}),
#(Conv2DLayer, {'num_filters': 32, 'filter_size': 3,'pad':1,'W':lasagne.init.Uniform()}),
#(Upscale2DLayer,{'scale_factor':2}),
#(Conv2DLayer, {'num_filters': 16, 'filter_size': 3,'pad':1,'W':lasagne.init.Uniform()}),
#(Conv2DLayer, {'num_filters': 16, 'filter_size': 3,'pad':1,'W':lasagne.init.Uniform()}),
#(Upscale2DLayer,{'scale_factor':2}),
#(Conv2DLayer, {'num_filters': 8, 'filter_size': 3,'pad':1,'W':lasagne.init.Uniform()}),
#(Conv2DLayer, {'num_filters': 8, 'filter_size': 3,'pad':1,'W':lasagne.init.Uniform()}),
#(Conv2DLayer, {'num_filters': 1, 'filter_size': 3,'pad':1,'nonlinearity':lasagne.nonlinearities.sigmoid}),
#(Conv2DLayer, {'num_filters': 1, 'filter_size': 3,'pad':1,'nonlinearity':None}),
#(FlattenLayer,{}),
# two dense layers with dropout
#(DropoutLayer, {}),
(DenseLayer, {'num_units': output_w*output_h*2}),
(FeaturePoolLayer, {'pool_size':2}),
# the output layer
#(DenseLayer, {'num_units': output_w*output_h,'nonlinearity':lasagne.nonlinearities.sigmoid}),
(DenseLayer, {'num_units': output_w*output_h,'nonlinearity':None}),
#(DenseLayer, {'num_units': 10, 'nonlinearity': softmax}),
]
net2 = NeuralNet(
# layers=[
# ('input', layers.InputLayer),
# ('conv1', layers.Conv2DLayer),
# ('pool1', layers.MaxPool2DLayer),
# ('conv2', layers.Conv2DLayer),
# ('pool2', layers.MaxPool2DLayer),
# ('conv3', layers.Conv2DLayer),
# ('pool3', layers.MaxPool2DLayer),
# ('hidden4', layers.DenseLayer),
# ('maxout6',layers.FeaturePoolLayer),
# ('output', layers.DenseLayer),
# ],
# input_shape=(None, 3, input_h, input_w),
# #conv1
# conv1_num_filters=16, conv1_filter_size=(5, 5),
# conv1_nonlinearity=lasagne.nonlinearities.rectify,
# conv1_W=lasagne.init.GlorotUniform(),
# conv1_pad=1,
# conv1_stride=1,
# conv4_num_filters=16, conv4_filter_size=(3, 3),
# conv4_nonlinearity=lasagne.nonlinearities.rectify,
# conv4_W=lasagne.init.GlorotUniform(),
# conv4_pad=1,
# conv4_stride=1,
# #pool1
# pool1_pool_size=(2, 2),
# #conv2
# conv2_num_filters=32, conv2_filter_size=(3, 3),
# conv2_nonlinearity=lasagne.nonlinearities.rectify,
# conv2_W=lasagne.init.GlorotUniform(),
# conv2_pad=1,
# conv2_stride=1,
# #pool2
# pool2_pool_size=(2, 2),
# #conv3
# conv3_num_filters=32, conv3_filter_size=(3, 3),
# conv3_nonlinearity=lasagne.nonlinearities.rectify,
# conv3_W=lasagne.init.GlorotUniform(),
# conv3_pad=1,
# #pool3
# pool3_pool_size=(2, 2),
# hidden4_num_units=output_w*output_h*2,
# maxout6_pool_size=2,output_num_units=output_h*output_w,output_nonlinearity=None,
layers=layers0,
#update=lasagne.updates.rmsprop,
update_learning_rate=theano.shared(float32(0.05)),
update_momentum=theano.shared(float32(0.9)),
#objective_loss_function=my_loss,#lasagne.objectives.squared_error,
regression=True,
on_epoch_finished=[
AdjustVariable('update_learning_rate', start=0.03, stop=0.0001),
AdjustVariable('update_momentum', start=0.9, stop=0.999),
#EarlyStopping(patience=150),
],
batch_iterator_train=FlipBatchIterator(batch_size=128),
max_epochs=800,
verbose=1,
)
X, y = load()
print net2.objective_loss_function,net2.train_split.eval_size
#print("X.shape == {}; X.min == {:.3f}; X.max == {:.3f}".format(X.shape, X.min(), X.max()))
#print("y.shape == {}; y.min == {:.3f}; y.max == {:.3f}".format(y.shape, y.min(), y.max()))
X = X.astype(np.float32)
y = y.astype(np.float32)
net2.fit(X, y)
with open('JuntingNet_SALICON.pickle', 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(net2, f, -1)







 本文介绍了一个使用Theano实现的深度学习模型,该模型用于显著性预测任务。文章详细展示了从数据预处理到构建Lasagne神经网络的过程,并分享了训练技巧。
本文介绍了一个使用Theano实现的深度学习模型,该模型用于显著性预测任务。文章详细展示了从数据预处理到构建Lasagne神经网络的过程,并分享了训练技巧。
















 8346
8346

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








